- Food as a daily art: ideas for its use as a method in development practice. Food can bring traditional and scientific knowledge together in an smorgasbord of ideas.
- Maize seed systems in different agro-ecosystems; what works and what does not work for smallholder farmers. Sure, purchasing hybrids from the formal sector seed system is gaining ground in Malawi, Zambia, and Chiapas, but not for home consumption, and only in high potential areas.
- Genome sequence of Jatropha curcas L., a non‐edible biodiesel plant, provides a resource to improve seed‐related traits. Is Jatropha even still a thing?
- Comparing genetic diversity and demographic history in co-distributed wild South American camelids. Vicuña (alpaca wild relative) display lower genetic diversity within populations than guanaco (llama) but more structure across Peru; strong bottlenecks happened at different times, but in both cases much later than domestication and before Spanish conquest.
- The Global Nutrient Database: availability of macronutrients and micronutrients in 195 countries from 1980 to 2013. Supply of micronutrients has increased during the period globally and across levels of development.
- Effects of Food Prices on Poverty: The Case of Paraguay, a Food Exporter and a Non-Fully Urbanized Country. Food price hikes are, overall, bad for everyone, but least bad for the poorest and richest.
- A western Sahara centre of domestication inferred from pearl millet genomes. Harlan’s non-centre not found. Free-to-read.
- Molecular basis of African yam domestication: analyses of selection point to root development, starch biosynthesis, and photosynthesis related genes. Domestication of wild yams was all about learning to grow in full sunlight, and it involved losing 30% of their diversity. But remember current wild yams are not all that wild.
- No net loss for people and biodiversity. How to ensure that people really are no worse off after an offset intervention.
- Identification of a novel interspecific hybrid yeast from a metagenomic open fermentation sample using Hi-C. Doesn’t work on its own, though.
- Length variations within the Merle retrotransposon of canine PMEL: correlating genotype with phenotype. Mobile DNA gets everywhere.
- Widespread sampling biases in herbaria revealed from large‐scale digitization. Blame mega-collectors.
- Nitrogen fixation in a landrace of maize is supported by a mucilage-associated diazotrophic microbiota. In aerial roots, no less.
Nibbles: Lad spuds, Assisi olives, Amazing maize art, Wild tea, Peruvian alpaca, TR4, Seed banks, Space Seed Force, Embrapa sweetpotato, ITPGRFA
- The hidden treasure of Colombian potatoes. In a lad mag, no less.
- Umbrian olive terraces get UN status, no less.
- Maize furniture, no less.
- New wild tea species found. In protected areas, no less.
- Saving the dreadlocked Suri alpaca of Peru through spinning.
- Saving the banana through lots of things.
- Seed banks for restoration, but also so much more.
- Even in space. No less.
- But don’t forget to safety duplicate .
- Seed Treaty scores important first, explained. I hope.
Brainfood: Ecology of domestication, Citizen soybeans, Silkworm domestication, Barley spread, Indigenous management, Maize domestication, Temperate maize, Nutrient yields, Amazon history double, Women & diets, Online classification, Charred breadcrumbs, Wheat drought
- Crop domestication: anthropogenic effects on insect–plant interactions in agroecosystems. Domestication can upset trophic webs. Poor dears.
- The soybean experiment ‘1000 Gardens’: a case study of citizen science for research, education, and beyond. 2492 gardens, in fact.
- The evolutionary road from wild moth to domestic silkworm. Domestication in China, followed by multiple independent spreads and differentiation.
- Barley heads east: Genetic analyses reveal routes of spread through diverse Eurasian landscapes. 3 taxa, 8 genepools, multiple routes for spread. A bit like silkworm but in the opposite direction.
- A spatial overview of the global importance of Indigenous lands for conservation. 40% of all terrestrial protected areas.
- Maize domestication and gene interaction. More than just the headline 5 genes.
- Hallauer’s Tusón: a decade of selection for tropical-to-temperate phenological adaptation in maize. Need to go back to tropical germplasm for adaptation to temperate conditions.
- Moving beyond calories and protein: Micronutrient assessment of UK diets and land use. Roots, tubers and vegetables are the most land-efficient producers of 23 nutrients.
- The legacy of 4,500 years of polyculture agroforestry in the eastern Amazon. It is still with us.
- Direct archaeological evidence for Southwestern Amazonia as an early plant domestication and food production centre. And not just in the east.
- Does women’s time in domestic work and agriculture affect women’s and children’s dietary diversity? Evidence from Bangladesh, Nepal, Cambodia, Ghana, and Mozambique. Yes, but varies with socioeconomic status.
- Remap: An online remote sensing application for land cover classification and monitoring. Use your training set to detect habitat type(s) in Google Earth.
- Archaeobotanical evidence reveals the origins of bread 14,400 years ago in northeastern Jordan. Before domestication.
- Drought tolerance during reproductive development is important for increasing wheat yield potential under climate change in Europe. The good news is that germplasm close to the optimized ideotype for 2050 is already out there.
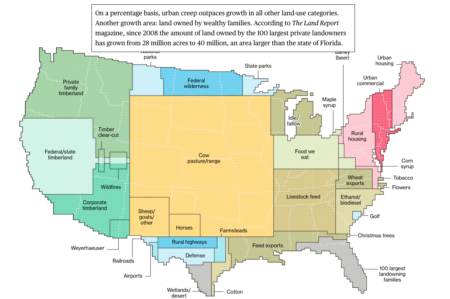
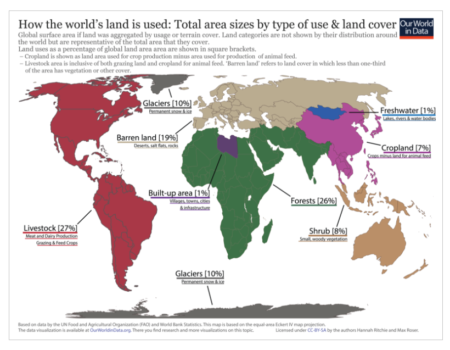
Feedlots
Nibbles: Carrot breeding, BIEN, Protected areas databases, Brazilian genebanks, Endangered coconut genebank, DSI, ABS, Climate pix, Botanical pix double, Potatoes galore, Pandanus language, Archaeological double, Palestinian seed saving
- Putting the polyacetylene back into carrots.
- The Botanical Information and Ecology Network gets an upgrade. Any CWRs among its 18,844,855 more observations?
- And any is protected areas? This will tell how well they’re managed. Mash up with this spatial database on indigenous lands?
- Otherwise, there are genebanks, though not enough in Brazil, apparently.
- And not always safe.
- What to do with Digital Sequence Information? Would be nice to be clear on what it is.
- ABS broken down by ISF. And the CGIAR. Not DSI though.
- Need climate visuals? Well, who doesn’t.
- The Columbian Exchange has visuals also.
- And the Royal Horticultural Society too.
- Speaking of Columbian Exchange: frites. And Vavilov, chefs, etc.
- Speaking about nuts in PNG. Comment by Jim Croft, who would know: “Except the species illustrated is the widespread oceanic strand species, Pandanus tectorius, not the endemic highland crop ‘karuka’, Pandanus julianettii.”
- 5000-year-old brewery in Egypt.
- 14,000-year-old bread.
- Fast forward 14,000 years.