- FAO has guidelines for making sure climate adaptation plans include crop diversity.
- A new agricultural biodiversity newsletter for your reading pleasure.
- And a new blog of global sustainability issues from Jonathan Foley.
- The Beaver Dam pepper back from the brink.
- Nice set of slides summarizing the Plant Treaty.
- The traditional Thanksgiving save-heirloom-turkeys story.
- Farming changed people.
- Crop elders?
- Women speak out about traditional African veggies.
Brainfood: Heirloom lentil, American oil palm, Trees on farms, Cowpea selection, Apple health benefits, Traditional remedies, Bean landscapes, Maize and CC
- Making Heritage: The Case of Black Beluga Agriculture on the Northern Great Plains. That would be Black Beluga lentils. Which seems a weird subject for feminist ethnography, generative criticism and reflexivity, but I’m game if you are.
- Genetic and phenotypic diversity of natural American oil palm (Elaeis oleifera (H.B.K.) Cortés) accessions. Four geographical clusters, and a core collection.
- Complementarity of native and introduced tree species: exploring timber supply on the east coast of Madagascar. Farmers on the edge of a protected area need a diverse mix of tree species to grow.
- Farmer participation in selection within segregating populations of cowpea in Volta Region, Ghana. From 6 F3 populations with parents from Botswana, Ghana, Nigeria, Senegal, and the USA to 24 lines which farmers liked.
- Apple juices from ancient Italian cultivars: a study on mature endothelial cells model. Old apple cultivars are good for you. Or at least for human umbilical vascular endothelial cells.
- Intellectual property rights, benefit-sharing and development of “improved traditional medicines”: A new approach. Ahem, what were those old apples again?
- Landscape genetics, adaptive diversity and population structure in Phaseolus vulgaris. Domestication sites (still only 2) pinpointed in the landscape.
- Changes in Climate, Crops, and Tradition: Cajete Maize and the Rainfed Farming Systems of Oaxaca, Mexico. Life is hard, and getting harder.
Nibbles: Tomato rhythm, Pumpkin poop, Domestic olive, Papaya deforestation, Orphan crops, Perennial wheat, Apple grafting, Australian genebanks, CIMMYT seeds, French genebank, Ethnic markets, Rice breeding impact, Biodiversity & services
- Domestication made the tomato run slower.
- Domestication saved the pumpkin from climate change, which had messed up its cozy relationship with megafaunal poop.
- Domestication may (or may not) have happened twice in the olive. No word on role of poop.
- Papaya trashing the Amazon.
- Orphan crops: their day is coming. But not yet?
- You mean like kernza?
- Grafting 101.
- Tasmanian forage collection joins the club.
- CIMMYT’s seed distribution operation in pix.
- How the French cereals genebank maintains quality.
- Medicinal plants in NYC.
- Yes, donors, rice improvement makes a difference.
- Biodiversity especially important when times are tough. Well, in microbial communities anyway.
Brainfood: Camel diversity, Livestock vs wildlife, Tunisian fig diversity, In vitro artichokes, Habanero diversity, Sorghum diversity double, Greek cherry diversity, Barley domestication, Omani bananas, IBPGR collecting, Buckwheat flow
- Molecular characterization of camel breeds of Gujarat using microsatellite markers. The two sympatric camel breeds Kachchhi and Kharai are genetically distinct.
- Beefing Up Species Richness? The Effect of Land-Use on Mammal Diversity in an Arid Biodiversity Hotspot. Livestock and wildlife can co-exist.
- Analysis of genetic diversity of Tunisian caprifig (Ficus carica L.) accessions using simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Diversity low and mixed up.
- A validated slow-growth in vitro conservation protocol for globe artichoke germplasm: A cost-effective tool to preserve from wild to elite genotypes. Sounds promising.
- Synthesis of a base population of Habanero pepper. That’s an equal mixture of F2 seeds from all crosses obtained among 31 accessions. Now go crazy, breeders!
- ISSR-based analysis of genetic diversity among sorghum landraces growing in some parts of Saudi Arabia and Yemen. Differentiates some white from dark-grained landraces, and among some geographic areas.
- Assessment of sorghum germplasm from Burkina Faso and South Africa to identify new sources of resistance to grain mold and anthracnose. Breeders book flight to Ouagadougou.
- Diversity of morpho-physiological traits in worldwide sweet cherry cultivars of GeneBank collection using multivariate analysis. The national and international material from the Greek genebank falls into 3 groups. Apparently that will be useful to breeders. Who are unavailable for comment.
- Barley domestication: the end of a central dogma? Non-centres, not centres.
- Distribution and diversity of banana (Musa spp.) in Wadi Tiwi, northern Oman. An unfavourable environment at a crossroads of trade routes makes for interesting diversity.
- Plant genetic resources collections and associated information as a baseline resource for genetic diversity studies: an assessment of the IBPGR-supported collections. IBPGR collecting missions in 136 countries between 1975 and 1995 collected over 200,000 samples: here comes the data.
- Social and environmental influences on tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum Gaertn.) varietal diversity in Yunnan, China. Lots of exchange of material among farmers, which needs to continue.
A LandMark that could leave more of a mark
“…these maps do us no good unless they become public knowledge and indigenous rights are recognized by all who have ambitions to grab our lands.”
That’s Abdon Nababan of the Indonesia’s Indigenous Peoples’ Alliance, on LandMark, “a new tool launched today by a broad partnership including the World Resources Institute (WRI), …the first online, interactive platform for mapping lands managed by native communities.” And I would add that such maps will remain of limited usefulness even when they’re in the public domain if they cannot be manipulated, combined and shared much more easily than is currently the case.
Here’s Exhibit A. It is possible, with a little (well, a lot) of techie fiddling (no, not by me), to superimpose an image of what’s in Genesys (the green dots) with an image of what’s in LandMark (the brown polygons showing officially community-managed lands).
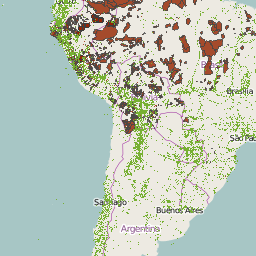
But it’s not pretty, I think you’ll agree: it gets even uglier when you zoom in, which is why I’ve decided not to let you do it. And you can’t do much with it anyway, apart from eyeball it. Plus it may well be against the terms of use of either or both Genesys and LandMark.
Well, we’ll see how LandMark develops, maybe a Google Earth export is in its future, in which case people like Abdon Nababan will be able to get the most out of it. And also the national plant genetic resources programme in Brazil, say, which may well be interested in supporting indigenous communities in protecting their crop diversity more than is perhaps occurring now. That would be a win-win. A triple win, in fact, if you add me.