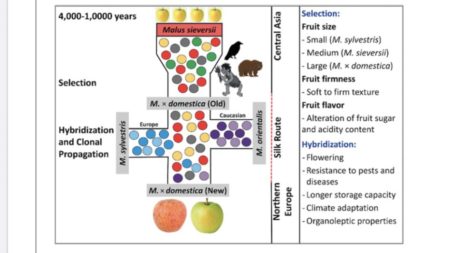
There’s been a lot happening lately, so hang on for a quick roundup. I may be able to follow-up in greater depth should work allow.
First, the draft post-2020 biodiversity framework is out from the CBD. You may have been following here efforts to make sure that genetic diversity was properly addressed, but the omens have not been particularly good, based on country reports.
Well, this is what is in the draft document, under the very first of four goals, Goal A:
by 2030: Milestone A.3 Genetic diversity of wild and domesticated species is safeguarded, with an increase in the proportion of species that have at least 90% of their genetic diversity maintained.
And among the indicators, at either the Goal or Target level, we can find the following:
A.0.4 The proportion of populations within species with a genetically effective population size > 500
4.0.2 Number of plant genetic resources for food and agriculture secured in medium or long-term conservation facilities
This does not look like much of an improvement over what we have now, but it is at least good to see ex situ conservation of crop diversity keep its profile.
Which leads me to the second thing I wanted to point to, a paper just out in Global Food Security, by Dr Fiona Hay and a whole bunch of genebank managers : “CGIAR genebank viability data reveal inconsistencies in seed collection management.” Analysis of 833,364 data points from seven CGIAR genebanks confirmed that high seed viability has been maintained for up to almost 40 years for a very wide range of crops and forage species.
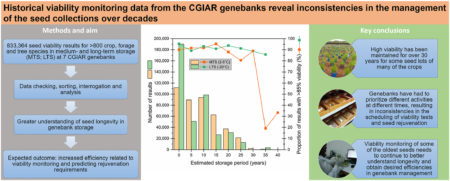
Nevertheless, improvements are possible, and the study suggests the following are needed to make sure they happen:
- Adequate and consistent data and effective data management systems designed for long-term data gathering, storage and analysis;
- Tools to facilitate the oversight and forward planning of collection management at a higher level, allowing managers to analyse the age of seed lots, patterns of their viability in storage, user demand and other factors that should feed into both annual planning of genebank activities such as regeneration but also the adaption of processes and monitoring regimes according to evident needs;
- Documented and regularly audited and reviewed processes that capture any necessary temporary deviations and facilitate staff succession;
- A culture, capacity and community that encourages active critical review and refinement of genebank operations and specialised research tailored to specific crops, collections and circumstances.
But those collections need to be used, right? Right. And, not so coincidentally, the third thing on my list is a blog post by Dr Alison Bentley summarizing the results of an online workshop that addressed how CGIAR genebanks can best serve current, emerging and future demands.
Genetic characterization serves as a first step to uncover value and can be combined with smart phenotyping and analytics approaches. Continuous engagement with diverse end-users is a necessity for ensuring relevance and application into impact. This will serve as a key to unlock the potential of genebanks as both conservators and promoters of the vast diversity they hold.
So, basically: genotype everything in your genebank, phenotype subsets of the collection carefully chosen on the basis of all the relevant data at your disposal, share the resulting information in ways that diverse genebank clients can make sense of and act on, and actively engage with as wide a range of users as possible to make sure you know what they need.
The eventual aim of all this, of course — or one of them anyway — is to “diversify the range of publicly bred crop varieties available to smallholder farmers and increase varietal turnover through commercial channels.” And yes, there is a white paper on that as well.
The White Paper expands on recommendations for how One CGIAR may want to adjust its approaches and collaboration with National Breeding Programs and private sector entities to (i) be more successful in developing and deploying newly developed varieties, and (ii) support the evolution towards a more effective, sustainable local seed sector, with appropriate public and regulatory capacities and a vibrant entrepreneurial sector. The White Paper makes recommendations for how to streamline handover to commercialization and the steps needed.
Which will no doubt lead to an agriculture that is not only more diverse and sustainable itself but also more protective of biodiversity. Which I think is where we came in.