- Video of the Canadian genebank.
- First video in series on Indian women farmers: Bowing to No One, by Sarah Khan.
- Whole bunch of coconut videos. See what I did there?
- Good news for cricketers: willow variety catalog out.
- The skinny of what crop models say about the effects of climate change. Spoiler alert: it ain’t good.
- The latest call for a new Green Revolution.
- Safe to say cantaloupes won’t feature much in that, which is a pity.
- Maybe some other weird plants will, though.
- Wild camels are pretty tough. And since we’re on the subject, what’s a heritage animal breed?
- Wait, they solved dog domestication?
- Top 100 development research questions for our SDG world, including ten on food security and agriculture.
Model livestock information systems
Attentive readers will know I occasionally take swipes at the state of genetic resources information systems, both in the crops and domestic livestock areas. But as far as the latter is concerned it’s getting more and more difficult to do so, a twinge of jealousy being the more usual reaction. Take for example the fact that you can now download the results of distribution modelling, under various climate change scenarios, for 8800 livestock breeds, as recorded in the Domestic Animal Diversity Information system (DAD-IS). Here they are for Vietnam’s Ga Dong Tao chicken. Light green is the area currently suitable, red is the area suitable in 2050, dark green is the area suitable under both current and future conditions. The grey polygon is the reported distribution of the breed.
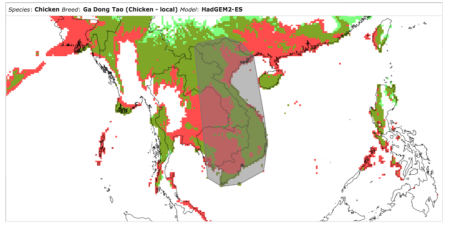
I suspect it will be some time before we’re able to do something similar for crops.
The trouble with Ipomoea
I think we may have mentioned in a recent Brainfood a “foundation monograph” of the genus Ipomoea in Bolivia, 1 without actually explaining what that is. Well, I’ll let one of the authors do that:
‘We wondered if we might be able to combine some of the speed of a Flora approach with some of the rigour of a Monograph,’ explains Dr Scotland. ‘And we’ve ended up with what we call “foundation monographs”.’ The new approach combines the time-limited approach and short descriptions of the Flora approach with the genetic analyses and fieldwork of Monographs, enabling species to be uncovered quickly, but accurately. Crucially, it borrows content like drawings and genetic analyses, where they exist, from existing studies, in order to avoid duplicating work.
Such work — whether floras or monographs — is largely based on existing herbarium specimens, of course, and a complementary study led by Zoë Goodwin, on which Dr Scotland is also a co-author, has just come out which sets out some of the problems associated with that.
…the team…scoured the records of Ipomoea — a large and diverse genus which includes the sweet potato — on the Global Biodiversity Information Facility database. Examining the names found on 49,500 specimens from the Americas, they found that 40% of these were outdated synonyms rather than the current name, and 16% of the names were unrecognisable or invalid. In addition, 11% of the specimens weren’t identified, being given only the name of the genus. 2
The work of the crop wild relatives mapper is never done.
A LandMark that could leave more of a mark
“…these maps do us no good unless they become public knowledge and indigenous rights are recognized by all who have ambitions to grab our lands.”
That’s Abdon Nababan of the Indonesia’s Indigenous Peoples’ Alliance, on LandMark, “a new tool launched today by a broad partnership including the World Resources Institute (WRI), …the first online, interactive platform for mapping lands managed by native communities.” And I would add that such maps will remain of limited usefulness even when they’re in the public domain if they cannot be manipulated, combined and shared much more easily than is currently the case.
Here’s Exhibit A. It is possible, with a little (well, a lot) of techie fiddling (no, not by me), to superimpose an image of what’s in Genesys (the green dots) with an image of what’s in LandMark (the brown polygons showing officially community-managed lands).
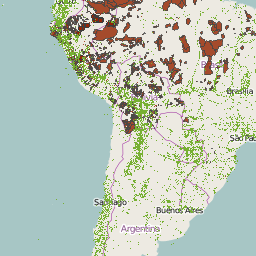
But it’s not pretty, I think you’ll agree: it gets even uglier when you zoom in, which is why I’ve decided not to let you do it. And you can’t do much with it anyway, apart from eyeball it. Plus it may well be against the terms of use of either or both Genesys and LandMark.
Well, we’ll see how LandMark develops, maybe a Google Earth export is in its future, in which case people like Abdon Nababan will be able to get the most out of it. And also the national plant genetic resources programme in Brazil, say, which may well be interested in supporting indigenous communities in protecting their crop diversity more than is perhaps occurring now. That would be a win-win. A triple win, in fact, if you add me.
Nibbles: Tomato breeding, Cacao phylogeny, Moroccan fig landraces, Filipino homegardens, Neolithic honey, LandMark, I say queso
- Breeding for organic tomatoes needs to be participatory.
- Theobroma cacao is the oldest species within the genus.
- Threatened local fig varieties being promoted in Morocco.
- Teach a fisherman to garden…
- Neolithic people were consuming honey early, but not in the north of Europe.
- Interactive map showing lands managed by native communities.
- The oldest surviving document in spanish is a list of cheeses.