Yes, even Europe has community seed banks, and a website to tell you all about them. Here’s where they are:
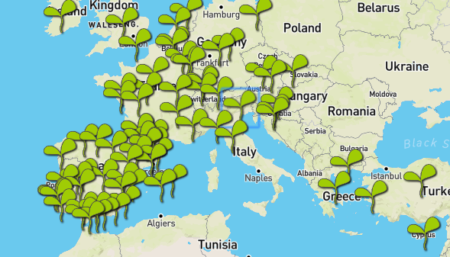
A lot more than I thought.
Agricultural Biodiversity Weblog
Agrobiodiversity is crops, livestock, foodways, microbes, pollinators, wild relatives …