- Sidama Agro-Pastoralism and Ethnobiological Classification of its Primary Plant, Enset (Ensete ventricosum). The Sidama feed the high-protein parts of enset to cattle and then get their protein from milk. Seems a roundabout way of going about things but I guess they know best.
- Evolution of wild barley at “Evolution Canyon”: adaptation, speciation, pre-agricultural collection, and barley improvement. One-stop shop for researching evolution of a crop wild relative.
- Spices and Condiments: Status of Genetic Resources and Setting Priorities for Introduction in India. National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources is on the job, collecting at home and acquiring from genebanks abroad.
- Inventory and conservation of fruit tree landraces as cultural heritage of Bohemian Forest (Czech Republic), indicators for former settlements of ethnic minorities. That would mean Germans. No word on whether the database has been cross-checked with that of BLE-IBV. Interested in the topic of European landraces in general? Try this from Bioversity.
- Forage Diversity: An Essential Resource to Support Forage Development. ILRI’s genebank deconstructed.
- Wild Sunflower Species as a Genetic Resource for Resistance to Sunflower Broomrape (Orobanche cumana Wallr.). Pretty much all the perennial species have resistance, and many of the annuals. Thank goodness for the USDA collection, eh?
- Agroecological Research: Conforming — or Transforming the Dominant Agro-Food Regime? Bit of both? Is that such a bad thing?
- A multidisciplinary approach to enhance the conservation and use of hazelnut Corylus avellana L. genetic resources. Holistic, even.
- The Cooked is the Kept: Factors Shaping the Maintenance of Agro-biodiversity in the Andes. Keep your culture, keep your crop diversity.
- Response of broomcorn millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) genotypes from semi arid regions of China to salt stress. 39 out of a core collection of 195. Result!
- Vital Signs: Integrating Data To Visualize the Human, Agriculture, and Nature Nexus. Sounds promising enough an effort to bring together livelihoods, production and environmental data, but when you go to the website (for Tanzania in this case), all you get is a bunch of admittedly very pretty pdf maps.
- Phenotypic and genotypic characterization in the collection of sour and duke cherries (Prunus cerasus and ×P. ×gondouini) of the Fruit Genebank in Dresden-Pillnitz, Germany. …give different results. If I had a dollar…
- Genome-wide association mapping of zinc and iron concentration in barley landraces from Ethiopia and Eritrea. There are QTLs. Now what?
Searching for Mangalitsa, and more
 Seeing this magnificent beast on Facebook inspired me to revisit an old post on livestock genetic resources information systems.
Seeing this magnificent beast on Facebook inspired me to revisit an old post on livestock genetic resources information systems.
First, DAD-IS. Turns out there’s data from Mangalitsa or Mangalitza from a number of countries, and it’s not all that difficult to find. Here’s the summary from the “Transboudary breed” section.
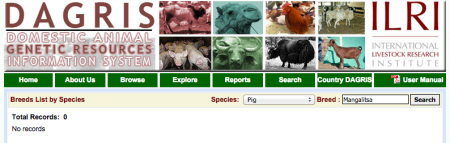
Then, DAGRIS. Over to the search page, type in the name, 1 and click go:
Uhm.
On the other hand…
 I then looked for this equally fabulous creature, Vietnam’s Ga Dong Tao chicken, also seen on Facebook, on DAD-IS. I got a nice “breed data sheet”, including photos, but I can’t link to it because there’s no permalink. You’ll have to take my word for it, or go and search yourself. And what is provided as the reference for said data sheet? Why, DAGRIS, of course, though if you go there, you don’t get any photos.
I then looked for this equally fabulous creature, Vietnam’s Ga Dong Tao chicken, also seen on Facebook, on DAD-IS. I got a nice “breed data sheet”, including photos, but I can’t link to it because there’s no permalink. You’ll have to take my word for it, or go and search yourself. And what is provided as the reference for said data sheet? Why, DAGRIS, of course, though if you go there, you don’t get any photos.
I think there’s some way to go yet in sorting out animal genetic resources information systems.
IPCC AR5 in easily digestible bites
#IPCC: global temperature rise >4°C combined with rising food demand would pose large risks to global food security. #Climate2014
— IPCC (@IPCC_CH) November 2, 2014
Yes, the latest IPCC report, the Fifth Assessment Report (AR5), is out, and the news is not great, as the tweet pithily points out. You should probably read the whole thing, but if you prefer diagrams, you can try The Guardian’s, or our own.
Embrapa’s “ark” on Globo
“If you have a disease, a pest or adverse climatic conditions, we can look for features that serve to combat that disease or that climatic situation, and then create new varieties that can cope with this challenge,” explains Mauro Carneiro, Head of Biotechnology/Embrapa.
One precaution that has already paid off: in 1994, the Kraho indians were able to recover with the help of Embrapa a kind of corn which for three decades had not been grown in the villages in the North and Northeast regions.
That’s the Google Translate version of part of an article on Embrapa’s new genebank in Brasilia, which includes a video. Attentive readers will remember we blogged about that Kraho story some years back. A second example of restoration of genetic resources from a genebank trumpeted on the internet — and TV in this case! — within a few days. One more and we have a trend.
Dia de los Muertos at CIMMYT
Thanks to Dr Denise Costich, manager of the maize collection at CIMMYT, for this photo of the decorations currently gracing the lobby of the genebank building.

And let’s all “Like” the genebank’s new Facebook page, which features this and other nice photos!