- Community forestry not making enough money in Namibia. Yeah, but who is?
- Southern African freshwater bodies in trouble. Gotta be some worried rice wild relatives out there.
- Salinity increasing in Bangladesh. That can’t be good.
- Let the people have seeds of local varieties!
- Australian takes acacias to Niger, coals to Newcastle.
- Breeding rice for tolerance to high Fe in West Africa.
- “One of the most abundant sources of fish in Asia, the lake feeds a hungry nation.”
Submergence resistant rice on the airwaves
“It was not in use,” said Pamela Ronald. “Very, very low yield and very poor flavor, so no one was eating it. It’s really more like a grassy weed, but it had these properties.”
“It” is a rice from eastern India which was known 1 to survive under water. Listen on VOA to how Pamela Roland identified the sub gene in this variety and then introduced it into the popular Swarna.
“We wanted to hear what kind of difference it made to their families, and a couple of the women told me that they were able to feed their families and they had extra rice to sell, which is really important in those areas to bring in a little cash,” said Pamela Ronald.
Agriculture blogged in Copenhagen
Climate Feedback is a blog hosted by Nature Reports: Climate Change to facilitate lively and informative discussion on the science and wider implications of global warming.
There’s not a huge amount on agriculture normally, but a post yesterday from the Copenhagen conference mentions not one but two people whose (independent) work on the effect of climate change on agriculture we’ve mentioned a number of times, Marshall Burke from Stanford and Andy Jarvis from Bioversity International.
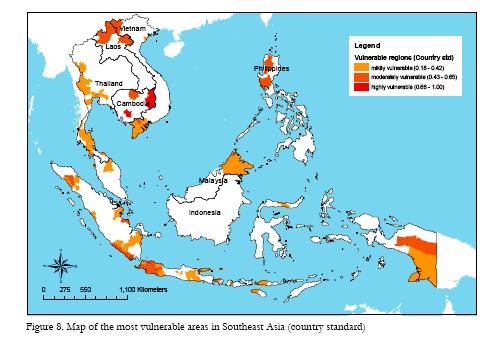
Climate vulnerability in SE Asia mapped
The International Development Research Centre’s Economy and Environment Program for South-East Asia (EEPSEA) has just published a study on the effects of climate change on SE Asia. The authors first mapped climate hazard, including all kinds of different things, from drought to cyclones to sea level rise. They then compared that with maps of population density and adaptive capacity. That allowed them to identify a number of vulnerability hotspots. And here they are, the most vulnerable areas in each country:
All good places in which to start looking for agrobiodiversity to collect for ex situ conservation before it disappears, and in which to test agrobiodiversity for its possible contribution to adaptation.
Nibbles: Breeding cucumbers, Seed exchange, Rice ecosystem, Viroids, GIS
- Psst, wanna breed a cucumber? With video goodness.
- Hudson Valley Seed Library.
- “One duck creates boundless treasure.â€
- Potato spindle tuber viroids go back to the beginning of life on Earth. Kinda.
- AGCommons’ Quick Wins: geospatial technology for smallholder farmers. Via.