Who doesn’t love old trees? I, for one, could read about them for days. And, alas, have occasionally done so. Especially if they are cultivated species. The internet is full of old, attractively gnarled olive trees, for example. Old grapevines, not so much. There was recently that piece in The Economist about recreating Leonardo’s vineyard, but that’s not quite the same thing.
So it was a pleasant surprise to come across the Old Vines Register, curated by wine expert Jancis Robinson. Turns out there are some 400-year-old vines out there. Which I’d really like to see some day.
Anyway, since I’m talking grapes, I might as well highlight the work of the Vitis Working Group of the European Cooperative Programme for Plant Genetic Resources (ECPGR). Note in particular their “On-farm inventory of minor grape varieties in the European Vitis Database.” There must be some pretty old vines among those.

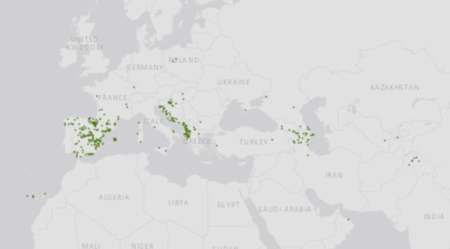
As for genebanks, there are 16,000 accessions of cultivated Vitis out there (plus 2,400 wild relatives), according to Genesys, though only about 1,900 are geo-referenced (see map below). Genesys, remember, brings data from ECPGR’s European genebank database, Eurisco, together with that from genebanks in other parts of the world. There is also a separate European Vitis Database, though I’m not sure of the exact overlap with Eurisco.
What of the future? Well, we’re probably going to need all that diversity given what climate change is already doing to the crop. A recent Twitter thread by Dr Sarah Taber analyzed the depiction of vineyards in an episode of Star Trek: The Next Generation set in the year 2367. We’ll just have to see if her decidedly critical view of twenty-fourth century management practices is borne out in the forthcoming series, which does seem to feature, at least according to the trailer, somewhat better kept, though not particularly old-looking, vines. No word yet on what varieties the Picards grew, and will grow.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ishyf14_yx0