We’ve been apprised, almost certainly by some sort of automated process, 1 that the author of the World Bank’s 2008 World Development Report, which focused on agriculture, will take your questions in a live, thrusting, very web 2.0 effort later today. You can submit questions here. We have.
Genetic Resources Action International examines A Green Revolution for Africa
GRAIN briefs the world on AGRA; Kofi talking to Bill.
New film about pastoralists and biodiversity
Keepers of Genes, a 28-minute documentary produced by award-winning filmmaker Moving Images, documents the role played by pastoralists in preserving animal biodiversity and the key issues confronting them today.
Anyone seen it? Anyone know more?
New pandanus poster from Pohnpei
Dr Lois Englberger of the NGO Island Food Community of Pohnpei, Federated States of Micronesia has just announced the release of a colorful new local food poster entitled “Pohnpei Pandanus: Carotenoid-rich Varieties.”Â

Photographs and nutrient content of nine varieties of pandanus from Mwoakilloa Atoll and two varieties from Kapingamarangi Atoll are presented, along with the message that these carotenoid-rich foods can help protect against cancer, heart disease, diabetes, vitamin A deficiency and anemia or weak blood.Â
The development of the poster started in 2003 with the collection of samples and arranging for analysis for provitamin A and other carotenoids, including beta-carotene, the most important of the provitamin A carotenoids. Note that rice contains no carotenoids.
We hope that this poster may help to promote this neglected food crop, to raise awareness about the distinct varieties of pandanus and to increase understanding about the important health benefits that may be obtained by consuming this fruit.
Warm thanks are extended to the Pohnpei Cancer Coalition, Global Environmental Facility Small Grant Program, Sight and Life, Center for Indigenous Peoples’ Nutrition and Environment, Australian Embassy, SPC GTZ Pacific German Regional Forestry Program, Pohnpei Agriculture, Pohnpei Departments of Health and Education, and the College of Micronesia-FSM for funding and other support, to the Secretariat of the Pacific Community in Suva, Fiji, for assistance in getting the poster developed, printed and laminated, and to all those assisting in this project.
We don’t grow food
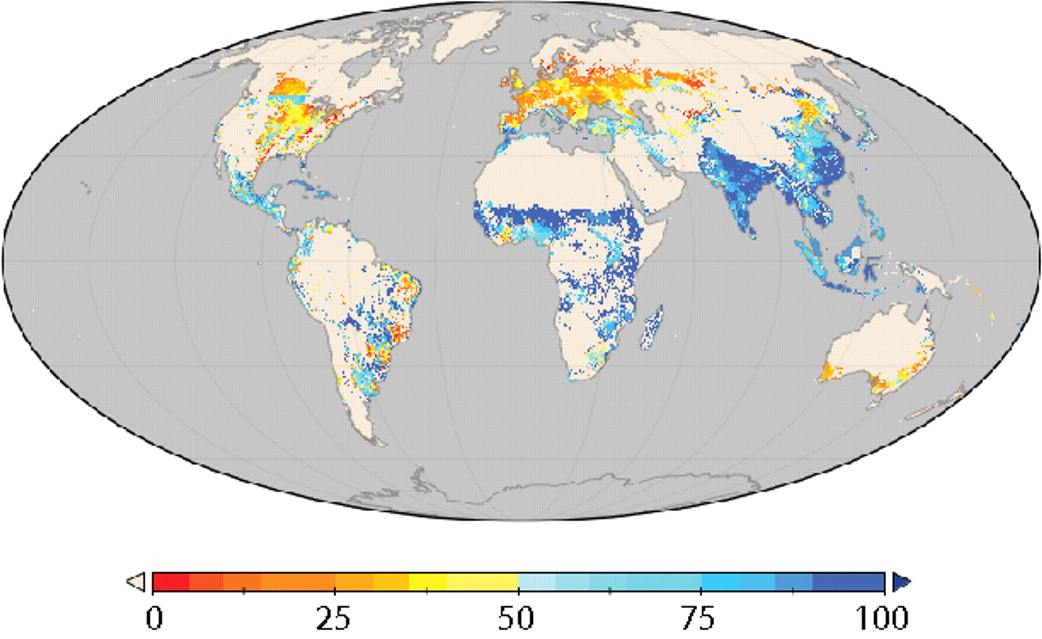 Our cartography nut is otherwise engaged, temporarily, but I know he’d love this one. Blue shows agricultural production consumed directly by people: food. Orange-red is consumed indirectly in processed products, mostly feed for livestock but also things like cotton and coffee. Notice anything interesting about the distribution? Yeah, me too.
Our cartography nut is otherwise engaged, temporarily, but I know he’d love this one. Blue shows agricultural production consumed directly by people: food. Orange-red is consumed indirectly in processed products, mostly feed for livestock but also things like cotton and coffee. Notice anything interesting about the distribution? Yeah, me too.
Hat tip to Resilience Science, which gives links to the original study.