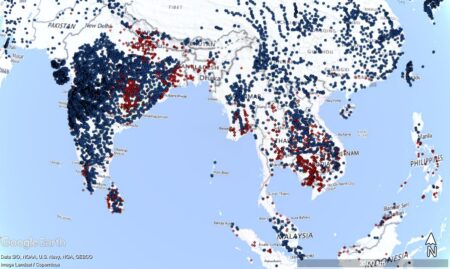
Every once in a while a new dam dataset crops up. Dam, not damn. Well, maybe damn as well. Anyway, when that happens, I feel compelled to mash it up with accession locality data. Because if I don’t do it, who will?
The new dataset is the Global Dam Tracker, and you can download it and everything of course. It’s pretty easy to then upload it to Google Earth and play around with it. Including combining it with data on wild Oryza accessions from Genesys, for example.
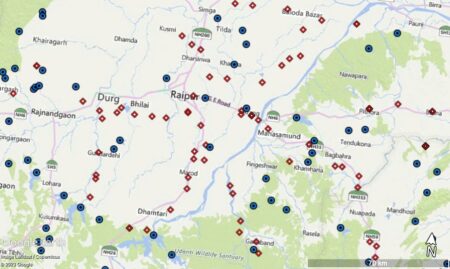
On this map, the dams are shown in blue and wild rice accessions in red.
You can zoom in if you’re worried about the long-term in situ future of any given population.
Not for the first time, I wonder about the feasibility of one day automatically and in real time combining data from multiple potential stressors, including dams, to predict the risk of genetic erosion around the world. Something that AI should be able to do, surely?