- Why they blog. At the Agriculture and Ecosystems Blog Agriculture and Ecosystems Blog that is. Can’t help thinking that the media should perhaps be alerted.
- Scholarships available at the Crops for the Future Research Centre.
- Yes, ok EurekAlert!, we get it , insects are really important to plant diversity.
- Yes, ok policy wonks, we get it, it’s really useful to see plant genetic resources as global commons.
- More tree cover means more diverse diet in Africa.
- Thyme, gentlemen, please.
- FAO Commission on Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture Ad Hoc Technical Working Group on Access and Benefit-sharing for Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture debates, well, access and benefit-sharing for genetic resources for food and agriculture. In Svalbard, of all places.
Nibbles: Ames genebank, G20 meet, European bison, Genomics training, Old words, Roadside Salvia
- Yet another USDA genebank in the news. This time it’s maize.
- G20 Agriculture vice-ministers recommend to “Support the development and promotion of a global information sharing system on plant and animal genetic resources.”
- Bison returns to Germany.
- Learn population genomics of crops and livestock.
- Ebony is a pretty old word.
- How Salvia got around.
Brainfood: Wild barley drought tolerance, GM cassava retraction, Lupinus ploidy, Diversity levels
- SSR analysis of introgression of drought tolerance from the genome of Hordeum spontaneum into cultivated barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp vulgare). Scary thing is that only two wild accessions are involved.
- Transgenic Biofortification of the Starchy Staple Cassava (Manihot esculenta) Generates a Novel Sink for Protein. Fancy biotech puts more of a substance in cassava that nobody eats cassava for. No, wait.
- Whole genome duplication in a threatened grassland plant and the efficacy of seed transfer zones. Mixing of seed from different populations can be a good idea for conservation of rare plants, but not when they also differ in ploidy.
- Genetic diversity in widespread species is not congruent with species richness in alpine plant communities. Cannot use one as a proxy for the other.
Nibbles: Innovative crops, twice, Seed saving, Jatropha, Cimmyt, Common ownership
- Of course garlic and dill are innovative crops – if you live in the Pamirs.
- So is Stevia, in Spain.
- A big new book on saving your own seeds. Ignore the rhetoric, and don’t try this in Europe, folks.
- Crops for the Future calls Jatropha a “debacle”. Hard to argue with that.
- All about CIMMYT at an agro-biodiversity fair.
- Put a price tag on natural resources, and you risk undermining common ownership.
Sacramental varieties
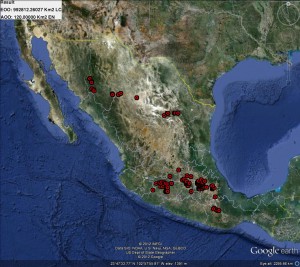 The CIMMYT genebank holds about 13,000 wheat lines (from a couple hundred populations) from Mexico that they call “sacramental wheats.” This collection was put together by the late Bent Skovmand, who established the CIMMYT genebank back in the 1970s. Sometimes collected in monasteries and cemeteries, and generally restricted to the fringes of cultivated zones, these mainly spring bread wheats are the remnants of the varieties introduced by the Spanish into the New World. You can see the collecting sites in the map above right. They were brought across the Atlantic both to provide familiar food, but also to make the sacramental bread used for Holy Communion. An excellent book relating this history is “Que vivan los tamales! Food and the making of Mexican identity” by Jeffrey M. Pilcher.
The CIMMYT genebank holds about 13,000 wheat lines (from a couple hundred populations) from Mexico that they call “sacramental wheats.” This collection was put together by the late Bent Skovmand, who established the CIMMYT genebank back in the 1970s. Sometimes collected in monasteries and cemeteries, and generally restricted to the fringes of cultivated zones, these mainly spring bread wheats are the remnants of the varieties introduced by the Spanish into the New World. You can see the collecting sites in the map above right. They were brought across the Atlantic both to provide familiar food, but also to make the sacramental bread used for Holy Communion. An excellent book relating this history is “Que vivan los tamales! Food and the making of Mexican identity” by Jeffrey M. Pilcher.
 Here’s my question. Are there some varieties that would have been used only for Holy Communion? I’ve heard it said that this was the case for grape varieties and sacramental wine, although I can find no evidence online for that, or indeed for purely sacramental bread wheat varieties. So I’m turning to the wisdom of the crowd. That means you. Are you aware of any wheat or grape varieties that are (or were) used solely (or mainly, let’s give ourselves some room for maneuver here) to produce sacramental bread or wine for the Eucharist? Or do you know someone who might know? Either way, leave us a comment, please.
Here’s my question. Are there some varieties that would have been used only for Holy Communion? I’ve heard it said that this was the case for grape varieties and sacramental wine, although I can find no evidence online for that, or indeed for purely sacramental bread wheat varieties. So I’m turning to the wisdom of the crowd. That means you. Are you aware of any wheat or grape varieties that are (or were) used solely (or mainly, let’s give ourselves some room for maneuver here) to produce sacramental bread or wine for the Eucharist? Or do you know someone who might know? Either way, leave us a comment, please.