- Large‐scale GWAS in sorghum reveals common genetic control of grain size among cereals. QTLs for grain size potential (rather than capacity to fill grains) identified in sorghum, turn out to be similar to other cereals.
- Linking global drivers of agricultural trade to on-the-ground impacts on biodiversity. Specific soy buyers with disproportionate impact on endemic and threatened cerrado species identified by fancy maths. Yes, you’re probably responsible for the plight of the giant anteater.
- Long-term conservation of potato genetic resources: Methods and status of conservation. Useful brief roundup.
- Impacts of Maize Domestication and Breeding on Rhizosphere Microbial Community Recruitment from a Nutrient Depleted Agricultural Soil. Hybrids changed the rhizosphere.
- Genome-wide diversity of northern South America cultivated Coconut (Cocus nucifera L.) uncovers diversification times and targets of domestication of coconut globally. Atlantic tall cultivar splits from Pacific cultivars approximately 5400 years ago, then Pacific Tall and Pacific Dwarf cultivars split from a shared common ancestor 1600 years ago.
- Forest pattern, not just amount, influences dietary quality in five African countries. Forests are good for you.
- Plant agro-biodiversity needs protection, study and promotion: results of research conducted in Lombardy region (Northern Italy). 78% of landraces lost in last 70-80 years, 72 left.
- Genomic prediction of grain yield in contrasting environments for white lupin genetic resources. It’s worth genotyping everything…
- Genetics without genes? The centrality of genetic markers in livestock genetics and genomics. …but genotyping-by-sequencing may not be necessary.
- Opportunities from the genetic diversity of the ILRI genebank forage germplasm collection. Genotyping-by-sequencing and morphology used to define mini-core subsets for important forages. So it is necessary for some things?
- The Green Revolution shaped the population structure of the rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Strong selection leads to adaptation, fast. Well I never!
- Land productivity dynamics in and around protected areas globally from 1999 to 2013. Productivity increases are most common outside protected areas. But does that increase or decrease pressure on them? See below.
- Assessing the ecological vulnerability of forest landscape to agricultural frontier expansion in the Central Highlands of Vietnam. This is how you find out.
- Weight Gains from Trade in Foods: Evidence from Mexico. Food imports from US explain 20% of the increase in obesity in Mexican women.
A bit more on what happened at GB8
I did suggest a couple of days ago that I’d have more to say about the Eighth Session of the Governing Body of the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture. And here it is, over at the work blog.
If you think I got anything wrong, or missed anything out, or you want further details or clarifications, you can leave comments here if you like, and I’ll try to reply, or get others to do so if I can’t.
Staving off the apocalypse
Multiplying the budget of CGIAR, the world’s largest global agricultural innovation network, would be a good start. And, in a time of great disruptions, we ought to prioritize Sustainable Development Goal 2.4, implementing resilient agricultural practices, with a greater focus on smallholder farmers in developing countries.
That’s from a post by Asaf Tzachor, research associate at the cheerfully named Centre for the Study of Existential Risk at the University of Cambridge, cheerfully entitled Down the Hunger Spiral: Pathways to the Disintegration of the Global Food System. Hard to argue with, except for maybe that SDG 2.5 may be even more important than 2.4
And it was soon backed up by a piece in The Economist which had agricultural R&D in the top 3 value-for-money development interventions for Africa, according to the Copenhagen Consensus.
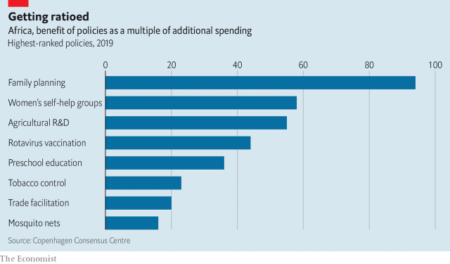
So what’s the hold-up?
No deal
I should of course have pointed this out before, but there was a hashtag for the recently concluded Eighth Session of the Governing Body of the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture. I’ll have more to say about this somewhat frustrating meeting in due course, but for the moment you can do a lot worse than read the summary in Earth Negotiations Bulletin. Here’s the bottom line, though, if you’re in a hurry:
What exactly happened remains obscure, largely because once negotiations started, they were closed to observers. The facts are the following: a small, closed group of negotiators met day and night from Wednesday evening to the early hours of Saturday morning; according to reports, the group discussed the main controversial items, such as benefit-sharing from DSI 1 use, and specific payment rates for benefit-sharing; and on Saturday afternoon, plenary was presented with a Chair’s proposed “package,” including a resolution, a revised SMTA text, text for the amendment of Annex I of the Treaty, and terms for intersessional work. Developing countries rejected it as unfair and unbalanced, particularly regarding DSI. In turn, developed countries opposed continuation of intersessional work on the item.
So, after years of negotiation, there was no agreement on enhancing the functioning 2 of the ABS regime the Treaty has put in place, called the Multilateral System 3. And no clear way forward to the next meeting, in India in 2021. There was some progress on other important issues, but it’s going to be a bumpy couple of years.
Payne gains
Many congratulations to Dr Tom Payne, Head of CIMMYT Wheat Germplasm Bank on receiving the Frank N. Meyer Medal, which recognizes outstanding contributions to the conservation and use of crop diversity.
