- Addressing critiques refines global estimates of reforestation potential for climate change mitigation. Better mapping shows there is less land available for reforestation than we thought, and there are limited opportunities for providing multiple benefits. Still, that’s an area the size of Mexico, and worth trying to get it right.
- Genomic approaches to accelerate American chestnut restoration. The American chestnut people seem to be getting it right.
- A native seed bank is restoring land in Canada’s north. Native people — and their genebanks — can help you get it right.
- Controlled Pollination and Reproductive Strategies in Coconut: A Framework for Farmer-Led Breeding, Seednut Production, and In Situ Conservation. Farmers can be helped to get it right.
- Dehulling the secret of the germination of crop wild relatives of Cenchrus, Digitaria, Echinochloa, Setaria and Urochloa. You need information on germination breaking to get it right. In the US Midwest, for example.
- How can Brazilian legislation on native seeds advance based on good practices of restoration in other countries? Not to mention the right policies.
Crowdsourcing crop diversity, and information
A couple of crowd-sourcing initiatives caught my eye.
First, the good people at the COUSIN project want to expand genebank collections of wild relatives of wheat, barley, lettuce, brassica, and peas in Europe. And they have a pretty good idea where the collecting needs to be done. Think you can help? Check out the call for proposals.
And from a bit further south comes a plea on LinkedIn from Chris Jones of the ILRI genebank. He needs help getting stuff out of the genebank rather than into it.
As part of the ‘low-methane forages’ project, funded by the Gates Foundation and the Bezos Earth Fund, we have been screening the methane emission intensity of a range of forage accessions, in vitro, from the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) genebank. The aim is to screen approximately 10% of the accessions held in our genebank and, to date, we have assessed 155 herbaceous legumes towards this goal, including several of our lablab accessions. From these, we have identified two accessions of interest. The methane emission intensity of accession #14447 was 27.7 ml/g total digestible dry matter (TDDM), 43% lower than the highest ten legumes measured so far, and methane emission intensity of accession #14458 was 33.8 ml/g TDDM, 30% lower. So, assuming that similar differences in methane emission intensity are realised in vivo (and that is no guarantee), the preferred candidate seems obvious. However, in our field plots #14458 produced 60% more biomass than #14447, which was an ‘average’ yielder. This higher level of production should be attractive to farmers who currently struggle to incorporate much in the way of legumes in their feed rations. So, which one would you prioritise?
I’ve added the links to the Genesys entries for the accessions in questions for people who want a bit more data to base their decision on. You can provide your input on Chris’ post, or right here and I promise to pass it on.
Another chance for Bambara groundnut
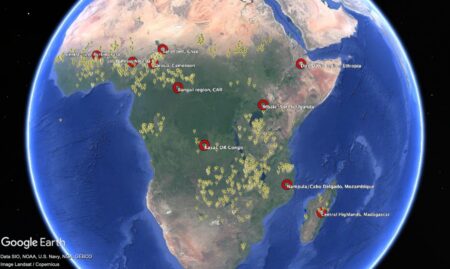
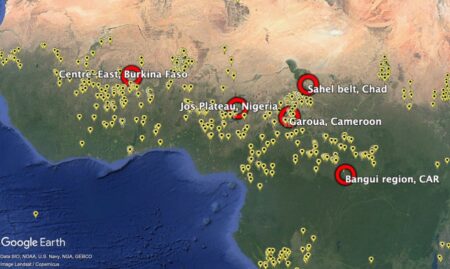
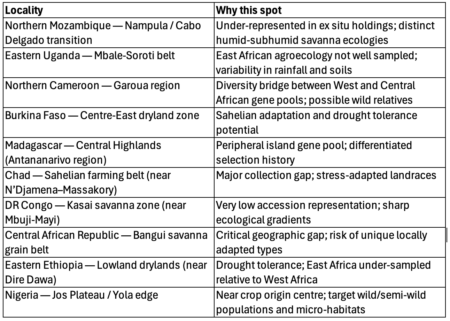
Yesterday’s Nibble on the annoyingly always-on-the-verge-of-breaking-through Bambara groundnut had me rummaging through the blog’s archives. Among dozens of references, I came across a post from almost 15 years ago that included some maps — of genebank accession localities and the distribution of the crop. On a whim, I downloaded the Genesys data and fed it into the maw of ChatGPT, asking it to identify gaps in the world’s ex situ holdings. For each of the top 10 priority collecting regions, I then asked for a best-bet locality for exploration. ChatGPT obliged with a KML file, which I then looked at in Google Earth, together with the accession localities.
This is the result.
And here’s close-up on West Africa, because that’s where accessions are densest, and the suggested “gaps” a little more difficult to understand.
Asked for a justification, this is what the LLM came up with.
Does it make any sense? Well, it’s not exactly where I would have plumped for, just eyeballing the data. But it is not complete nonsense. Maybe it was the prompt? Any ideas what that should look like to get the best results?
Not that any of this is going to help Bambara groundnut much, I suspect.
Nibbles: German genebank, Bambara groundnut, Community seedbanks, Atacama genebank, Georgian traditional crops
- Seed saving at IPK handed over.
- Why Bambara groundnut needs saving.
- Kenyan women get together to save seeds.
- Saving seeds in the Atacama Desert.
- Saving wheat and vines in Georgia.
Brainfood: Genebanks edition
- Seed collection and processing practices affect subsequent seed storage longevity in durum wheat and wild relatives. Immature seeds can still usefully be harvested for long-term storage of properly handled.
- Two-step drying of soya bean seed germplasm often improves subsequent storage longevity. “Proper handling” includes drying at higher temperatures.
- Seed-stored transcript integrity as a molecular indicator of viability in conserved common bean germplasm. mRNA degradation predicts loss of seed viability.
- Developing a cryopreservation protocol for the conservation of coconut palm (Cocos nucifera L.) using a novel type of explant, meristematic clumps. Who needs seeds anyway?
- Pollen cryobanking at the USDA-ARS National Laboratory for Genetic Resources Preservation. Well, who needs meristematic clumps?
- Mapping pea seed composition through strategic selection of accessions from the Nordic gene bank. Image analysis can be used to maximise diversity in nutritional composition in pea seeds, thus facilitating use of genebank collections. Can’t do that with pollen, I suspect.
- A small-scale assessment of the availability of EURISCO accessions. Facilitating use needs all the help it can get.
- Strengthening national genebanks through genomics and regional collaboration: Lessons from Latin America and the Caribbean. I guess genomics capacity could help with use.
- Enhancing farmers’ access and use of conserved germplasm for improved food security and climate resilience: The case of sorghum at Kenya’s national genebank. Genomics unavailable for comment. Farmers, on the other hand….
- Linking the ICRISAT Genebank to Poverty Reduction and Welfare in Malawi. Facilitating use by farmers is important.
- Farmers as breeders and seed producers: Insights from 30 years of scaling up seed clubs in Vietnam. It’s super cool when farmers organize. Including for genebanks.
- Elephant ear yam Xanthosoma robustum Schott (Araceae), a neglected crop native to Central America. Needs more attention from genebanks. And farmers and their clubs for that matter.
- Plant genebank of Sudan: Towards recovery from the wreckage of war to a new era of further capacity development based on lessons learnt from similar situations. We must de-risk genebanks. Wouldn’t want to lose all those elephant ear yam collections we’ll be making.