- Getting the right seeds to Nepali farmers.
- An organic farmer visits the Vavilov Institute.
- Conservation: beyond hotspots, beyond markets.
- Letting the market deal with insect foods.
- Hybrids 101.
- Tamil Nadu women millet farmers show us all how it’s done. In Milan.
- Climate change? Let them eat rice bean.
- End of an era at the Land Institute.
- And the biggest environmental footprint goes to…lamb.
- Drought tolerance: a geneticist explains.
- International wheat meeting in the news.
- How does the European seed industry support crop diversity conservation and use? Let me map that for you.
The right tree in the right place
Much excitement at the World Forestry Congress yesterday over the launch of the World Agroforestry Center’s fancy-shmanzy new app.
New app 4 identifying+selecting the right tree launched today! Try it. http://t.co/kLUCvjFJAN #Forests2015 pic.twitter.com/mPq4EG7lpw
— CIFOR-ICRAF (@CIFOR_ICRAF) September 7, 2015
Long story short, it’s version 2 of a potential natural vegetation map of eastern and southern Africa. 1 You can consult it in a browser, including on mobile devices, in Google Earth, or in your own GIS. Once you know where you are, or where you’d like to grown some trees anyway, you can get an idea of the natural vegetation there, and of what species might do well, for a variety of different purposes (honey production, say, or firewood).
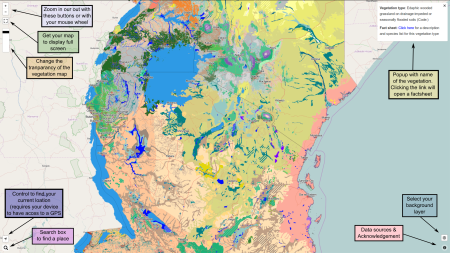
Once you’ve selected a likely tree, you can get more information on it from ICRAF’s Agroforestry Species Dashboard. It’ll need a bit more road-testing than I have time for just at the moment, but it looks promising at first blush. One immediate reaction I do have is that it’s not possible to look for species that fulfil multiple functions: honey production and firewood, in other words. But I may be doing the thing an injustice.
Brainfood: Brassica rethink, Camel colours, Parsing the ITPGRFA, Static buffalo, Traits not taxa, Expert tyranny, Chinese pollinators, Heritage landscapes, Mining text, Diversity & nutrition
- Domestication of Brassica oleracea L. It happened in the balmy Mediterranean, not along those blustery Atlantic cliffs.
- Validating local knowledge on camels: Colour phenotypes and genetic variation of dromedaries in the Nigeria-Niger corridor. The locally recognized colour-based breeds are not supported by the genetics.
- The Battle over Plant Genetic Resources: Interpreting the International Treaty for Plant Genetic Resources. The Treaty phrase “genetic parts and components, in the form received” can be interpreted in ways that do not clash with TRIPS. The author also suggests that the Benefit Sharing Fund should be used to pay lawyers, but I’m not sure if that’s tongue-in-cheek.
- The response of the distributions of Asian buffalo breeds in China to climate change over the past 50 years. Fancy maths says it’s minimal.
- Functional traits in agriculture: agrobiodiversity and ecosystem services. It’s not the taxa. Or it shouldn’t be.
- Expert opinion on extinction risk and climate change adaptation for biodiversity. In situ most preferable, ex situ most feasible.
- Conserving pollinator diversity and improving pollination services in agricultural landscapes.The view from China is much like the view from everywhere else.
- Heritage Values and Agricultural Landscapes: Towards a New Synthesis. Back to the future: heritage can mean resilience.
- Using legacy botanical literature as a source of phytogeographical data. Text parsed to yield maps. Brave new world.
- Production diversity and dietary diversity in smallholder farm households. Want better nutrition? Access to markets better than promoting production diversity.
Brainfood: Apple diversity, Wheat diversity, Wild lettuce diversity, Picking cores, Saudi rice diversity, Indian minor millets, Species distribution modelling, Pollinator diversity
- Chloroplast heterogeneity and historical admixture within the genus Malus. Three genetic networks within the genus, with the cultivated species in one of them.
- Subgenomic Diversity Patterns Caused by Directional Selection in Bread Wheat Gene Pools. Five subpopulations, dividing the European from the Chinese material. Some parts of the genome more in need of diversity than others.
- Biodiversity of Lactuca aculeata germplasm assessed by SSR and AFLP markers, and resistance variation to Bremia lactucae. Some race-specific resistance in the wild relative in Israel-Jordan, but nothing extraordinarily efficient.
- Using Multi-Objective Artificial Immune Systems to Find Core Collections Based on Molecular Markers. Very fancy math not only picks populations to maximise diversity, but also potentially at the same time minimises distance from the office.
- Assessment of ISSR based molecular genetic diversity of Hassawi rice in Saudi Arabia. It’s not just one thing.
- Minor Millets as a Central Element for Sustainably Enhanced Incomes, Empowerment, and Nutrition in Rural India. Holistic mainstreaming pays dividends.
- Minimum required number of specimen records to develop accurate species distribution models. Depends on prevalance, but 15 is a good rule of thumb.
- Microsatellite Analysis of Museum Specimens Reveals Historical Differences in Genetic Diversity between Declining and More Stable Bombus Species. Species which declined less diverse than species which did not.
Mapping responsible soy irresponsibly
Good thinking by the Round Table on Responsible Soy (RTRS) to map where it is most — and least — environmentally responsible to extend soy cultivation in South America.
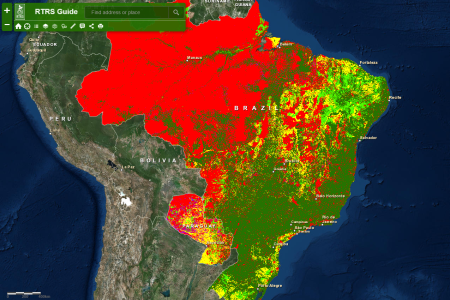
“An interesting exercise, isn’t it?” they ask. No doubt it was meant rhetorically, but I’ll answer anyway: definitely, you bet! But how much more interesting if there had been a way of adding your own data to theirs. I’d really like to know, for example, about any crop wild relatives found in those light green areas in particular: “Areas where existing legislation is adequate to control responsible expansion (usually areas with importance for agriculture and lower conservation importance).” I know where to get the CWR data. 2 But how do I mash them up with this?