- Virginia Gewin on GB8.
- Mapping water risks around the world.
- The decline and rise of Georgian tea.
- Virus hits tilapia. A lot of people could be hurt.
- Amaranthus in Mexico.
- Just one of many relatively neglected crops around the world that shouldn’t be.
- How wheat took over China. That was kinda underused at first too.
- Long webinar on organic maize breeding. Amaranthus next?
- The rise of fabric.
Brainfood: Cereal grains, Cerrado threats, Potato conservation, Maize rhizosphere, Coconut diversification, Lombard landraces, Lupinus evaluation, Genetic markers, Pathogen evolution, PAs & productivity, Agricultural expansion, Trade & obesity, ILRI genebank
- Large‐scale GWAS in sorghum reveals common genetic control of grain size among cereals. QTLs for grain size potential (rather than capacity to fill grains) identified in sorghum, turn out to be similar to other cereals.
- Linking global drivers of agricultural trade to on-the-ground impacts on biodiversity. Specific soy buyers with disproportionate impact on endemic and threatened cerrado species identified by fancy maths. Yes, you’re probably responsible for the plight of the giant anteater.
- Long-term conservation of potato genetic resources: Methods and status of conservation. Useful brief roundup.
- Impacts of Maize Domestication and Breeding on Rhizosphere Microbial Community Recruitment from a Nutrient Depleted Agricultural Soil. Hybrids changed the rhizosphere.
- Genome-wide diversity of northern South America cultivated Coconut (Cocus nucifera L.) uncovers diversification times and targets of domestication of coconut globally. Atlantic tall cultivar splits from Pacific cultivars approximately 5400 years ago, then Pacific Tall and Pacific Dwarf cultivars split from a shared common ancestor 1600 years ago.
- Forest pattern, not just amount, influences dietary quality in five African countries. Forests are good for you.
- Plant agro-biodiversity needs protection, study and promotion: results of research conducted in Lombardy region (Northern Italy). 78% of landraces lost in last 70-80 years, 72 left.
- Genomic prediction of grain yield in contrasting environments for white lupin genetic resources. It’s worth genotyping everything…
- Genetics without genes? The centrality of genetic markers in livestock genetics and genomics. …but genotyping-by-sequencing may not be necessary.
- Opportunities from the genetic diversity of the ILRI genebank forage germplasm collection. Genotyping-by-sequencing and morphology used to define mini-core subsets for important forages. So it is necessary for some things?
- The Green Revolution shaped the population structure of the rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Strong selection leads to adaptation, fast. Well I never!
- Land productivity dynamics in and around protected areas globally from 1999 to 2013. Productivity increases are most common outside protected areas. But does that increase or decrease pressure on them? See below.
- Assessing the ecological vulnerability of forest landscape to agricultural frontier expansion in the Central Highlands of Vietnam. This is how you find out.
- Weight Gains from Trade in Foods: Evidence from Mexico. Food imports from US explain 20% of the increase in obesity in Mexican women.
The sweetest things
There’s been a lot of action on the cucurbit domestication front lately. Hot on the heels of a comprehensive Tansley review of all the crops in the family in New Phytologist 1 now come two papers out of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences focusing on the melon and watermelon:
- Zhao, G., Lian, Q., Zhang, Z. et al. A comprehensive genome variation map of melon identifies multiple domestication events and loci influencing agronomic traits. Nat Genet 51, 1607–1615 (2019) doi:10.1038/s41588-019-0522-8.
- Guo, S., Zhao, S., Sun, H. et al. Resequencing of 414 cultivated and wild watermelon accessions identifies selection for fruit quality traits. Nat Genet 51, 1616–1623 (2019) doi:10.1038/s41588-019-0518-4.
There are press releases on each of these, of course. But the more interesting take is provided by some IPK researchers 2, who mash up the two studies. 3 And provide a nice graphic to summarize the whole thing.
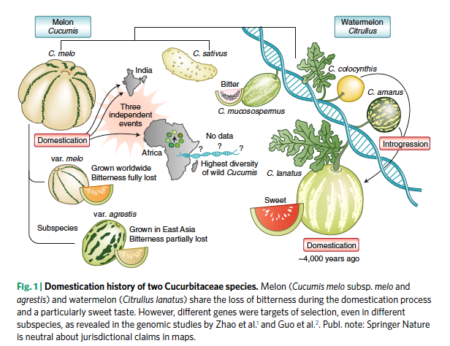
The bottom line(s)? The two different subspecies of melon acquired sweet flesh through different mutations, independently but probably both in India; there was a third domestication event in Africa, but the authors had too little material at hand to say much about this. Melon and watermelon lost their bitterness through convergent evolution, and the latter has benefitted from introgression from two wild relatives, one of which was separately domesticated for its seeds.
Nibbles: Root & tuber breeding, Potato fun, Melon domestication, Maize conservation, Millet diversification, Business as usual
- A backyard breeder evaluates USDA’s potato accessions. Among other things.
- The Onion roasts potatoes.
- How melons got sweet.
- Mexican Senate considers in situ/on farm conservation areas for maize.
- Millets for climate change resilience in India.
- Business for biodiversity. Yeah, right.
Brainfood: Tree SDM, TR4 in Colombia, Genebanks double, Pacific ag, Gums, Defaunation, Oil palm, Agroforestry, Moldy cheese, Ecosystem services, Meat, Desert ag, Maize evolution
- Species distribution modelling to support forest management. A literature review. Embrace the uncertainty.
- First report of Fusarium wilt Tropical Race 4 in Cavendish bananas caused by Fusarium odoratissimum in Colombia. Inevitable.
- Seed Banking as Future Insurance Against Crop Collapses. “Although the basic technology of seed- (gene-)banking is relatively simple, there are nonetheless significant costs involved in effectively managing seed- (gene-)bank collections.” Elevator pitch desperately needed.
- Rapid loss of seed viability in ex situ conserved wheat and barley at 4°C as compared to −20°C storage. Colder the better.
- Origin and Development of Agriculture in New Guinea, Island Melanesia and Polynesia. Maybe 5-6 distinct stages since 7000 BP.
- Exotic eucalypts: From demonized trees to allies of tropical forest restoration? Maybe.
- Quantifying the impacts of defaunation on natural forest regeneration in a global meta-analysis. Forests need vertebrates. No word on where eucalypts stand.
- Market-mediated responses confound policies to limit deforestation from oil palm expansion in Malaysia and Indonesia. Bans are not enough…
- The ‘Capitalist Squeeze’ and the Rise and Fall of Sumatra’s Krui Agroforests. …you need active forest conservation too.
- Rapid Phenotypic and Metabolomic Domestication of Wild Penicillium Molds on Cheese. Wild molds adapt to cheese, can eventually make camembert.
- A global synthesis reveals biodiversity-mediated benefits for crop production. Need species richness for pollination, biological pest control and final yields.
- Animal source foods: Sustainability problem or malnutrition and sustainability solution? Perspective matters. Let them eat meat.
- The vitality of fruit trees in ancient Bedouin orchards in the Arid Negev Highlands (Israel): Implications of climatic change and environmental stability. Recycling centuries-old infrastructure in the desert.
- The Genomic Basis for Short-Term Evolution of Environmental Adaptation in Maize. Significant shift in adaptation of tropical landrace to temperate conditions in 10 generations with little loss of genetic diversity.