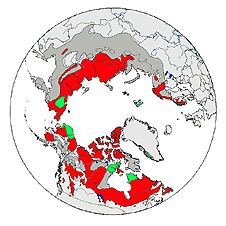
The species Rangifer tarandus is divided into seven subspecies, but all are in trouble, according to a survey of their status published in a recent paper in Global Change Biology. We’re talking about the animals that are usually called reindeer in Europe and caribou in North America. All across their circum-polar range their populations are undergoing an unprecedented synchronous decline (red denotes herds in decline in the map below, which I hacked from the BBC article quoted below, green indicates those on the increase and dark grey means no data is available).
One subspecies — R. t. tarandus — comprises the semi-domestic and wild reindeer that live across northern Scandinavia and Russia and are so important to the Sami people and others. Here’s one of the authors quoted by the BBC on the causes of the decline:
“If global climate change and industrial development continue at the current pace, caribou and reindeer populations will continue to decline in abundance,” says Vors.
“Currently, climate change is most important for Arctic caribou and reindeer, while anthropogenic landscape change is most important for non-migratory woodland caribou.”
Interestingly, reindeer were recently re-introduced to Britain after a gap of 800 years. I guess their long-term future there must be in question.