- In praise of common names. Meh. You won’t see a Latin name in this whole Nibbles. See how you like it.
- Building a tomato. In Spanish.
- Tracking a tomato.
- The dark side of tomatoes.
- Amaranth to rescue Mexicans from obesity.
- Seeds of contention.
- Finding the lost Least Lettuce.
- Indigo goes back to the future.
- What if the monsoon fails? MS Swaminathan has some answers.
- Nice chocolate infographic from FAO.
- A diverse microbial community in and around roots helps plants thrive. The Science article is behind a paywall, but there’s a helpful infographic on Twitter.
- The US has a National Seed Strategy for Rehabilitation and Restoration. Vision? The right seed in the right place at the right time. Wish I’d thought of that.
- When otherwise useful trees attack. Ah, the irony of this coming right after the previous one.
- UK’s Global Food Security programme says extreme weather events are increasing and we must adapt agriculture. Good to know.
- And today’s Five Plants That Will Save the World are…
- Maybe add pawpaw to that?
- Japanese rice farmers: change gonna come.
- Nice coffee museum in Brazil.
- Early agriculture in the Caribbean: Cuba and Trinidad.
- The babaçu breakers of Maranhão are under threat. What’s babaçu? Yeah, well, look it up.
- “Seed banking began about 30 years ago as an improvement to individual farmers storing and using their own seeds.” Riiiiight.
- That Vilsak is a card.
Nibbles: CIAT job, Rice revolution, Pomegranate genebank, Spiderplant, Floating heritage, Lager origin, Amaro history, Golden Rice et al.
- CIAT genebank looking for a leader.
- IRRI soon-to-be-former (Thanks, Mike) DG looking for a new Green Revolution.
- Looking for pomegranates? Look no further.
- Cleome looking for markets. With genomics.
- Looking to the floating gardens of Bangladesh for answers.
- Looking for the origin of lager yeasts. And finding two of them.
- Looking to understand amaro.
- A good look at biofortification.
Frozen fruits
A recent Nibble describing work in South Dakota to extend ever northward the range of the grape, including using wild relatives to breed new cold-tolerant varieties, brought back childhood memories for one of our readers:
Hansen was a proponent of stretching agriculture for the harsh northern environments. My grandparents lived in northern South Dakota and hence Hansen was one of the horticultural heroes from my childhood.
Hansen is — or was — Dr Niels Hansen, “South Dakota’s Great Plant Pioneer.” He sounds a fascinating character:
Already in his senior year as an undergraduate in 1887, N.E. Hansen was writing to his father, “There is both money and honor to be gained by someone who succeeds in bringing out fruits, better than old ones.” The money seemed to elude Hansen, though – he never got wealthy from his work as a plant breeder. But he did win honor, and he cultivated it carefully.
As chance would have it, there was another article on a northern fruit yesterday, this time the blueberry. That also has a long history of breeding in the Great Plains, though it all really started in New Jersey, of all places, as the article describes. Perhaps not surprisingly, though, the blueberry has expanded more southwards than northwards recently.
No word on whether macadamia is next for the cold treatment.
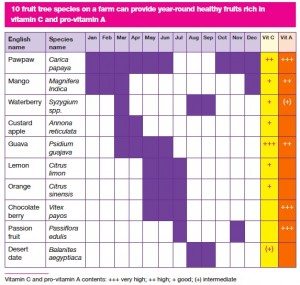
Phenological diversity for nutrition
A recent blog post by the World Agroforestry Centre described their idea of a phenologically varied “fruit tree portfolio” to provide nutrition throughout the year. In Machakos, Kenya, where the portfolio is being tested out, these would be the species involved, a mixture of the local and the exotic:
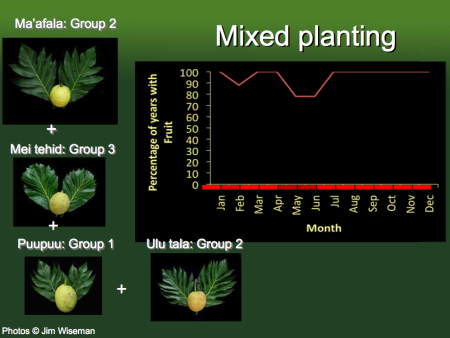
A nice idea, and it reminded me that you can also do something similar by exploiting within-species diversity in seasonality. The example I know best comes from Diane Ragone’s work on breadfruit. This is from a presentation she gave recently at USAID.
Planting multiple varieties carefully chosen from each of these different groups means you can count on having some fruit throughout the year, most years. Great to have diversity at multiple levels to play around with.
Princely state of the British apple
Our readers have known for some years now that HRH Prince Charles has taken over a collection of apple varieties. Not so readers of the Sunday Times, apparently. Unfortunately, the article describing the Prince’s efforts to save the British apple is behind a paywall, so we cannot for now say whether it adds anything to the story we already knew. Maybe someone out there with a subscription can help us.