- US honeybees really in trouble.
- Europeans also worried.
- Chesapeake oyster, on the other hand, are recovering.
- Series of posts on old herbals.
- Q&A on Svalbard Global Seed Vault.
Nibbles: Youthful ideas, IK, Variety testing, GMO philosophy, Organic GMOs, Oline disease, Cacao doctors, US wheat, Cary Fowler, Bison renaissance, UCDavis, Andean grains, Alaskan ag, Lettuce latex, Collecting strategies, Pulses racing, Huitlacoche, Ecoagriculture, Bowel movement
- Australian yoofs make suggestions for a better agriculture. Not as bad as you might think.
- Emulate, don’t imitate, desert dwellers.
- Webinar on variety trialing.
- A philosopher tackles GMO labelling. Not many people hurt.
- Meanwhile, Pamela Ronald is trying to find a middle way.
- This Italian olive disease thing is getting worrying.
- Indonesians have their own problems with cacao, but at least they seem to be fixing them.
- And the US is gonna have trouble with wheat. The solution: plant maize? No, wait…
- The European bison is back!
- A decade of Plant Sciences at UCDavis.
- Call for more breeding of Andean grains. By an Andean grain breeder.
- “It might not be the Fertile Crescent when it comes to corn and potatoes, but south-central Alaska just might be the cradle of the coming Rhodiola renaissance.”
- Rubbery lettuce? Shhh, or everybody will want some.
- Can’t collect seed at random throughtout a population? Collect more!
- Yeah, yeah, it’s the International Year of Pulses, we get it.
- The Mexican truffle?
- Ecofarming pays. In Kenya. In 2014.
- Sometimes crop wild relatives are a real pain in the ass.
Nibbles: Biofortification, NUS, Wakehurst Place, Cheesy map, Seeds2Zim, Food bibliography, Eucalypt genome, Oregano in the US, CFC, Rotations, Malaria drugs, Quinoa in Colorado, Pacific pineapple, Rhubarb event, Mango festival, Araucaria, American chestnut, Potato casserole, Coffee breeding, Tulips galore, George Harrison Shull, Seed saving, Chinese agriculture, European agroforestry, Eat This Podcast
- Webinar on biofortification, today.
- Book on Asian underutilized plant species, which we somehow missed when it came out in 2014. Unless it didn’t.
- The Millennium Seed Bank isn’t just great in and of itself, it also sits in a wonderful garden: the man who has been keeping that going for the past decade has just retired. Best wishes!
- A map of French cheese. Internet surrenders.
- North Jersey donates organic seeds to Zimbabwe. In related news, they also sending coals to Newcastle.
- Online bibliography of food history. There goes the morning.
- All hail the eucalyptuzzzzz genome.
- The unintended consequences of WW2: oregano.
- Follow the construction of the Crops for the Future Centre HQ. Over 10 episodes, mind, so gird your loins.
- Breaking down crop rotation.
- Malaria drugs through the ages. Make mine a G&T.
- Yes, how is quinoa doing in Colorado?
- New pineapples for the Pacific. They’ll probably end up canned.
- Good news: Clumber Park has a Rhubarb Weekend. Bad news: we missed it. Ditto the Goa Mango Festival.
- Mapping every monkey puzzle tree in Britain. Well, someone has to.
- Transgenic chestnuts taking over New York State. You can bet someone’s going to map them.
- The US potato renaissance we all knew was happening finally hits the headlines.
- The latest on coffee improvement, including news from the CATIE collections.
- Tulipmania: The video.
- The father of hybrid corn.
- Would he have approved of saving seeds? I suspect yes.
- Chinese agriculture adds a few (thousand) years.
- Europe has agroforestry too, and lots of it.
- Think I missed something? Check if Jeremy caught it in his Tasty Morsels.
Brainfood: Chinese CWR, Black-bone goat, Agrobiodiversity & nutrition, Niger rice, Rabbit diversity, On farm, Adding value, Native Americans & Svalbard, USDA wheat core, Cooperatives & food security, Maize & CC
- China’s crop wild relatives: Diversity for agriculture and food security. 871 wild species related to crops important in China, some of them endemic and endangered.
- Black-bone goat: An investigation report on new genetic resource of farm animal. Out of China…
- Effects of agricultural biodiversity and seasonal rain on dietary adequacy and household food security in rural areas of Kenya. More dietary diversity is better for your kids’ nutrition, and so is rain.
- Farmers’ rice knowledge and adoption of new cultivars in the Tillabéry region of western Niger. The landrace is hippopotamus-resistant.
- An invasive non-native mammal population conserves genetic diversity lost from its native range. Same for some crop wild relatives?
- Diversifying mechanisms in the on-farm evolution of crop mixtures. Diversity within mixture of 4 French wheat landraces changes in different ways in different places.
- The Role of Local Sheep and Goat Breeds and Their Products as a Tool for Sustainability and Safeguard of the Mediterranean Environment. Cheese made from local breeds is better. Well, at least different.
- Saving seeds: The Svalbard Global Seed Vault, Native American seed savers, and problems of property. “…the Svalbard Global Seed Vault is unique in its potential ability to cross the political and cultural divide over the ownership and conservation of seeds and thereby promote the vital ecological need for both ex situ and in situ seed preservation.”
- Genetic Diversity among Wheat Accessions from the USDA National Small Grains Collection. Geography is a good basis on which to base a core collection.
- Food sovereignty, food security and fair trade: the case of an influential Nicaraguan smallholder cooperative. They can all be integrated, but food security is the difficult one.
- Maize migration: key crop expands to higher altitudes under climate change in the Andes. 10m a year.
Dam the genetic resources, full speed ahead
Global Forest Watch now has a dam dataset, covering 50 major river basins. Here’s what it looks like:
You can mash it up online with various forest datasets, but you can also download it as a kml. Which of course means you can mash it up with your own dataset. That’s what I’ve done here with wild rice from Cambodia. The white arrows are dams, most of them either planned or under construction, the yellow dots samples of wild Oryza according to Genesys.
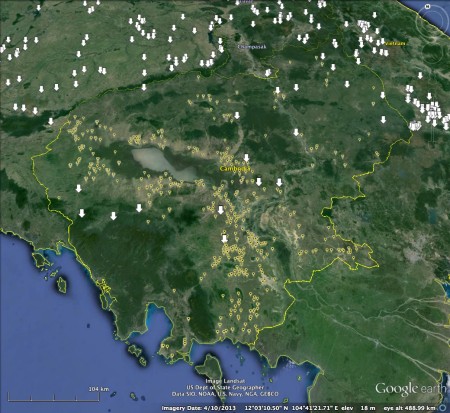
You’ll notice a few dams with few or no nearby specimens. Off the top of my head, those would seem to be places where collecting might be in order, before the disruption goes too far. But what do the rice experts out there think?
LATER: Seems I might be on to something…
@AgroBioDiverse @RiceResearch @BrianFLloyd And not just rice of course. Yes, I would expect a serious consequence.
— Mike Jackson OBE (@mikejackson1948) May 5, 2015