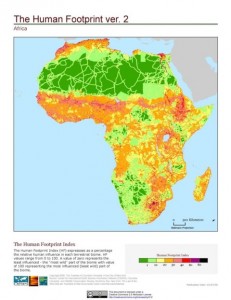
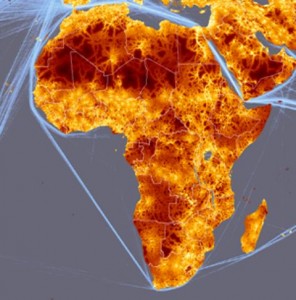
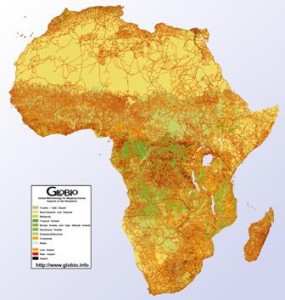
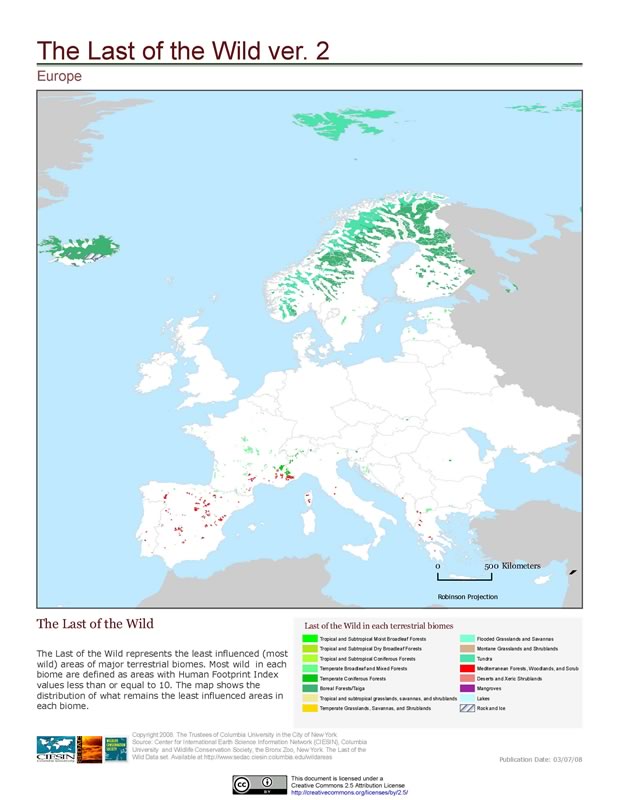
Glenn Hyman has a great map over at AGCommons. It shows the sites in Africa where international crop networks carried out yield trials in the 1960’s, 70’s and 80’s (and some beyond). Here it is:
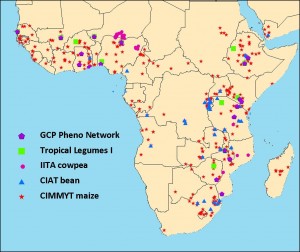
Would be interesting to compare with the various accessibility maps I posted a couple of days ago, and indeed with agroclimatic maps. No doubt Glen is doing it as we speak, and lots of other stuff too.
Read the interesting comment too: “Africa’s green revolutions will be fundamentally different from Asia’s — because Africa and Asia are fundamentally different, because times have changed, and because we have learnt a few tricks in the meanwhile!!”