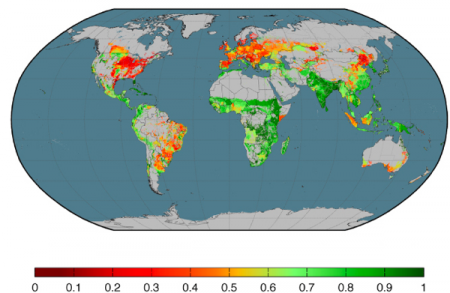
Take a look at the graphic up there and tell me what you see? If you’re anything like me, you’ll be a bit surprised. In this kind of “heat map” green is usually good and red is usually bad, but what on Earth is good across much of sub-Saharan Africa and Asia and bad just about everywhere else?
Yield — if you think about it properly.
![]() A recent paper by Emily Cassidy and her colleagues at the University of Minnesota 1 got a lot of press recently focused on the claim that feeding more people a nutritionally sound diet would be a lot easier if we just ate lower on the food chain. That’s an argument that lots of people have made, backed up to varying degrees with good numbers. What’s different this time is that the numbers are a lot more rigorous and, in my opinion, a lot more accessible. That map above, for example, shows the calories delivered to the food system per calorie produced. In other words, crudely, the amount of human food as opposed to animal feed.
A recent paper by Emily Cassidy and her colleagues at the University of Minnesota 1 got a lot of press recently focused on the claim that feeding more people a nutritionally sound diet would be a lot easier if we just ate lower on the food chain. That’s an argument that lots of people have made, backed up to varying degrees with good numbers. What’s different this time is that the numbers are a lot more rigorous and, in my opinion, a lot more accessible. That map above, for example, shows the calories delivered to the food system per calorie produced. In other words, crudely, the amount of human food as opposed to animal feed.
Obvious, when you think about it, that the number of people fed per hectare is surely a better measure of agricultural productivity than the simple yield. That’s what underpins the money quote:
We find that, given the current mix of crop uses, growing food exclusively for direct human consumption could, in principle, increase available food calories by as much as 70%, which could feed an additional 4 billion people (more than the projected 2–3 billion people arriving through population growth). Even small shifts in our allocation of crops to animal feed and biofuels could significantly increase global food availability, and could be an instrumental tool in meeting the challenges of ensuring global food security.
There are other eye-opening graphics in the paper, for example a ranking of the major crops based on calories delivered to the food system versus calories lost. As you can imagine, maize doesn’t do well at all. Nor does barley, because so much goes to feed. I highly recommend taking a look at the full paper, which is freely available.
Cassidy et al. are decidedly not calling for everyone to go vegan. For a start, that would leave a lot of grass and other forages uneaten and a lot of nutritional holes in the diet of many people. They are suggesting that the “problem” of feeding future global population may be easier to solve than currently imagined, if people shift their diet. The problem of how to help people shift their diet, they don’t address.
 It is hot in Rome at the moment, and hotter still at my desk. In fact, my computer gave up the ghost on Friday and had to have a brain transplant. All back to normal, for now, but not a lot to report, apart from trying to maintain a steady stream of Nibbles. A couple that didn’t fit there. First, the picture: an undoctored image of two consecutive items from my Twitter stream that just happened to take my fancy. Secondly, a
It is hot in Rome at the moment, and hotter still at my desk. In fact, my computer gave up the ghost on Friday and had to have a brain transplant. All back to normal, for now, but not a lot to report, apart from trying to maintain a steady stream of Nibbles. A couple that didn’t fit there. First, the picture: an undoctored image of two consecutive items from my Twitter stream that just happened to take my fancy. Secondly, a 
