- People in the Nejapan Sierra Sur in Oaxaca, Mexico had a seed bank 400-700 years ago so they could re-create their complex cuisine after disruptions.
- How MSSRF revived millets in Odisha, India. You think a seed bank was involved?
- Meanwhile, in Meghalaya (also India), foraged foods are helping to diversify state-provided school lunches and address chronic malnutrition. Talk about complex cuisine. Are all these species in a seed bank somewhere, though? Do they need to be?
- How the National Soybean Germplasm Collection at the Agricultural Research Service lab in Urbana, Illinois helped save soybeans in Iowa.
- University breeding programmes are keeping the apple afloat in the USA. That and genebanks.
- Farmers and agrotourism are bringing back some cool flavors in Albania. Well, that and the Albanian Gene Bank.
- Fish need genebanks too, and Bangladesh is on it. Did ancient Bangladeshis have them, I wonder?
Nibbles: Corn diseases, German potato collection, Vietnam rice trials, Endophyte strain, Fish nutrition, Himalayan pea, Subversive seeds
- The US needs better maize.
- German genebank looks for the best potatoes.
- Vietnam looks for better rice in IRRI’s genebank.
- New Zealand markets an endophyte for better grass performance.
- Some Timor-Leste fish are better than others.
- The Himalayas have a better pea. Of some kind.
- How’s that for subversive cataloguing?
A breed is a breed is a breed?
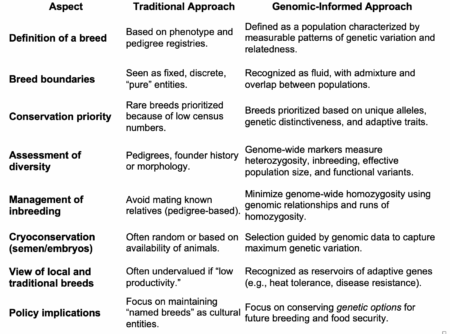
I feel maybe yesterday’s Nibble on the definition of a “breed” may have been a bit too laconic, even for me. So let me give a bit more context.

The link was to a YouTube playlist, which was described thus (link added):
The presentations in this playlist are from the webinar on “Genomic assessment of genetic variation and the future of the breed concept”, originally held on 12.12.2024 under the umbrella of the Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO). This represents the culmination of collaborative work by a diverse group of experts from institutions from all around the world to prepare materials for a sub-chapter in the upcoming 3rd Report on the State of the World’s Animal Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture.
It amounts to over an hour of talks, but if I had to summarize the point the playlist is making, it is that genomics is redefining a breed as a fluid, porous, genotypically-characterized population rather than a fixed, pedigree-based, phenotypic entity. Thus, it is shifting livestock conservation from saving labels (“Breed A”) to preserving genetic options.
Here’s a handy table I came up with to describe the change:
Interesting to juxtapose this to the post a few days ago on how to value and use Indigenous knowledge to solve today’s problems. Would Indigenous livestock keepers necessarily care about those genetic options more than their traditional breed?
It would be great to hear from people engaged in livestock conservation on this. It’s unfortunately not a community I interact with much.
Nibbles: Supermarkets, Cate Blanchett, ABS, Transformation, Medieval haymaking, Aurochs rewilding, Breed concept
- What’s wrong with supermarkets.
- Cate Blanchett on the Millennium Seed Bank. Attitude to supermarkets unknown.
- Access & Benefit Sharing 101. Cate Blanchett unavailable for comment.
- Experts weigh in on how we should change how we eat. Nobody but Cate Blanchett will listen, but supermarkets and seeds feature, for what it’s worth.
- How they ate in the Middle Ages without supermarkets. Or at least harvested.
- After we’re done with medieval haymaking, let’s bring back the aurochs too. And put it in a supermarket?
- Yeah but what is a breed anyway? Or an aurochs, for that matter.
Brainfood: Agroecology, Afghan wheat, CWR microbes, Chocolate microbes, Liberica coffee, Wild apples, USDA cotton collection, Parmesan cattle, Sweetpotato genome, Vertical tomatoes
- Embracing new practices in plant breeding for agroecological transition: A diversity-driven research agenda. Plant breeding for agroecology will need access to locally-adapted plant diversity, sure, but also the involvement of a diversity of stakeholders and the use of a diversity of co-design strategies.
- Conservation and Utilization of Wheat Genetic Resources in Afghanistan Expanded with the Homecoming Wheat Landraces Collected Half a Century Ago. The above could also be said of wheat breeding in Afghanistan. Fingers crossed.
- Blueprints for sustainable plant production through the utilization of crop wild relatives and their microbiomes. Oh, wait, breeders (agroecological and otherwise) will also need the diversity of microbiomes associated with crop wild relatives.
- A defined microbial community reproduces attributes of fine flavour chocolate fermentation. Oh, wait, we will also need the diversity of the microbes involved in fermentation, at some point.
- Genomic data define species delimitation in Liberica coffee with implications for crop development and conservation. It might help if we knew how many species made up a crop in the first place. In the case of Liberica coffee, it turns out to be 3. No word on the microbiomes involved.
- Assessment of genetic diversity and population structure of Malus sieversii and Malus niedzwetzkyana from Kazakhstan using high-throughput genotyping. It would also help to know where interesting diversity was concentrated within crop wild relatives. In apples, it’s not necessarily the ancestor.
- The National Plant Germplasm System cotton collection—a review of germplasm resources, phenotypic characterization, and genomic variation. Lots of morphological characterization and agronomic evaluation, not so much molecular data, but increasing. No word on the microbes.
- Establishing a genomic-driven conservation of a cattle genetic resource: the case of the Parmigiano-Reggiano cheese iconic breed. In contrast, these guys have genotyped practically a whole breed. But yeah, no microbes.
- Phased chromosome-level assembly provides insight into the genome architecture of hexaploid sweetpotato. The contributions of different wild relatives to the sweetpotato genome are to be found intertwined along chromosomes rather than restricted to subgenomes. Unclear what that will mean to agroecologial breeders.
- Harnessing Green Revolution genes to optimize tomato production efficiency for vertical farming. Agroecological breeders unavailable for comment.