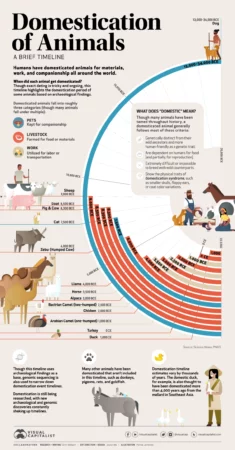
 Pretty good infographic on the history of animal domestication from the oddly named Visual Capitalist. References and a map would be good, but we mustn’t…ahem…look a gift horse in the mouth.
Pretty good infographic on the history of animal domestication from the oddly named Visual Capitalist. References and a map would be good, but we mustn’t…ahem…look a gift horse in the mouth.
Brainfood: Wild scarlet runner beans, Wild coffee, Mexican vanilla, Hybrid barley, Zea genus, Wild maize gene, N-fixing xylem microbiota, Drone phenotyping, Wild tomato, Potato breeding, Wild potato, Wheat evaluation, Rice breeding returns
- The genomic signature of wild-to-crop introgression during the domestication of scarlet runner bean (Phaseolus coccineus L.). The wild Mexican genepool is helping to counteract the effects of the domestication bottleneck.
- Genetic variation in wild and cultivated Arabica coffee (Coffea arabica L.): Evolutionary origin, global distribution, and its effect on fungal disease incidence in Southwest Ethiopia. Domesticated disease-resistant cultivars are threatening the genetic integrity of the wild genepool. You win some, you lose some.
- Uncovering haplotype diversity in cultivated Mexican vanilla species. Plenty of evidence of past hybridization events in cultivated vanilla in Mexico. Maybe it can swap stories with scarlet runner bean.
- Six-rowed wild-growing barleys are hybrids of diverse origins. In the case of barley, the wild-cultivated hybrids even got a separate Latin binomial.
- Portrait of a genus: genome sequencing reveals evidence of adaptive variation in Zea. Lots of variation in interesting adaptive traits in the wild relatives of maize. Did they, or will they, make their way into the crop, I wonder?
- An adaptive teosinte mexicana introgression modulates phosphatidylcholine levels and is associated with maize flowering time. This one did.
- A highly conserved core bacterial microbiota with nitrogen-fixation capacity inhabits the xylem sap in maize plants. Its wild relatives are not the only wild organisms maize benefits from.
- Phenomic data-facilitated rust and senescence prediction in maize using machine learning algorithms. Drones and fancy maths can be used to predict and document southern rust infection in maize. Maybe in wild relatives too one day, who knows.
- A Solanum lycopersicoides reference genome facilitates insights into tomato specialized metabolism and immunity. A tomato wild relative has a gene for resistance to bacterial speck disease, so of course they had to sequence its genome.
- Genetic gains in potato breeding as measured by field testing of cultivars released during the last 200 years in the Nordic Region of Europe. Genetic gains for yield (measured in non-target environments) were not that great and contributed about half of productivity gains. Results for other traits were even worse, mainly because of stringent market demands. So no chance of using wild relatives I suppose.
- Genotypic Response and Selection of Potato Germplasm Under Heat Stress. Not so fast…
- Dataset of historic and modern bread and durum wheat cultivar performance under conventional and reduced tillage with full and reduced irrigation. I wonder to what extent wild relatives contributed to the differences.
- Assessing returns to research investments in rice varietal development: Evidence from the Philippines and Bangladesh. Net returns from collaboration in rice breeding between IRRI and national partners are still strong in the Philippines and Bangladesh, but declining, and faster in the former than the latter. Plenty of genes from wild relatives in IRRI lines of course. Maybe there could be more?
Nibbles: Organic ag, Local ag, Pigeonpea, African cereals, Vanilla genebank, Ag R&D, Ziziphus
- Blaming organic agriculture for Sri Lanka’s woes is a little…simplistic.
- Deriding food localism as luddite is a little…simplistic. I wonder if there will be a rural re-exodus in Sri Lanka.
- Pigeonpea is back on the menu in Malawi. Organically produced, no doubt.
- Will it be closely followed by sorghum and millet in Zimbabwe?
- Brazil puts together a vanilla collection. Because you can only go so far on sorghum and pigeonpea.
- Meanwhile, “…China Has Become the World’s Largest Funder of Agricultural R&D,” displacing the US. Including local and organic ag, pigeonpea and sorghum? I wonder…
- Looks like jujube might be an example of US-China collaboration on ag research. Maybe.
Documenting agricultural biodiversity everywhere
Nice to see a couple of examples of agrobiodiversity catalogues, albeit of very different kinds, available online.
The Catàleg de varietats locals de Catalunya (from that autonomous community of Spain’s Department d’Acció Climàtita, Alimentació i Agenda Rural) can be searched online by either cultivated species (hint: “mongueta” is Phaseolus vulgaris) or the “entitat” that is managing the landrace.
On the other hand, the Field Guide to the Cultivated Plants of the Philippines (Volume 1: Commonly cultivated species) from the Southeast Asian Regional Center for Graduate Study and Research in Agriculture (SEARCA) can be downloaded as a beautifully produced PDF.
And since I’m here, I might as well point to a nice infographic summarizing the cultivated Citrus family tree. I may have shared this (or something similar) before, but I’m hoping that if I keep doing so some of the details will eventually stick in my brain.
Nibbles: Algal genebank, Baking, Distilling, Ft Collins genebank, Community genebanks, Trinidad genebank, Agriculture & climate change, Nigerian coconuts, Organic agriculture
- Saving an algal germplasm collection in the US.
- Saving ancient grains via baking in Israel and distilling in Minnesota.
- Saving seeds (and more) in a famous genebank in Ft Collins, Colorado.
- Saving seeds in community genebanks in Nepal.
- Saving seeds for the community in Trinidad & Tobago.
- Saving agriculture from climate change in Hainan. Someone tell India.
- Saving the Nigerian coconut sector.
- Saving organic agriculture from politicians.