- Who needs plants anyway?
- Who needs seedless grapes anyway?
- Who needs livestock anyway?
- Who needs the CIMMYT genebank anyway?
- Who needs information on germplasm collecting missions anyway?
- Who needs science communications anyway?
Strategizing about forages
My latest over at the work blog is about forages, their genebanks, and my mother-in-law.
Cows get a lot of bad press these days. They are blamed for climate change and deforestation and even unhealthy diets, as if it’s their fault that people like to scoff down cheeseburgers. In fact, the widely repeated assertion that “animal agriculture and eating meat are the biggest causes of global warming” is nothing but a myth. Livestock production is a significant contributor to carbon emissions, to be sure, but the real problem is how the production is done in rich countries. For a billion mostly poor farmers in developing countries, cattle and other livestock are not a problem: they’re a solution.
Nibbles: Yeast phylogeny, Jurassic beer, Welsh drink, Italian fruits, Vinegar museum, Lethal yellowing, Wilderness loss
- Beer yeast was domesticated in the 1600s. Or maybe not.
- I see that and raise you 65 million years.
- If you don’t like beer, try Lurvill’s Delight, but it’s only about 100 years old, I warn you.
- Preserving ancient fruits in an Italian orchard.
- And how many different types of vinegar do you think the vinegar museum has?
- The Caribbean coconut is under attack.
- We’ve been such bastards to the environment.
Brainfood: Eurisco, Saline barley, ICRISAT sorghum, Hardy kiwi, Pepper diversity, Pakistani dates, W Africa & climate change
- EURISCO: The European search catalogue for plant genetic resources. 43 countries, 400 institutes, 1.8 million accessions, and a vital part of Genesys!
- Yield-related salinity tolerance traits identified in a nested association mapping (NAM) population of wild barley. Salinity allele found in wild barley.
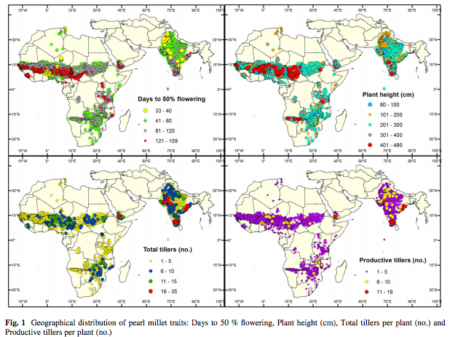
- Geographical distribution of traits and diversity in the world collection of pearl millet [Pennisetum glaucum (L.) R. Br., synonym: Cenchrus americanus (L.) Morrone] landraces conserved at the ICRISAT genebank. Plant height in Burkina Faso ranges from 80 to 490cm.
- Hardy Kiwifruit Genetic Resources. They’re wild.
- Deciphering Genetic Diversity in the Origins of Pepper (Capsicum spp.) and Comparison with Worldwide Variability. Diversity is decreasing in Ecuador.
- Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) markers show greater similarity among morphologically diverse Date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) cultivars grown in Pakistan. Morphologically diverse varieties show little genetic diversity.
- Assessing climate adaptation options and uncertainties for cereal systems in West Africa. About the only thing that’s going to work is increased temperature resilience during flowering.
Dissecting pearl millet diversity
![]() Our friends at ICRISAT have been busy describing their pearl millet collection, and their latest offering is a thorough analysis of the geographic distribution of morphological traits. That follows, among other things, a general review of the collection, and an analysis of latitudinal patterns in morphological diversity.
Our friends at ICRISAT have been busy describing their pearl millet collection, and their latest offering is a thorough analysis of the geographic distribution of morphological traits. That follows, among other things, a general review of the collection, and an analysis of latitudinal patterns in morphological diversity.
That last paper showed that although pearl millet landraces reach basically similar latitudes in both the N and S hemispheres (about 34°), there is much more cultivation north of the equator than south, as one would perhaps expect from the relative distribution of landmasses, except perhaps for the 15°–20° range, from which there is more cultivation south of the equator than north. Mid-latitude regions (15°–20°) in both hemispheres have proved the most useful as sources of material for developing high-yielding cultivars (they are early-maturing, producing long and thick panicles with large seeds). So it seems that southern hemisphere germplasm has a greater chance of being useful in breeding, although most cultivation is in the north. Another example of interdependence.
The latest paper 1 goes in a lot more detail for individual traits. It’s very difficult to summarize patterns in 8 quantitative traits (days to 50% flowering, plant height, total and productive tillers per plant, panicle exsertion, length and thickness and 1000 seed weight) and 8 qualitative traits (panicle shape and density, bristle length, seed shape and color, endosperm texture, green fodder yield potential and seed yield potential) from 15,969 accessions from 30 countries. So I’ll limit myself to one recommendation. If you want to see huge variation in pearl millet height, go to Burkina Faso.