I’m not sure I was aware of the fact that grasspea (khesari dal, or Lathyrus sativus) was actually banned in parts of India due to its toxicity. Devinder Sharma, a food and trade policy analyst, thinks the ban should not be lifted, International Year of Pulses notwithstanding. Instead, alternative crops should be promoted, such as pigeonpea (arhar, or Cajanus cajan). It’s interesting that there’s no Indian grasspea in the genebanks that Genesys knows about (red), 1 in stark comparison to pigeonpea (blue).
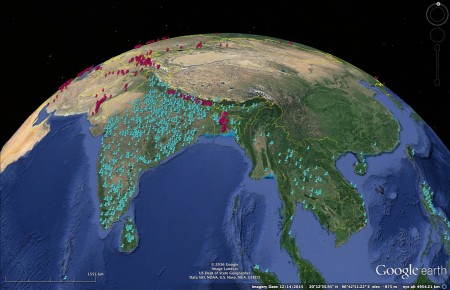
Lathyrism is a problem in situations where grasspea is pretty much the only thing you have to eat. In former times, when famines were more frequent, the ban probably made sense. But is this still the case? And in any case there’s also lots of research going on low-neurotoxin varieties. A ban is hardly likely to provide much of an incentive for such breeding work.