Many congratulations to Dr Tom Payne, Head of CIMMYT Wheat Germplasm Bank on receiving the Frank N. Meyer Medal, which recognizes outstanding contributions to the conservation and use of crop diversity.

Agricultural Biodiversity Weblog
Agrobiodiversity is crops, livestock, foodways, microbes, pollinators, wild relatives …
Many congratulations to Dr Tom Payne, Head of CIMMYT Wheat Germplasm Bank on receiving the Frank N. Meyer Medal, which recognizes outstanding contributions to the conservation and use of crop diversity.

There’s been a lot of action on the cucurbit domestication front lately. Hot on the heels of a comprehensive Tansley review of all the crops in the family in New Phytologist 1 now come two papers out of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences focusing on the melon and watermelon:
There are press releases on each of these, of course. But the more interesting take is provided by some IPK researchers 2, who mash up the two studies. 3 And provide a nice graphic to summarize the whole thing.
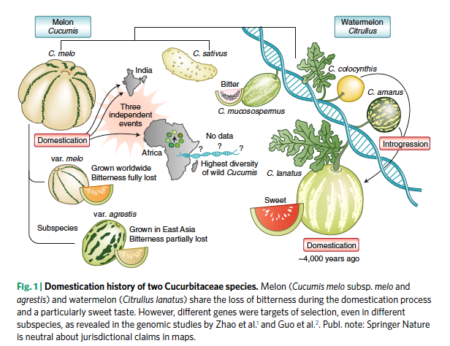
The bottom line(s)? The two different subspecies of melon acquired sweet flesh through different mutations, independently but probably both in India; there was a third domestication event in Africa, but the authors had too little material at hand to say much about this. Melon and watermelon lost their bitterness through convergent evolution, and the latter has benefitted from introgression from two wild relatives, one of which was separately domesticated for its seeds.