- Britain gets a tree seed bank. Wait, it didn’t already have one? St Helena seems to, sort of. And Cameroon. And why they’re needed more than ever; and more. Although in Brazil trees can be the bad guys.
- Bill Gates praises CIMMYT, and the CGIAR as a whole.
- A Renaissance garden recreated in NYC.
- A survey on moringa. And one on achocha and oca.
- And speaking of deconstructing weird crops, how about saffron?
- Yet another one of those GMOs-are-not-as-bad-as-you-think pieces. Is any of this getting through, I wonder?
- Free range pigs in Kenya and the USA.
- Speaking of free range livestock… Well, a species distantly related to livestock anyway. Oh, and here’s another restoration story, from another continent.
- Free range glass eels too. And salmon, after a fashion.
- Traditional potatoes in fancy Lima restaurants. Maybe with pork or fish?
Brainfood: Carrot domestication, Nigerian diets, Rotations & ecosystem services, Bangladeshi diets, Maize breeding sites, Olives and climate change, Mixtures and invertebrates, Genebank information systems
- Genetic structure and domestication of carrot (Daucus carota subsp. sativus) (Apiaceae). Origin in Central Asia, but no genetic bottleneck (sic).
- Data collection and assessment of commonly consumed foods and recipes in six geo-political zones in Nigeria: Important for the development of a National Food Composition Database and Dietary Assessment. Nigerians eat a lot of soup.
- The integration of crop rotation and tillage practices in the assessment of ecosystem services provision at the regional scale. Good trick if you can do it.
- Nutritional composition of minor indigenous fruits: Cheapest nutritional source for the rural people of Bangladesh. If only the rural people knew about this.
- Effectiveness of selection at CIMMYT’s main maize breeding sites in Mexico for performance at sites in Africa and vice versa. Is high. Phew.
- Olive trees as bio-indicators of climate evolution in the Mediterranean Basin. Olives in Germany by 2100?
- Crop genetic diversity benefits farmland biodiversity in cultivated fields. Mixed wheat fields better for soil invertebrate biodiversity than fields with single varieties.
- IT background of the medium-term storage of Martonvásár Cereal Genebank resources in phytotron cold rooms. The interesting thing is that the system links genebank data with breeders’ data. Don’t see that a lot.
Nibbles: GMO promises promises, African livestock outside & in, Vegetables galore, Farmer videos from US & Sri Lanka, Fermentation beery & otherwise, Yam people & traits, Botanic garden diversity, ECPGR, CWR in US & Benin, Herbarium data, Baobab info, Olean info, Pix, Indian cooking
- Nature “celebrates” 30 years of GMOs.
- African pastoralists know how not to destroy their livelihoods shock.
- African urban dwellers keep livestock shock.
- Vegetables can be perennial too. Oh yes indeedy. Not bitter gourd though, alas. Nor cucumber. And in other news, there’s a Bitter Melon Council. And also a campaign to promote zucchini in Iowa.
- Climate change reaches farmers in the Pacific NW. Can their Sri Lankan colleagues be far behind?
- Always good to have a beer story. Well, maybe not.
- Speaking of fermentation, this WSJ piece looks interesting, from the two sentences of it I can read. No, wait. Oh crap, try this.
- A hummus dip goes really nicely with beer. Is this the quinoa story again?
- A yam conference for the ages. Will they discuss the new trait ontology?
- Botanic gardens reach out. Genebanks next? Maybe not.
- You mean like the European ones, perhaps?
- That US CWR paper from the horse’s mouth. And a similar thing from Benin. But where does all that data come from?
- Baobab notes to go with all those factsheets.
- The Saharan olive needs a factsheet too. IRD obliges.
- Cool set of agriculture photos.
- A couple of different views of Indian food. Thanks to Cara de Silva and Diana Buja.
Wheat diversity collections seen and unseen
A couple of things on wheat today, thanks to Tom Payne at CIMMYT, our go-to guy for all things triticaceous. First, Kew’s new page on Bread Wheat, which has a lot of useful information, including this:
About 250,000 samples of bread wheat are held in agricultural gene banks around the world, so the plant is far from being threatened. However, there is cause for concern in terms of bread wheat landraces, which are being replaced by modern cultivars and under threat of extinction if not already conserved in ex-situ collections.
The figure is I suspect from Genesys, from which the map below is taken. WIEWS, which covers many more genebanks, gives 546,797, but there’s probably much more duplication in that number than in the Genesys one.
And second, from the just published study “Agricultural Innovation: The United States in a Changing Global Reality,” a wide-ranging analysis of the benefits to the US of investment in international agricultural research, a discussion of the pedigree of the hard red winter wheat variety Jagger, the most widely planted wheat variety in the United States:
The breeders who developed Jagger drew on genetic material from all over the world and throughout the United States. Jagger was formed by crossing the breeding line KS82W418 (developed by the Kansas agricultural experimental station) with the variety Stephens (developed jointly by the Oregon agricultural experiment station and USDA-ARS). In turn, these two varieties stand firmly on the shoulders of the investments in scientific crop breeding over the past century and the eons of selection and seed-saving efforts of farmers since wheat was first domesticated around 10,000 years ago. Jagger’s ancestry includes varieties like Turkey Red from Russia, Noe from France, Federation and Purplestraw from Australia, Yaqui from Mexico, and Etawah from India.
Too bad that the closest the authors come to saying where those ancestors of Jagger, along with their 250,000 or 500,000 or whatever cousins, may be found, despite numerous references in the text to CIMMYT and USDA, is this laconic sentence:
In addition to the efforts of private citizens, the US Department of Agriculture (USDA) sent its scientists to the far corners of the globe in search of better plant varieties.
Maybe I’ll send them that Kew link.
US crop wild relatives inventoried
Our friend Colin Khoury and his associates have a paper out in Crop Science on inventorying crop wild relatives in the US. The press release that goes with it is getting picked up. The bottom line is easy to summarize, and Colin does so in the abstract:
We prioritize 821 taxa from 69 genera primarily related to major food crops, particularly the approximately 285 native taxa from 30 genera that are most closely related to such crops. Both the urgent collection for ex situ conservation and the management of such taxa in protected areas are warranted, necessitating partnerships between concerned organizations, aligned with regional and global initiatives to conserve and provide access to CWR diversity.
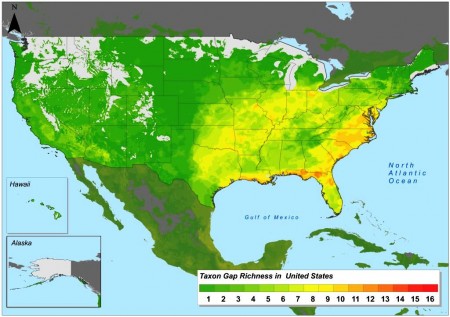
But where to start with all that collecting and in situ work? Well, here’s a little peek at the next phase of Colin’s work, which will answer that question. He’ll be modelling the distribution of the priority species using the GIS resources at CIAT, and mapping areas of high species diversity, and also areas which are under-represented in conservation efforts (gaps). Using just a portion of the data, and therefore yielding only very preliminary results, this is the sort of thing that comes out:
We look forward to the final results in due course. Good luck, Colin, and thanks for the sneak preview.