- Meaty presentation on how biodiversity in the food system delivers a diverse diet. Could hardly fail to, really, could it.
- What’s a diverse diet ever done for me, asks ancient farmer.
- Vegetables an important part of diverse diets, of course. Especially in urban areas.
- Interesting EU project on the phylogenetics of medicinal plants. Any vegetables in there?
- Improved cowpeas only improved when farmers know they are improved. Wow.
- Some glimmers of hope on adaptation? Maybe.
- Not all livestock bad for climate change. And room for improvement on those that are.
- Yeah, but who cares, global warming is just a giant natural fluctuation, no? No.
- Legalize it, already! Poppy cultivation as a climate change adaptation measure?
- Australian agriculture unprepared for climate change? With all these fancy breeders and access to the world’s genebanks?
- Meanwhile, in China, the focus is on food sovereignty.
- And in Japan on its spaced out cherry tree.
That IPCC report in 3 handy diagrams
Too busy to go through the latest IPCC report and extract the nuggets relevant to agriculture (including crop wild relatives)? Fear not, we’re not. Here’s three figures which pretty much tell the story, and the relevant bits of text from the report to go with them. There’s lots of commentary and opinion out there on the report. We thought you’d like to hear it straight.
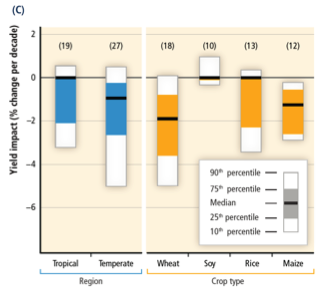
Based on many studies covering a wide range of regions and crops, negative impacts of climate change on crop yields have been more common than positive impacts (high confidence). The smaller number of studies showing positive impacts relate mainly to high-latitude regions, though it is not yet clear whether the balance of impacts has been negative or positive in these regions (high confidence). Climate change has negatively affected wheat and maize yields for many regions and in the global aggregate (medium confidence). Effects on rice and soybean yield have been smaller in major production regions and globally, with a median change of zero across all available data, which are fewer for soy compared to the other crops. Observed impacts relate mainly to production aspects of food security rather than access or other components of food security. See Figure SPM.2C. Since AR4, several periods of rapid food and cereal price increases following climate extremes in key producing regions indicate a sensitivity of current markets to climate extremes among other factors (medium confidence).
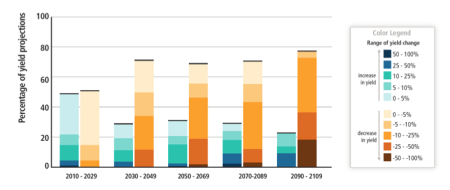
For the major crops (wheat, rice, and maize) in tropical and temperate regions, climate change without adaptation is projected to negatively impact production for local temperature increases of 2°C or more above late-20th-century levels, although individual locations may benefit (medium confidence). Projected impacts vary across crops and regions and adaptation scenarios, with about 10% of projections for the period 2030-2049 showing yield gains of more than 10%, and about 10% of projections showing yield losses of more than 25%, compared to the late 20th century. After 2050 the risk of more severe yield impacts increases and depends on the level of warming. See Figure SPM.7. Climate change is projected to progressively increase inter-annual variability of crop yields in many regions. These projected impacts will occur in the context of rapidly rising crop demand.
All aspects of food security are potentially affected by climate change, including food access, utilization, and price stability (high confidence). Redistribution of marine fisheries catch potential towards higher latitudes poses risk of reduced supplies, income, and employment in tropical countries, with potential implications for food security (medium confidence). Global temperature increases of ~4°C or more above late-20th-century levels, combined with increasing food demand, would pose large risks to food security globally and regionally (high confidence). Risks to food security are generally greater in low-latitude areas.
Distribution of impacts: Risks are unevenly distributed and are generally greater for disadvantaged people and communities in countries at all levels of development. Risks are already moderate because of regionally differentiated climate-change impacts on crop production in particular (medium to high confidence). Based on projected decreases in regional crop yields and water availability, risks of unevenly distributed impacts are high for additional warming above 2°C (medium confidence).
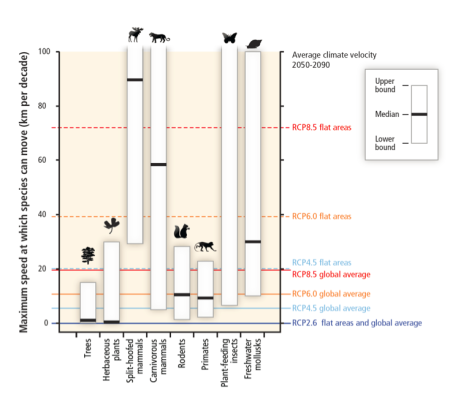
Within this century, magnitudes and rates of climate change associated with medium- to high-emission scenarios (RCP4.5, 6.0, and 8.5) pose high risk of abrupt and irreversible regional-scale change in the composition, structure, and function of terrestrial and freshwater ecosystems, including wetlands (medium confidence). Examples that could lead to substantial impact on climate are the boreal-tundra Arctic system (medium confidence) and the Amazon forest (low confidence). Carbon stored in the terrestrial biosphere (e.g., in peatlands, permafrost, and forests) is susceptible to loss to the atmosphere as a result of climate change, deforestation, and ecosystem degradation (high confidence). Increased tree mortality and associated forest dieback is projected to occur in many regions over the 21st century, due to increased temperatures and drought (medium confidence). Forest dieback poses risks for carbon storage, biodiversity, wood production, water quality, amenity, and economic activity.
Nibbles: Rice intensification, Community genebank, Biodiversity & poverty, Borlaug, Deconstructing recipes, Biofortification conference, IPCC, Kenyan agricultural changes, Collecting wild chickpeas, African peanuts, Insurance for herders, Old fields, Millet fairs & diseases, GDP and malnutrition, Yeast evolution
- From SRI to SARI. Rice has never had it so good.
- Look there’s even a guy in Orisha who grows 920 varieties.
- Biodiversity conservation and poverty reduction: Unproven. Doesn’t sound like they looked at agricultural biodiversity though.
- Contrary take on the Borlaug legacy.
- From Map Your Recipe to Compare Your Recipe. h/t Rachel Laudan.
- Follow that biofortification conference in Kigali. Maybe they’ll talk about recipes.
- Guardian Environment blogger breaks down the agricultural bits of the IPCC report for you. Lots of that going around.
- No conceivable reason for growing jatropha in Kenya. One of those times when you wonder whether anyone had predicted this would happen at the time.
- So does anyone know now whether switching from coffee to banana might be a bad idea in the long run? This is your chance.
- Wild chickpea to the rescue.
- The ups and downs of groundnut research in Africa.
- Islamic insurance for herders. Demand, meet supply.
- Celtic fields can still be seen, if you know what to look for.
- Seed fair in Senegal exchanges pearl millet. Could usefully do the same in Namibia, it looks like.
- Does economic growth help in reducing child malnutrition? It depends on whether you plot % malnutrition against GDP per capita or annual change of the first against annual change in the latter.
- The complicated story of yeast, unravelled.
Brainfood: Sunflower genomics, Omani chickens, Ozark cowpea, Amerindian urban gardens, Thai homegardens, Global North homegardens, African pollination, Ugandan coffee pollination, Use of wild species, Wheat and climate change, Iranian wheat evaluation, Tunisian artichokes, Fig core, Onion diversity, Distillery yeasts
- Genomic variation in Helianthus: learning from the past and looking to the future. Paleopolyploid events, transposable elements, chromosomal rearrangements. Is there anything these plants don’t have? But then these guys would say that, wouldn’t they.
- Assessment of genetic diversity and conservation priority of Omani local chickens using microsatellite markers. Unsurprisingly, the Dhofar (far S) and Musadam (far N) populations are the most different. I collected crops in both places way back when, and I bet you it would be the same for things like alfalfa and sorghum. Or cowpea, which brings me to…
- Just Eat Peas and Dance: Field Peas (Vigna unguiculata) and Food Security in the Ozark Highlands, U.S. Still important after all these years. (I suspect Gary Nabhan would have predicted this, but I can’t even get an abstract of his paper Food Security, Biodiversity and Human Health: Ethnobiology as a Predictive Science.)
- Amerindian Agriculture in an Urbanising Amazonia (Rio Negro, Brazil). Traditional systems survive move to cities just fine.
- Human-Induced Movement of Wild Food Plant Biodiversity Across Farming Systems is Essential to Ensure Their Availability. Just like in Brazil, people move wild species to their homegardens in Thailand too.
- Urban home food gardens in the Global North: research traditions and future directions. Uhm, could maybe Brazilian and Thai homegarden studies guide similar work in the North… Yep, and here’s how.
- Priorities for Research and Development in the Management of Pollination Services for Agricultural Development in Africa. Old and traditional may not mean weak and out of date, but change gonna come anyway.
- Social and Ecological Drivers of the Economic Value of Pollination Services Delivered to Coffee in Central Uganda. No wait, change here already.
- Use it or lose it: measuring trends in wild species subject to substantial use. Wild species which are being used by people tend to be doing better than those that are not. Yeah, but settle down, the data are not that great.
- An assessment of wheat yield sensitivity and breeding gains in hot environments. The successes have been coming from the lower potential material, not the elite of the elite.
- Adaptation Patterns and Yield Stability of Durum Wheat Landraces to Highland Cold Rainfed Areas of Iran. It’s not always about heat. Anyway, in either case, thank goodness for diverse worldwide germaplasm collections.
- Karyological and genome size insights into cardoon (Cynara cardunculus L., Asteraceae) in Tunisia. The wild populations from Sicily and Tunisia are closest to the crop.
- Ex situ conservation of underutilised fruit tree species: establishment of a core collection for Ficus carica L. using microsatellite markers (SSRs). Fancy maths allows Spanish researchers to recover all microsats within a collection of 300 figs in only about 10% of the accessions. So who gives a fig for the rest, right?
- Assessing the genetic diversity of Spanish Allium cepa landraces for onion breeding using microsatellite markers. Alas, all the Spanish Allium cepa landraces fall in the same cluster, so a core could be tricky. These guys really know their onions.
- Biodiversity of non-Saccharomyces yeasts in distilleries of the La Mancha region (Spain). Gonna need some booze to wash down the figs and onions, right?
Nibbles: GMO debate, IPCC report, SPC ag strategy, Teff, Biofortification conference, Urban protected areas, Costa Rican ecosystems
- Our Nature Comment genebank paper used to both denigrate and promote GMOs. Must be doing something right.
- Same thing likely to happen with Fifth Assessment Report?
- SPC’s Land Resources Division new strategic plan. Good to see an important role for the Centre for Pacific Crops and Trees.
- The future of teff. Two sides to every story. But does it feature in your breakfast?
- Biofortification conference off the ground.
- Urban protected areas: I wonder how many crop wild relatives are involved.
- Costa Rican ecosystems in trouble: I wonder how many crop wild relatives are involved.