- EcoregionsTreeFinder—A Global Dataset Documenting the Abundance of Observations of > 45,000 Tree Species in 828 Terrestrial Ecoregions. The right native tree for your ecoregion of choice. Which, given lots of the stuff below, is good to know. Oh, and BTW, there’s also the Agroforestry Species Switchboard.
- Modelling the distribution of plant-associated microbes with species distribution models. Would be cool to mash up with the above one day.
- The promise of digital herbarium specimens in large-scale phenology research. Something else you can use herbarium specimens for, if you’re careful.
- A global indicator of species recovery. The Green Status Index of Species Recovery, no less. Herbaria surely involved again.
- Valorization of feral pigs in the tropics, from the genetic characterization to the re- domestication. Wish there was a Green Status Index of Breed Recovery.
- Global staple food trade exacerbates biodiversity loss: a network perspective. Soybeans are messing with the Green Status Index of Species Recovery of lots of species, I suspect.
- Prospects for cereal self-sufficiency in sub-Saharan Africa. Prospects for self-sufficiency are not bad, but will require yield increases if the Green Status Index of Species Recovery is not going to take a hit.
- Protecting crops with plant diversity: Agroecological promises, socioeconomic lock-in, and political levers. Agroforestry and diverse landscapes are best for pest control, but cultivar mixtures are worth a try too. Wonder what they will do for cereal self-sufficiency in Africa. I lot, I bet, if given a chance.
- The dynamics of crop diversity and seed use in the context of recurrent climate shocks and poverty: Seasonal panel data evidence from rural Uganda. Farmers use crop diversity to cope with climate change, and wealthy farmers do it better. Pest control too, maybe?
- Understanding Farmer Preferences to Guide Crop Improvement: The Case of Grasspea in Ethiopia. Breeders should provide jam today and jam tomorrow.
- Crop diversity trends captured by Indigenous and local knowledge: introduction to the symposium. Indigenous and local knowledge can help you keep track of all of the above.
Modified ecosystems and the conservation of crop diversity
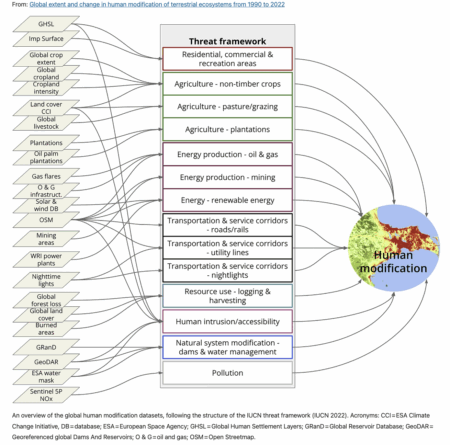
A new global assessment of the state of terrestrial ecosystems has just been published, focusing on the extent of human modification due to “industrial pressures based on agriculture, forestry, transportation, mining, energy production, electrical infrastructure, dams, pollution and human accessibility.” 1
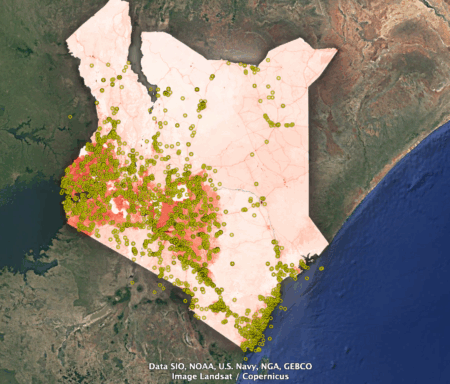
As is my wont, I tried to find a form of the data that I could shoehorn into Google Earth, but I failed. Fortunately GIS guru Kai Sonder of CIMMYT was able to snip out a kml file of overall human transformation as of 2020 covering Kenya — don’t ask me how. But thanks, Kai. I put on top of it genebank accessions from Kenya classified as wild or weedy in Genesys.
I don’t know quite what to make of this. The wild populations seem to have been mainly collected in areas that in 2020 were very highly affected by human activity. But is that good or bad?
It could be good — in a sense — if the high degree of human transformation means that the original populations are not there any more. 2 Phew, good thing they were collected! On the other hand, it could be bad if the concentration on easily accessible and modified areas means that the genetic diversity currently being conserved is not representative of what’s out there.
What do you think?
But of course what I really want is a version of this which focuses on agricultural areas and is updated in real time. Yes, a perennial favourite here: a real early warning system for erosion of crop diversity.
Brainfood: Complementarity, Temporality, Communality, Fonio trifecta, Atriplex domestication, Egyptian clover in India, Genebank information systems
- A significantly enhanced role for plant genetic resource centres in linking in situ and ex situ conservation to aid user germplasm access. On-farm conservation must result in use of the conserved diversity, and genebanks can help with that. Just another way of saying the two approaches are complementary?
- Looking back to look ahead: the temporal dimension of conservation seed bank collections. Those genebanks may need to do repeated sampling of the same population though.
- Landrace diversity and heritage of the indigenous millet crop fonio (Digitaria exilis): Socio-cultural and climatic drivers of change in the Fouta Djallon region of Guinea. Repeated sampling would defintely have helped.
- Community seedbanks in Europe: their role between ex situ and on-farm conservation. Repeated sampling is kind of what community seedbanks do, no?
- Impacts of climate change on fonio millet: seed germination and suitability modelling of an important indigenous West African crop. Community seedbanks may not be enough though.
- Phylogenetics, evolution and biogeography of four Digitaria food crop lineages across West Africa, India, and Europe. Maybe the wild relatives will help.
- Black Ash – a Forgotten Domestication Trait in Garden Orach (Atriplex hortensis L.). It’s amazing what people domesticated plants for in the past. And might in the future.
- Quality seed production scenario of Egyptian clover (Trifolium alexandrinum) in India: A 24-year retrospective analysis. But in the end, you have to get high quality certified seeds out, and that’s not always easy.
- The potential of seedbank digital information in plant conservation. Will definitely need a pretty good documentation system to keep all the above straight.
What makes a good coffee… map?
Thanks to Christian Bunn for throwing some shade on the work underlying the map of putative changes in coffee suitability that I so blithely shared yesterday. Maps can be both pretty and also the result of suspect methodology, I guess.
Brainfood: Maroon rice, Dutch aroids, Sicilian saffron, Inca agriculture, Native American agriculture, Mexican peppers, Afro-Mexican agriculture, Sahelian landraces, Small-scale fisheries, Coconut remote sensing
- The Mystery of Black Rice: Food, Medicinal, and Spiritual Uses of Oryza glaberrima by Maroon Communities in Suriname and French Guiana. There’s a rich oral history of African rice in Maroon communities, but that doesn’t mean either the traditional knowledge or diversity of the crop is safe.
- The Invisible Tropical Tuber Crop: Edible Aroids (Araceae) Sold as “Tajer” in the Netherlands. Another example of traditional knowledge on crops surviving far from their home.
- Rethinking Pliny’s “Sicilian Crocus”: Ecophysiology, Environment, and Classical Texts. There might have been two distinct saffron species in ancient Sicily. Another way of recovering traditional knowledge is by reading ancient texts.
- Trees, terraces and llamas: Resilient watershed management and sustainable agriculture the Inca way. The sedimentary record can be used to recover traditional knowledge too. No word on what ancient text have to say, but I’m sure it’s something.
- Yield, growth, and labor demands of growing maize, beans, and squash in monoculture versus the Three Sisters. Sometimes traditional knowledge can use a helping hand from scientists. And vice versa.
- Interdisciplinary insights into the cultural and chronological context of chili pepper (Capsicum annuum var. annuum L.) domestication in Mexico. About the only thing that’s missing here is traditional knowledge.
- Afro-Indigenous harvests: Cultivating participatory agroecologies in Guerrero, Mexico.
Makes one wish these authors had been involved in the pepper study above. - Tradeoffs between the use of improved varieties and agrobiodiversity conservation in the Sahel. The effect of improved varieties on local landraces (and presumably associated traditional knowledge) is different for pearl millet and groundnut, and for Mali and Niger.
- Illuminating the multidimensional contributions of small-scale fisheries. I’m sure lots of traditional knowledge is involved.
- Satellite imagery reveals widespread coconut plantations on Pacific atolls. They could have just asked the small-scale fisherfolk, but ok.