- SeedUSoon: A New Software Program to Improve Seed Stock Management and Plant Line Exchanges between Research Laboratories. Great name.
- Building a Global System for the conservation and use of all plant diversity. Botanical gardens learning from crop genebanks?
- Understanding potato with the help of genomics. Crop genebank learning from genomics.
- What are the socioeconomic implications of the value chain of biodiversity products? A case study in Northeastern Brazil. Two Amazonian fruits, very different markets.
- Weak Genetic Structure in Northern African Dromedary Camels Reflects Their Unique Evolutionary History. Severe bottlenecks and long-distance movement makes for quite a genetic mess.
- Genetic variation for tuber mineral concentrations in accessions of the Commonwealth Potato Collection. Is considerable, and might be useful in breeding. I’m shocked.
- The Domestic Livestock Resources of Turkey: Social Aspects, Genetic Resources and Conservation of Companion Animal Cats (Felis Catus). The nondescript cats are not in danger.
- Feasting, Social Complexity, and the Emergence of the Early Neolithic of Upper Mesopotamia: A View from Göbekli Tepe. Agriculture as a result of religious feasting. No word on the role of cats.
- Economic Development and Forest Cover: Evidence from Satellite Data. More money = more deforestation.
Nibbles: Coffee & chocolate redux, American Indian food, Crop seed size, Oca breeding club, Black chicken, Deadly lychees, Arctic potatoes, Eat this animal-derived food
- Genetics will save coffee.
- And probably chocolate too, but not alone: new podcast from Simran Sethi.
- Must be catching.
- Native American foodways get a resource guide.
- Cultivated plants have larger seeds than wild relatives. Well I never.
- Wanna breed oca?
- A chicken after my own black heart.
- Even tasty fruits can be deadly.
- Commonwealth Potato Collection goes to Svalbard.
- Got milk! Jeremy’s latest pod.
Migrant coconuts
A couple of days ago, Jay Bost asked about the origin of coconuts in the Americas:
Anyone ever explore possibility of dispersal of coconut to Americas by Polynesians? Given movement of sweet potato and chickens, any chance they brought coconut?
The answer, it turns out, is out there. I take the liberty here of highlighting what might otherwise remain somewhat buried in a comment on a comment:
Gunn et al. (2011) suggest that the species, “a native of the Old World tropic…was spread to eastern Polynesia and subsequently introduced to the Pacific coasts of Latin America, most likely by pre-Columbian Austronesian seafarers from the Philippines”. Figure 2. is a great schematic showing coconut dispersal routes by humans
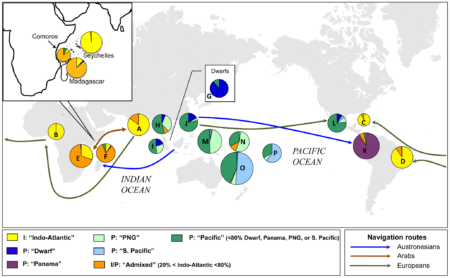
Brainfood: Wheat elements, Coconut movement, Wild lettuce, Pacific yams, Wild VIR oats, PREDICTS, Potato leaves, Perennial wheat, Wheat adoption
- Genetic Nature of Elemental Contents in Wheat Grains and Its Genomic Prediction: Toward the Effective Use of Wheat Landraces from Afghanistan. Only one significant marker, for Zn.
- Strategies for exchange of coconut germplasm in Brazil. Zygotic embryos in Petri dish containing Y3 culture medium without sucrose can last a couple of days without bacterial infection.
- Phylogenetic relationships within Lactuca L. (Asteraceae), including African species, based on chloroplast DNA sequence comparisons. The African species are probably not Lactuca at all.
- The Pacific yam (Dioscorea nummularia Lam.), an under-exploited tuber crop from Melanesia. It can be improved through crossing with itself, or with other species.
- Eco-geographical assessment of Avena L. wild species at the VIR herbarium and genebank collection. Some more collecting to be done.
- The database of the PREDICTS (Projecting Responses of Ecological Diversity In Changing Terrestrial Systems) project. Including 15,000 plants. No word on whether any of them Avena.
- Your Poison in My Pie—the Use of Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) Leaves in Sakartvelo, Republic of Georgia, Caucasus, and Gollobordo, Eastern Albania. Only used as first vegetable in spring in isolated high mountain areas in the southern Balkans.
- Toward a taxonomic definition of perennial wheat: a new species ×Tritipyrum aaseae described. Not entirely clear why naming it as a new species is necessary, but it’s still pretty cool.
- Dynamics of variety change on wheat farms in Pakistan: A duration analysis. For marginal farmers, it’s about yield, for others, quality. No word on how perennial wheat might do.
Filipino rice landraces documented
Congratulations to all concerned for the launch of the catalogue of Philippine Traditional Rice Varieties. I’m reliably informed it will be available online soon. In the meantime, I’ve had the privilege of consulting a PDF, and I can confirm that it is really as cool as it sounds.
