- Probably way more than you want to know about food security in Yemen, but stunning nonetheless.
- NordGen tells us how to measure seed moisture content. In Russian.
- The Irish have benefited from at least one bank. Alas, that bank is Pavlovsk.
- Indian farmers turning their back on traditional crops because of climate change. Hope NBPGR is on the case.
- Goji berries only as good as other fruit and veg, with “significant placebo effect”.
- [W]e are in the midst of shaping a new perspective on sustainable agriculture, it says here. Right.
- All you ever wanted to know about Green Revolution 2.0, thanks to Anastasia.
- Speaking of which .. sustainable ag under discussion.
TLB resistant varieties kicking their heels, twiddling their thumbs
 Readers with a long memory will remember that it was back in the summer that we first pointed to worrying signs that Taro Leaf Blight might be in West Africa. By October TLB was pretty much confirmed in Cameroon and the Pacific had offered its resistant varieties. The offer has not yet been taken up. Now there’s another flurry of activity at Pestnet, triggered by news of devastating losses in Nigeria. And John Cho from Hawaii informs us that there has been success in breeding for the disease in the Dominican Republic too. What will it take to get the TLB resistant varieties that we know exist in a few places around the world to where they are clearly urgently needed? This from the blurb on a new, and very timely, book on taro just out from Bioversity:
Readers with a long memory will remember that it was back in the summer that we first pointed to worrying signs that Taro Leaf Blight might be in West Africa. By October TLB was pretty much confirmed in Cameroon and the Pacific had offered its resistant varieties. The offer has not yet been taken up. Now there’s another flurry of activity at Pestnet, triggered by news of devastating losses in Nigeria. And John Cho from Hawaii informs us that there has been success in breeding for the disease in the Dominican Republic too. What will it take to get the TLB resistant varieties that we know exist in a few places around the world to where they are clearly urgently needed? This from the blurb on a new, and very timely, book on taro just out from Bioversity:
While new market opportunities and taro’s versatility are responsible for its growing popularity in markets, diseases and climate change also pose ever greater threats to its production and distribution. The current outbreak and spread of the devastating taro leaf blight in West Africa clearly highlights this vulnerability. By taking a global approach to the crop, the authors highlight ways to address new outbreaks of pathogens such as taro leaf blight.
Nibbles: Pacific PGR, Millet, Fruits
- Nth regional meeting on Pacific crop genetic resources under way.
- ICRISAT has climate-ready crops. Well, I find that reassuring.
- England has a new fruit genebank. Wait, what? I thought it was having trouble holding on to the old fruit genebank. Rational national system, anyone?
Nibbles: Disease, Tobacco, CGIAR, Food Security, Nutrition, Soil, Popcorn, Quinoa, Aegilops
- How to breed a better brassica.
- Kenya encourages farmers to switch from tobacco to food.
- The King is dead … Long live the King.
- A very long post about Challenges to Genetic Diversity and Implications For Food Security in South Asia.
- Plumpy’nut set free, more or less.
- Dirt, the movie — I’d like to see that.
- Real popcorn, Yaqui style.
- Quínoa andina podría cultivarse en desiertos del mundo. Don’t they have their own orphan crops?
- Red List assessment of nine Aegilops species in Armenia. New wheat wild relatives paper.
Earth Engine and crop wild relatives
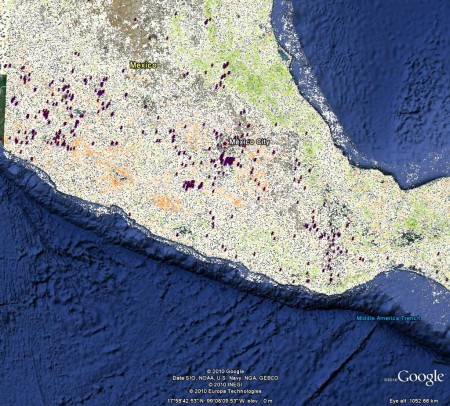
The other recent Google Earth innovation is Earth Engine, where you can check out a bunch of interesting visualizations of environmental data. Spurred by something Julian said, I downloaded the MODIS VCF global tree cover change dataset (2000-2005). And then I went to Genesys and downloaded data on wild beans (Phaseolus spp). It was not very difficult to put the two together in Google Earth. In the map below, which just looks at central Mexico, orange means high deforestation, and green afforestation. Is it me, or do germplasm accession seem to be concentrated in areas of high deforestation? Anyway, with a little work, this could be a cheap and cheerful way to identify particularly threatened areas for germplasm collecting.
Who wants to be the first to put crop wild relatives data in Earth Engine?