- USDA should think about agroecology more. Or at all?
- The latest from PAGXXII. Lots on domestication, genebanks, crop improvement, all that cool stuff.
- There’s also AETFAT going on, and it’s just as cool. Maybe more so. Though less socially networked, I guess.
- How public gardens should build up living plant collections. You’d have thought they’d know.
- An update on plant genetic resources from ISHS. Lots happening…
- How to support agrobiodiversity through sustainable sourcing.
- KFC must have read that slideshare above.
- Breaking down the terroir. And not for the first time.
- Does vanilla have terroirs? I bet it does. Should ask the world’s expert.
- Dye mushrooms? Are you kidding me?
- ARCAD, DIADE: No matter how you spell it, lots of French interest (and money) in crop and livestock genetics.
- Likewise in India, it looks like from this piece on NBPGR.
- The Bioversity Policy Unit is apparently still alive and kicking.
- European eels a conservation success story?
- Let the ancient DNA sequencing begin!
Brainfood: Diversity in restoration, Niche model validation, Dutch diets, Markets in conservation, Genomics for stress, Protected agroecosystems, Cocksfoot diversity, Tree breeding, Organic in India, Coconut origins, Dope diversity
- Application of genetic diversity–ecosystem function research to ecological restoration. Cultivars vs local populations vs genetic diversity approaches in restoration reviewed. More research needed, natch, but genetic diversity should not be dismissed out of hand in a bid for rapid establishment or long-term persistence, as it may well be best for ecosystem functioning.
- Application of consensus theory to formalize expert evaluations of plant species distribution models. Given arm-twisting, experts like models.
- Exploring dietary guidelines based on ecological and nutritional values: A comparison of six dietary patterns. The Dutch should eat less meat. No word on beer.
- Market-based mechanisms for biodiversity conservation: a review of existing schemes and an outline for a global mechanism. You can’t monetize what you can’t measure.
- Genomic resources for breeding crops with enhanced abiotic stress tolerance. You still need the phenotyping.
- Perceptual distinctiveness in Native American maize (Zea mays L.) landraces has practical implications. Kernel colour diversity is a marker for other, more interesting, kinds of diversity.
- Can agro-ecosystems efficiently complement protected area networks? Yes, but only in combination with expansion of protected natural habitats. For birds in Israel, that is.
- Indicators for genetic and phenotypic diversity of Dactylis glomerata in Swiss permanent grassland. Management alters both genotype and phenotype.
- A ‘Reality Check’ in the Management of Tree Breeding Programmes. Have come far, but still a ways to go, in particular with regard to the balance between DNA-based vs conventional breeding and genetic gain vs genetic preservation.
- Yield and Economic Performance of Organic and Conventional Cotton-Based Farming Systems — Results from a Field Trial in India. Organic soybean may be a viable long-term option. Cotton and wheat, jury still out. But early days yet, these rotation trials take a long time to get going.
- Long-distance dispersal of the coconut palm by migration within the coral atoll ecosystem. Hugh Harries, one of the authors, in a recent email to us: “Recent reviews have blown dust from old reports of pre-Colombian coconuts in Panama and demonstrated how the rate of germination distinguishes the naturally selected wild coconut from the domestically selected sort. This review formulates a hypothesis which could identify a previously unconsidered route along which the primordial coconut might travel between the South American and Indian tectonic plates without being indigenous on either.” That is, atoll-hopping.
- Differentiation between fiber and drug types of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) from a collection of wild and domesticated accessions. Must have been fun doing the evaluation.
Dope diversity denied?
There’s one thing I want to know about what’s going to happen now that marijuana has been legalized in a couple of states in the US. And it’s not on CNN’s list. 1 No, not where a visitor can actually smoke the stuff legally, as opposed to just buying it. Or how I can get a job in the industry. What I want to know is what will happen to diversity. There are some indications that legalization may lead to an increase in intellectual property protection over particular strains. I hope someone out there is gathering the baseline data, and saving the seeds, just in case. Not to mention learning lessons that could then be applied to, I dunno, opium in Afghanistan?
Dorian Fuller on domestication, and not only of donkeys
Speaking of Dorian Fuller, in addition to his always fascinating The Archaeobotanist blog, he also curates five — count them — topics on Scoop.it, reflecting the wide range of his interests. Unlike many others on Sccop.it, including me, Dr Fuller always provides trenchant commentary on the material he posts. Browsing through his stuff, I ran across a post on a paper on donkey domestication which I had missed last year. I hope he won’t mind if I reproduce his insights here, to give a flavour of what you can expect if you follow him.
Donkey’s are undoubtedly one of the most important domesticates from Africa, but less well-documented then cattle or many crops, as they have rarely been food sources. This article provides updated review of the archaeology and genetics of donkey, including some ancient DNA evidence such as Uan Muhhgiag donkeys from prehistoric Libya. Of interest is the argument that reports of “wild” donkeys in the Levant or Arabia, such as the quantities from Ash-Shumah in Yemen, are early domesticates and not endemic wild populations. If this is the case then it would put donkey herding back to the early Holocene before 6000 BC, putting them in competition of Bos africanus for the earliest African domesticates [excluding Pleistocene bottlegourds]. Alternatively, as mapped in Boivin & Fuller (2009 in J. of World Prehistory) we extend the map of wild donkeys through the Sinai and down the west coast of Arabia to make the Ash-Shumah remains those of hunted wild animals. The latter would open the possibility of southern Levant donkey domestication. The current review by Kimura, Marshall and colleagues makes an interesting but inconclusive case against this. (Historical linguistic evidence does tend to point to African domestication among Afroasiatic/Cushitic sub-groups). As this paper concludes there is a need for more targetted research on donkeys!
Which also allows me to post one of the pix from my recent holiday on Lamu island off the coast of Kenya, where donkeys are of course the only form of transportation.
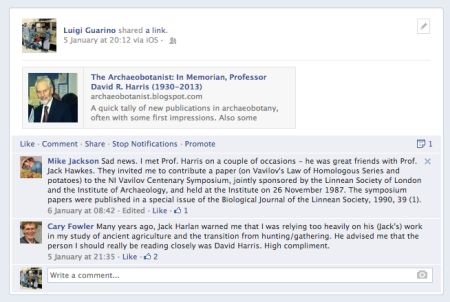
Prof. David Harris RIP
Prof. David Harris, one of the giants of the study of the origins of agriculture, died during the holiday period. He was Professor Emeritus of Human Environment at the Institute of Archaeology (UCL) and a former director of the institute (1989-1996). Dorian Fuller, a friend and colleague at the institute, has an informative and touching piece about Prof. Harris on his blog. The comments there, and on my re-posting of Dr Fuller’s piece (see below), are ample evidence of Prof. Harris’ impact and legacy.