- “USDA’s Bourlaug International Science Fellows Program has partnered with non-profit and for-profit organizations to identify new agricultural techniques for cocoa cultivation and to control cocoa diseases.” And do some conservation and breeding, surely.
- Big shots call for a decent global digital soil map. Seconded.
- Cool photos of rice agricultural landscapes.
- Roasting maize, Mexico style. Oh yeah, there’s also a nifty new maize mapping population out.
- Peruvian apple cactus doing just fine in Israel.
Nibbles: Urban bees, Borlaug, Cotton, Income, Mammals, Human disease, Caribou, Chestnut, IRRI
- There are 227 bee species in New York City. Damn! But not enough known about the work they (and other pollinators) do in natural ecosystems, alas.
- Borlaug home to be National Historic Site?
- Archaeobotanist tackles Old World cotton.
- FAO suggests ways that small farmers can earn more. Various agrobiodiversity options.
- About 400 new mammal species discovered since 1993 (not 2005 as in the NY Times piece). Almost a 10% increase. Incredible. Who knew.
- But how many of them will give you nasty diseases?
- The caribou wont, I don’t think. And by the way, its recent decline is cyclical, so chill.
- Saving the American chestnut through sex. Via the new NWFP Digest.
- “The best thing IRRI can do for rice is to close down and give the seeds it has collected back to the farmers.” Yikes, easy, tiger! Via.
Nibbles: Drought resistant rice, Bees, Bison, Coffee in Kenya, Cassava in Africa, Pigeon pea, Chickens in Uganda, Green ranching in the Amazon, Climate change, Dates, Museums and DNA, Organic, Ecology meet
- “Sahbhagi dhan is drought-tolerant and can survive even if there are no rains for 12 days.”
- Keeping bees in cities. Not as crazy as it sounds.
- More on the problems of the European bison. What is it with the BBC today?
- Coffee berry borer coming to Kenya. Not boring at all.
- Cassava helping Cameroonians and Ugandans.
- ICRISAT pigeon pea a hit in Kenya.
- Ugandan fishermen crying fowl. What is is with allAfrica today?
- No trees were harmed in the making of this beef.
- “How many of the changes we see happening around us are really attributable to climate change.” Pretty good question. In two parts, be sure to catch both, agrobiodiversity comes into the second.
- How to get a date.
- “By using museum specimens to look back in time, we can potentially assess … [human] impact in detail.” And genebanks, don’t forget genebanks, Olivia.
- Organic better after all. Zzzzzzzzzzzzz.
- Fisheries not as bad as was thought after all. But still pretty bad.
- For best results, use perennials in diverse landscapes and no tilling.
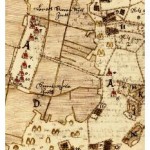
Old maps used to track down hops in Sweden
![]() I’ve done a fair amount of reading and thinking about the theory and practice of germplasm collecting in my time, but I don’t think I’ve ever come across an example similar to the one described in a recent paper in Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution. ((Strese, E., Karsvall, O., & Tollin, C. (2009). Inventory methods for finding historically cultivated hop (Humulus lupulus L.) in Sweden. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution. DOI: 10.1007/s10722-009-9464-9.))
I’ve done a fair amount of reading and thinking about the theory and practice of germplasm collecting in my time, but I don’t think I’ve ever come across an example similar to the one described in a recent paper in Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution. ((Strese, E., Karsvall, O., & Tollin, C. (2009). Inventory methods for finding historically cultivated hop (Humulus lupulus L.) in Sweden. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution. DOI: 10.1007/s10722-009-9464-9.))
In it, Swedish researchers describe how they took advantage of a couple of interesting quirks in the history of Sweden to devise what I think is a pretty novel strategy for sampling agrobiodiversity. They were interested in collecting germplasm of hops (Humulus lupulus) for a new genebank that’s under development. Now, the thing is that, although this crop is no longer grown in Sweden now, for 400 years from 1442 doing so was compulsory, in order to guarantee sufficient domestic production for beer-making. Very sensible, too.
Initially, all peasants were required to grow at least 40 hop poles. By 1483, the quantity was increased to 200 hop poles. The law was not formally repealed until 1860. As a result of this law, the plant has left several financial, fiscal and legal imprints on Swedish history.
The second historical curiosity about Sweden is that it boasts a unique set of some 12,000 large-scale maps dating back to the mid-17th century. Because of the hops law, hop gardens are actually marked on these maps in some detail (click to enlarge).
So the collectors used what they call a “history to plant” method to identify likely areas for collecting, using not only maps such as the one reproduced above, but also…
…medieval charters from the fifteenth century files of land belonging to the abbey of Vadstena, documents from the expeditions of Carl von Linné and his pupils from the eighteenth century and also documents from the breeding program in Svalöf from the beginning of the twentieth century.
And a pretty successful strategy it was too.
We found no hop plants at locations which were not indicated in the maps as hop gardens. Today living plants were possible to find in more then 33% of the total inventoried sites, indicated as hop gardens on large-scale maps.
As I say, I can’t think of another example of the use of historical maps to locate specific crops for sampling. No doubt the specific circumstances that made this possible in Sweden are not all that common around the world. Anyway, if you know of similar work, let me know. Always interested in keeping up to date with the latest in germplasm collecting.
Nibbles: Dogs squared, Afghanistan’s poppies, Rice at IRRI, Book on sapodilla chicle in Mexico, Opuntia, Trees
- DNA survey of African village dogs reveals as much diversity as in East Asian village dogs, undermines current ideas about where domestication took place.
- Fossil doubles age of dog domestication.
- “When children felt like buying candy, they ran into their father’s fields and returned with a few grams of opium folded inside a leaf.”
- “The rice, a traditional variety called kintoman, came from my grandfather’s farm. It had an inviting aroma, tasty, puffy and sweet. Unfortunately, it is rarely planted today.”
- “An era of synthetic gums ushered in the near death of their profession, and there are only a handful of men that still make a living by passing their days in the jungle collecting chicle latex…The generational changes in this boom-and-bust lifestyle reflect a pattern that has occurred with numerous extractive economies…”
- Morocco markets prickly pear cactus products.
- TreeAid says that sustainable agriculture depends on, well, trees.