- Genetic and phytochemical analysis to evaluate the diversity and relationships of mate (Ilex paraguariensis A. St.-Hil.) elite genetic resources in a germplasm collection. Some have low caffeine, which makes them especially useless.
- Genetic factors in threatened species recovery plans on three continents. Are ignored more often than you’d think.
- Climate Change and Food Systems Research: Current Trends and Future Directions. Current research on the effects of climate change on food systems doesn’t pay enough attention to the fact that food production is indeed a system, varies regionally and depends on political structures.
- World data centre for microorganisms: an information infrastructure to explore and utilize preserved microbial strains worldwide. All you need to know about 708 culture collections from 72 countries and >368,000 strains on one website.
- Characterising root trait variability in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) germplasm. Core collection of 270 reveals 3 main groups based on root architecture in hydroponics.
- RAINBIO: a mega-database of tropical African vascular plants distributions. Who will fillet out the CWR species?
- Genetic Variability for Yield and Nutritional Quality in Yam Bean (Pachyrhizus sp.). Can’t access the high dry matter material? No problem.
- Diversity Among a Wide Asian Collection of Bitter Gourd Landraces and their Genetic Relationships with Commercial Hybrid Cultivars. 114 accessions fall into 5 geographic groups based on SSRs. Commercial cultivars are all very similar.
- Yeast biodiversity from Vitis vinifera L., subsp. sylvestris (Gmelin) Hegi to face up the oenological consequences of climate change. Yeasts from wild grapes will save our wine. Look, I’ll take anything.
- The Potato Cryobank at the International Potato Center (CIP): A Model for Long Term Conservation of Clonal Plant Genetic Resources Collections of the Future. 70% of over 1000 accessions are considered successfully cryoconserved.
- Probabilistic viability calculations for cryopreserving vegetatively propagated collections in genebanks. Were these used in the above?
Brainfood: Truffle diversity, Pig diversity, SDMs
- How the truffle got its mate: insights from genetic structure in spontaneous and planted Mediterranean populations of Tuber melanosporum. More outbreeding in plantations, but strong structure still.
- Comparing genetic diversity of pig populations on the US mainland, Pacific Islands and China: Y chromosome evaluation. 16 breeds, 5 haplotypes, 10 breeds with only 1.
- What we use is not what we know: environmental predictors in plant distribution models. Edaphic factors are being ignored. ‘Twas ever thus.
Nibbles: Yeast phylogeny, Jurassic beer, Welsh drink, Italian fruits, Vinegar museum, Lethal yellowing, Wilderness loss
- Beer yeast was domesticated in the 1600s. Or maybe not.
- I see that and raise you 65 million years.
- If you don’t like beer, try Lurvill’s Delight, but it’s only about 100 years old, I warn you.
- Preserving ancient fruits in an Italian orchard.
- And how many different types of vinegar do you think the vinegar museum has?
- The Caribbean coconut is under attack.
- We’ve been such bastards to the environment.
Nibbles: Turkish seeds, KBA, Wild ginger, ICARDA, AGRA, Weird agrobiodiversity, Coffee journey
- Ancient seeds put on life support. Not holding my breath.
- Key Biodiversity Areas to be mapped. Agrobiodiversity also? Not holding my breath.
- Botany on reality TV? Not holding my breath. No, wait…
- More on the ICARDA story. Holding my breath.
- Kofi Annan on that “uniquely African Green Revolution.” Not holding my breath, but here’s the latest report on how AGRA is doing. Oh, and there’s more on Africa, from IFPRI this time.
- A caterpillar on the Silk Road. Now, that I’d like to see.
- But not before coffee.
Home is where conservation begins
Thanks to Jade Philips (see her on fieldwork below) and Åsmund Asdal, two of the authors, for contributing this post on their recent paper on the conservation of crop wild relatives in Norway.
![]() Norway may be an unlikely spot in which to look for agrobiodiversity, but seek and ye shall find. A recent paper discusses the development and implementation of an in situ and ex situ conservation strategy for priority crop wild relatives (CWR) in the country. 1 Some 204 taxa were prioritized, which included forage species, berries, vegetables and herbs. Distribution data collected from GBIF and species distribution modelling software including MaxEnt and the CAPFITOGEN tools were used to identify conservation priorities.
Norway may be an unlikely spot in which to look for agrobiodiversity, but seek and ye shall find. A recent paper discusses the development and implementation of an in situ and ex situ conservation strategy for priority crop wild relatives (CWR) in the country. 1 Some 204 taxa were prioritized, which included forage species, berries, vegetables and herbs. Distribution data collected from GBIF and species distribution modelling software including MaxEnt and the CAPFITOGEN tools were used to identify conservation priorities.
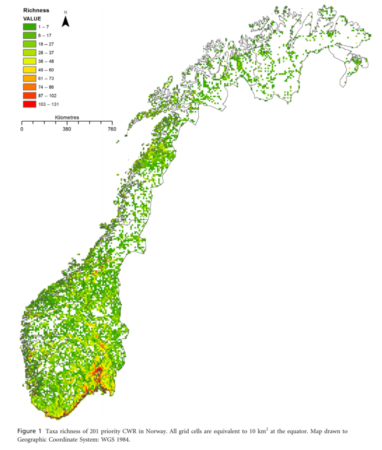 A proposal was made for a network of in situ genetic reserves throughout Norway to help capture the genetic diversity of priority CWR and allow them to evolve along with environmental changes. Some 10% of priority species do not seem to be found in existing protected areas.
A proposal was made for a network of in situ genetic reserves throughout Norway to help capture the genetic diversity of priority CWR and allow them to evolve along with environmental changes. Some 10% of priority species do not seem to be found in existing protected areas.
Complementary ex situ priorities were also set out in the paper to ensure the full range of ecogeographic diversity across Norway, and hence genetic diversity, was captured within genebanks and therefore easily available for plant pre-breeders and breeders to utilise. Some 177 species have no ex situ collections at all. The priority CWR identified and the methodology used within Norway are applicable both in other countries and internationally. We hope that now the scientific basis for the conservation of these vital resources within Norway has been identified, integration of these recommendations into current conservation plans will begin. This will take us one step closer to the systematic global protection and use of our wild agrobiodiversity, a need which is growing increasingly urgent each day.
