- Cytotaxonomic investigations to assess diversity and evolution in Amorphophallus Blume ex Decne. (Araceae). Out of 25 accessions and 7 wild species, “A. dubius may be the immediate ancestor of cultivated forms.”
- Physiological phenotyping of plants for crop improvement. High-throughput phenotyping is only the start.
- Geographic origin is not supported by the genetic variability found in a large living collection of Jatropha curcas with accessions from three continents. 900 global accessions fall into 2 genetic groups, but not related to geography.
- Genetic diversity of donkey populations from the putative centers of domestication. Sudan and/or Yemen.
- Genetic and Biochemical Evaluation of Natural Rubber from Eastern Washington Prickly Lettuce (Lactuca serriola L.). I look forward to seeing those rubber lettuce plantations.
- An approach on the in vitro maintenance of sugarcane with views for conservation and monitoring of plant nuclear DNA contents via flow cytometry. It’s possible to conserve sugarcane in vitro, but it won’t be straightforward.
- Geographical Gaps and Diversity in Deenanath Grass (Pennisetum pedicellatum Trin.) Germplasm Conserved at the ICRISAT Genebank. 194 provinces in 21 countries? That’s a lot of gaps.
- Realizing access and benefit sharing from use of genetic resources between diverging international regimes: the scope for leadership. As supplied by Norway, that is.
- Classification of seed storage behaviour of 67 Amazonian tree species. 1000-seed weight and seed moisture content at shedding are good, together, at predicting seed storage behaviour.
- Genetic Diversity and Population Structure in a Legacy Collection of Spring Barley Landraces Adapted to a Wide Range of Climates. 10 climatic clusters.
- Assessment of genetic variation within a global collection of lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) cultivars and landraces using SNP markers. Geographic pattern for commercial varieties, but not for landraces.
- Omne Ignotum pro Magnifico: characterization of commercial Bilberry extracts to fight adulteration. That would be Vaccinium myrtillus. You need to keep a sharp eye on the whole production process.
- The Contribution of the Solanaceae Coordinated Agricultural Project to Potato Breeding. It boils down to the Infinium 8303 Potato SNP Array, and it’s contribution to potato breeding has apparently been important.
- Horses as Sources of Proprietary Information: Commercialization, Conservation, and Compensation Pursuant to the Convention on Biological Diversity. You need a value chain with “a sequence of proprietary rights agreements governed and regulated by both tangible and intangible property regimes.” Well, yeah.
Genebanks galore on the BBC
Never rains but it pours, BBC edition. Hot on the heels of the Food Programme on the conservation of heritage wheats, here comes Gardeners’ Question Time on the cacao genebank at the University of Reading.
Wheat roundup
Great to get an email update from Andy Forbes yesterday on the latest developments at Brockwell Bake. They’ve been busy with their Nordic colleagues of late, as you can read in the latest edition of True Loaf. 1 But the big news is they’ll be on the BBC’s Food Programme later today, along with lots of other heritage wheat enthusiasts.
And the wonderful Wheat Gateway has had a couple of tweaks over Christmas:
Wheat *hub *pages such as for Hen Gymro are intended to link up available historical references, morphological descriptions and modern imagery to germplasm data and in due course current cultivation and usage reports for landrace and other heritage lines of specific interest.
“*with image*” searches on the database has been added so the various image resources (USDA, INRA, BBA, NordGen) can be targeted by users – inspired to do so by the immaculate image collection of the Nordic Genebank.
Brockwell seem to be cornering the market in wheat genetic resources information systems.
Oh, and since we’re at it, here’s philosopher Julian Baggini on our duty of stewardship towards einkorn.
India declares crops covered under Seed Treaty exempt from Biodiversity Act

This edition of the Gazette of India, dated 18 December 2014, communicates a very significant decision for all of us who have an interest in the conservation and use of crop diversity. Here’s the exact language:
What this means is that genebanks under the management and control of the Government of India now have the formal go-ahead to fully implement the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture, which India actually ratified a while back, of course. They won’t need to run every request for access to ex situ germplasm by the biodiversity authorities. Facilitated access indeed.
Wild potato diversity halved
![]() David Spooner and co-workers have written a comprehensive overview of the systematics and genetics of wild and cultivated potato species (Solanum section Petota) 2. This nicely illustrated and very accessible paper is essential reading for anyone interested in potato diversity — or indeed the study of plant diversity in general.
David Spooner and co-workers have written a comprehensive overview of the systematics and genetics of wild and cultivated potato species (Solanum section Petota) 2. This nicely illustrated and very accessible paper is essential reading for anyone interested in potato diversity — or indeed the study of plant diversity in general.
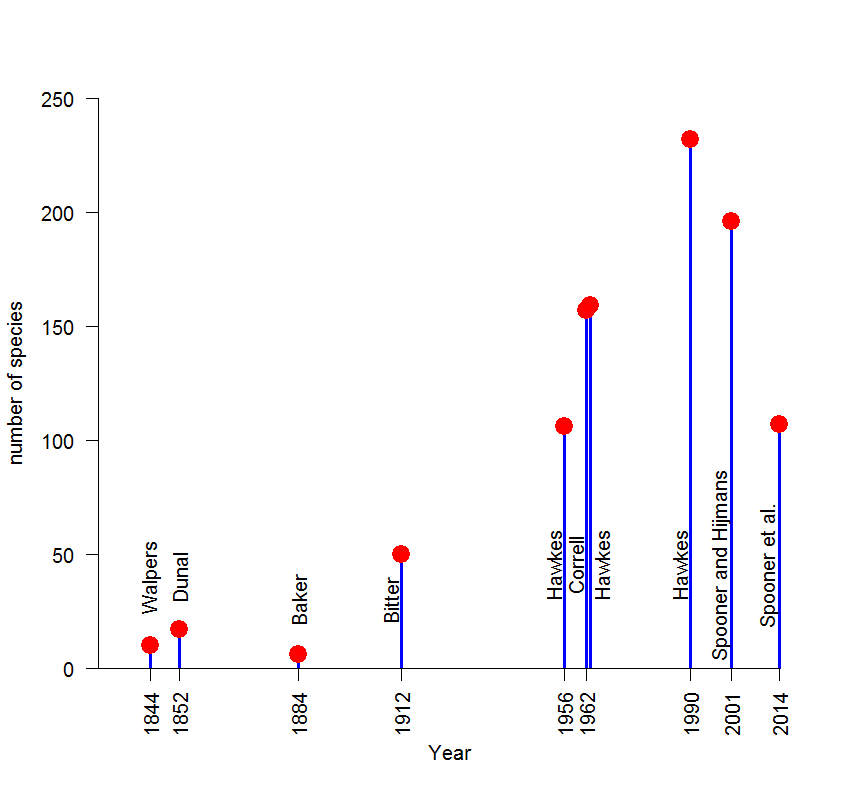
A remarkable aspect of wild potato systematics is the way the number of recognized species has fluctuated over time. In 1956, Hawkes recognized 106 species, but in his 1990 treatment of the group this had increased to 232. This will likely be the highest number we’ll see, because it has come down drastically since, and Spooner et al.’s paper puts it at 107 — almost exactly where it was back in 1956. This does not mean that we are back to the same set of taxa though. Many new species were described after 1956, notably by Carlos Ochoa, who named about 25% of the 107 species. 3
The graph below shows the number of species over time, based on published compilations, and the name of the authors 4 .
It is not easy to determine where a wild potato species begins and where it ends. Many species look very similar, and there is “lack of strong biological isolating mechanisms and the resulting interspecific hybridization and introgression, allopolyploidy, a mixture of sexual and asexual reproduction, and recent species divergence.” A smaller number of species is not necessarily better, but, in the case of wild potatoes, Spooner et al. think it will help us move away from “a taxonomy that is unnatural, unworkable, and perpetuates variant identification” to a system that hopefully enables better conservation and use of these plants.
It also creates a mess, though, because previous analyses based on species level diversity, for example to set collection and conservation priorities, may need to be revised. Spooner et al. update some of the analysis of geographic pattern in wild potato species richness described previously.
The reduction in the number of species is in large part due to new insights from David Spooner’s incessant work on this group, through molecular and morphological studies, and observations during collecting expeditions. His kind of naturalist is a species that is also declining in numbers, or so it seems. That is not a good thing, as there is a lot of work to do.