- An ethnographic exploration of perceptions of changes in dietary variety in the Kolli Hills, India. Cassava cash cropping has had unforeseen effects on dietary diversity.
- Mapping and assessing crop diversity in the irrigated Fergana Valley, Uzbekistan. More crops on the edges.
- An Analysis on Crops Choice and Its Driving Factors in Agricultural Heritage Systems—A Case of Honghe Hani Rice Terraces System. Established for “red rice”, but that’s not enough.
- Prebreeding Using Wild Species for Genetic Enhancement of Grain Legumes at ICRISAT. It’s not easy, but it’s been worth it.
- A Multispecies Collecting Strategy for Crop Wild Relatives Based on Complementary Areas with a High Density of Ecogeographical Gaps. Collecting in Spain in “…top 10 selected complementary areas would allow the capture of 59 of the 88 targeted taxa and 31% of the 683 different taxa-ELC category combinations identified in the ecogeographical gaps.”
- Antioxidant power, anthocyanin content and organoleptic performance of edible flowers. Tycoon Blue will be quite the marketing challenge.
- Diversifying Food Systems in the Pursuit of Sustainable Food Production and Healthy Diets. And nary an edible flower mentioned.
- Cereal price shocks and volatility in sub-Saharan Africa: what really matters for farmers’ welfare? Prices.
How many genebanks are there in the world?
The UN Statistics Division (UNSD) is responsible for bringing together data on the Sustainable Development Goals, and does a generally pretty good job of explaining the just-agreed targets and indicators on its new(ish) website. Let’s remind ourselves that Goal 2 is: “End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture.” And that Target 2.5 and its associated indicators are as follows:

The UNSD website presents the challenge under the heading: Increased efforts are needed to achieve the 2020 target on maintaining genetic diversity. But what’s the baseline? Here’s what it has to say specifically on genebanks (Indicator 2.5.1):
By the end of 2016, 4.7 million samples of seeds and other plant genetic material had been conserved in 602 gene banks across 82 countries and 14 regional and international centres. Over the past 11 years, the rate of increase in gene-bank holdings has slowed.
There’s even a graph:
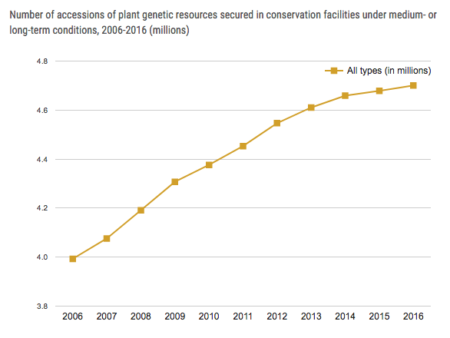
These figures, however, are a bit of a departure from the ones we usually use, which come from the Second Report on the State of the World’s Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (SoWPGR2). That said there were 7.4 million accessions in 1,750 genebanks in 2010. This is from the “synthetic account” of SoWPGR2, a kind of executive summary:
Have 1,148 genebanks up and disappeared? No, I don’t think so. What’s happened is that UNSD is using data from FAO’s ongoing efforts to monitor implementation of the Global Plan of Action on PGRFA, and prepare the third SoWPGR, and these are still incomplete, not all countries having reported yet (there’s a couple of years still to go on that process, but an update was provided to the FAO Commission on Genetic Resources for Food & Agriculture earlier this year). Likewise, 2 million-odd accessions have not gone up in smoke. It could be just incomplete data again. Or maybe UNSD is using data on Annex I crops only? The metadata behind the UNSD information on Target 2.5 refers to “unique” accessions in long- and medium-term conservation, rather than total number of accessions, so it could be that too. Here’s the relevant excerpt from SoWPGR2:
Based on figures from the World Information and Early Warning System (WIEWS) and country reports, it is estimated that about 7.4 million accessions are currently maintained globally, 1.4 million more than were reported in the first SoW report. Various analyses suggest that between 25 and 30 percent of the total holdings (or 1.9-2.2 million accessions) are distinct, with the remainder being duplicates held either in the same or, more frequently, a different collection.
Germplasm of crops listed under Annex I of the ITPGRFA is conserved in more than 1,240 genebanks worldwide and adds up to a total of about 4.6 million samples. Of these, about 51 percent is conserved in more than 800 genebanks of the Contracting Parties of the ITPGRFA and 13 percent is stored in the collections of the CGIAR centres.
Anyway, I’m sure all this will be sorted out in due course. Let’s not quibble. It’s difficult pulling these data together from dozens of countries, plus regional and international organizations as well, and just having genebanks recognized as crucial to the goal of ending hunger is pretty cool, no matter how you count them.
Nibbles: Dwarf rice, Ricestoration, Tarostoration, Biorepositories, Sustainable coffee, Cactus wars, Goaty portraits, Spandrels, Potato genebank, Forests and nutrition
- The long and short of Green Revolution rice.
- Restoring historical slave-worked rice fields in North Carolina.
- Kinda similar, but taro in Hawaii.
- There’s a bank for milk diversity.
- Nice review of sustainable coffee production.
- Opuntia: tasty but deadly (to some).
- Handsome goat pix.
- Festoons of fruits at the Farnesina: Jeremy is incensed.
- Great new webpages for the CIP genebank.
- Another report on a report that living close to forests is good for nutritional security, up to a point. But bushmeat?
Nibbles: Visionary edition
- New guy in charge Peter Wenzl gives us his vision for the CIAT genebank.
- Agriculture and Irrigation Minister of Peru gives us his vision for the Peruvian genebank.
- CIMMYT’s annual report gives us a vision of conserving maize in Guatemala.
- Farmer Somashekhara gives us his vision for finger millet farming in India. And two makes a trend…
- Retired agriculture expert Malcolm Hazelman gives us his vision for Samoan gardens.
- A Tagorean vision of radical relocalization involving perennial edimentals.
- Lots of people give us their vision for saving the wild apple.
- IFPRI gives us their vision for the future of food in a changing world. With infographic goodness.
- Natalie Mueller et al. give us their vision for reviving the forgotten crops of the Eastern Agricultural Complex.
- A vision of a planet protected in situ, in multiple ways. Yes, even pigeons. And yes, even cities, though agrobiodiversity neglected as usual.
- A vision of permanent identifiers everywhere.
- DNA gives us a vision of domestication explained. Yes, even sugarcane.
Brainfood: Taste breeding, Cat domestication, ITPGRFA in USA, CWR extravaganza, Ecology & ag, Brassica identification, Biodiversity monitoring, Languages, Species recovery, Benin pigeonpea
- Sensory sacrifices when we mass-produce mass produce. You need consumer-assisted selection.
- The palaeogenetics of cat dispersal in the ancient world. Two Middle-Eastern sub-populations of one sub-species contributed to domestication, at different times, and the result spread first with agriculture and then aboard ships. But we haven’t changed them in the same way we’ve changed dogs etc. You don’t say.
- U.S. ratification of Plant Treaty: benefit sharing ambiguity for plant genomics researchers does not change. But what about genomics data?
- Wading Into the Gene Pool: Progress and Constraints Using Wild Species. Introduction to the Special Section on CWR.
- Plant ecological solutions to global food security. Introduction to the Special Feature on Ecological Solutions to Global Food Security. The intersection with the above is probably here.
- A multiplex PCR for rapid identification of Brassica species in the triangle of U. Now there’s no excuse.
- Connecting Earth observation to high-throughput biodiversity data. I don’t see any reason why the same thinking couldn’t be applied to crop diversity.
- Linguistic diversity of natural UNESCO world heritage sites: bridging the gap between nature and culture. 80% of Natural WHSs intersect at least one indigenous language.
- Overcoming barriers to active interventions for genetic diversity. Embrace the hybrid by focusing on process, not form.
- Utilization and farmers’ knowledge on pigeonpea diversity in Benin, West Africa. For some reason, farmers don’t like coloured seeds.
