Tom Payne of CIMMYT was a bit worried about that Global Crop Loss Survey:
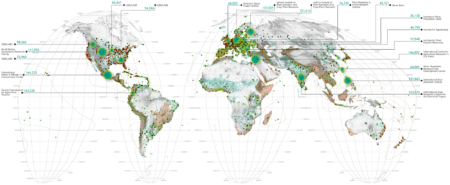
The wheat data suggests that a preponderance of responses came from Europe (where the trio of disease septoria tritici-yellow rust-fusarium head blight are prevalent). Interestingly, the emerging threats of “Ug99 types” of stem rust and wheat blast are not revealed though they may have far more dramatic impacts on a global basis.
But Andy Nelson has it covered:
Around 30% of wheat responses came from Europe, with the rest fairly well distributed in wheat growing areas around the rest of the world. Stem rust and wheat blast are in the complete list of response with numbers and locations that reasonably reflect their emerging threat status. They’re just not in the top five that we included in this preliminary report to the ISPP. More analysis and details will come though.