- Seed saving at IPK handed over.
- Why Bambara groundnut needs saving.
- Kenyan women get together to save seeds.
- Saving seeds in the Atacama Desert.
- Saving wheat and vines in Georgia.
Brainfood: Genebanks edition
- Seed collection and processing practices affect subsequent seed storage longevity in durum wheat and wild relatives. Immature seeds can still usefully be harvested for long-term storage of properly handled.
- Two-step drying of soya bean seed germplasm often improves subsequent storage longevity. “Proper handling” includes drying at higher temperatures.
- Seed-stored transcript integrity as a molecular indicator of viability in conserved common bean germplasm. mRNA degradation predicts loss of seed viability.
- Developing a cryopreservation protocol for the conservation of coconut palm (Cocos nucifera L.) using a novel type of explant, meristematic clumps. Who needs seeds anyway?
- Pollen cryobanking at the USDA-ARS National Laboratory for Genetic Resources Preservation. Well, who needs meristematic clumps?
- Mapping pea seed composition through strategic selection of accessions from the Nordic gene bank. Image analysis can be used to maximise diversity in nutritional composition in pea seeds, thus facilitating use of genebank collections. Can’t do that with pollen, I suspect.
- A small-scale assessment of the availability of EURISCO accessions. Facilitating use needs all the help it can get.
- Strengthening national genebanks through genomics and regional collaboration: Lessons from Latin America and the Caribbean. I guess genomics capacity could help with use.
- Enhancing farmers’ access and use of conserved germplasm for improved food security and climate resilience: The case of sorghum at Kenya’s national genebank. Genomics unavailable for comment. Farmers, on the other hand….
- Linking the ICRISAT Genebank to Poverty Reduction and Welfare in Malawi. Facilitating use by farmers is important.
- Farmers as breeders and seed producers: Insights from 30 years of scaling up seed clubs in Vietnam. It’s super cool when farmers organize. Including for genebanks.
- Elephant ear yam Xanthosoma robustum Schott (Araceae), a neglected crop native to Central America. Needs more attention from genebanks. And farmers and their clubs for that matter.
- Plant genebank of Sudan: Towards recovery from the wreckage of war to a new era of further capacity development based on lessons learnt from similar situations. We must de-risk genebanks. Wouldn’t want to lose all those elephant ear yam collections we’ll be making.
Brainfood: Diversity of Sugarcane, Rice, Lentils, Olives, Sweetpotato, Cassava, Beans, Buckwheat, Pigeon pea, Landscapes
- The genomic footprints of wild Saccharum species trace domestication, diversification, and modern breeding of sugarcane. The genome of modern sugarcane is a mosaic of wild introgressions, including one from an unknown source.
- Evolutionary histories of functional mutations during the domestication and spread of japonica rice in Asia. Selection by biotic stresses acted differently on standing variation in rice across geographic regions. Colour me surprised.
- Ancient DNA from lentils (Lens culinaris) illuminates human-plant-culture interactions in the Canary Islands. Local lentils trace back a thousand years in the Canaries.
- An olive parentage atlas: founder cultivars, regional diversification, and implications for breeding programs. Modern cultivars derive from a surprisingly small set of founding genotypes…
- Intraspecific variation and phenotypic plasticity of olive varieties in response to contrasting environmental conditions. …but cultivated olives maintain high within-species variation and plasticity, enabling adaptation across Mediterranean environments.
- Deciphering the Origins of Commercial Sweetpotato Genotypes Using International Genebank Data. One Brazilian sweetpotato traced back to a CIP accession with a different name, but others did not match anything in the genebank.
- Exploring genetic diversity and selective signatures, a journey through Colombian cassava’s landscape. Colombia’s farmers and environments have shaped its cassava diversity. No word on whether any of it traces back to the CIAT genebank.
- Novel germplasm of tepary and other Phaseolus bean wild relatives from dry areas of southwestern USA. The available genepool for bean breeding gets a welcome boost.
- Insight into root system architecture of buckwheat through genome-wide association mapping-first study. Want drought-resilient, high-yielding buckwheat varieties? Here are the genes — and genotypes — to play with. So the available genepool doesn’t need a boost?
- Non-destructive prediction of nitrogen, iron and zinc content in diverse common bean seeds from a genebank using near-infrared spectroscopy. High-throughput, non-destructive phenotyping methods capture nutritional trait variation across a bean core collection. Wild teparies unavailable for comment.
- Germplasm exploration and digital phenotyping reveal indigenous diversity and farmer preferences in pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.) for climate-smart breeding. Not all phenotyping can be high-throughput, but that doesn’t mean it’s not useful, at least in pigeon peas.
- Agricultural landscape genomics to increase crop resilience. Could have been applied to all of the above, I guess.
Joining up the crop diversity impact dots a bit better
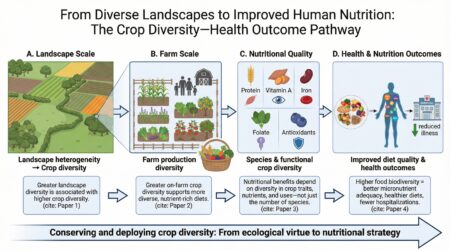
I think I was a bit too gnomic in the last Brainfood. What I was trying to do was arrange a bunch of recent papers on the pipeline from diverse farm landscapes to better health and nutrition outcomes. But I could have been more explicit about it, I agree. So here goes.
First, Global spatial co-variation between crop diversity and landscape heterogeneity shows that in areas with a moderate extent of cropland, landscape diversity is associated with crop diversity. Ok, fine, but so what? Well, next, The role of farm production diversity in enhancing dietary diversity and food security in Southern Bangladesh links that crop diversity — the diversity that farming families grow — with the diversity of the food that they eat: farms growing a wider range of crops tend to support more varied and nutrient-rich diets. Ok, but, again, so what? Hang in there, we’re almost there. The next paper, Linking species and functional crop diversity in South Asia: a spatial assessment of agrobiodiversity for nutrition-sensitive agriculture, sharpens up the focus by showing that what matters nutritionally is not just more crops, but crops that differ in traits, nutrients and uses. And finally, the pièce de résistance, Food biodiversity and its association with diet quality and health outcomes – A scoping review, connects the dots at the consumption end, associating higher food biodiversity with improved micronutrient adequacy and a better overall diet. So the arc is: conserving and deploying species diversity in fields and landscapes is not merely an ecological virtue, but a nutritional strategy, one that translates more diverse seeds in the soil to more nutrients on plates to fewer people in hospitals.
Better now?
Brainfood: Crop (species) diversity edition
- Small farms contribute a third of the food consumed in high-income nations. And those small farms are disproportionately diverse…
- The Global Spatial Co-Variation Between Crop Diversity and Landscape Heterogeneity. …and crop diversity on farms goes with landscape diversity.
- Beyond Crop Hotspots: Why Overlooked Marginal Agricultural Lands Deserve Urgent Attention. I’m willing to bet landscape diversity is often associated with marginality, but that’s not the end of the world.
- Food Biodiversity and its Association with Diet Quality and Health Outcomes-A Scoping Review. Why should we care about diverse farms? Because diversity in your food is associated with nutritional adequacy, a reduced risk of mortality, or a reduced risk of gastrointestinal cancers. Ok, I know, I missed a step there. There was nothing in the past few weeks in the literature specifically linking farm diversity and food diversity, but you know the link is there. At least sometimes.
- Long-term agricultural diversification increases financial profitability, biodiversity, and ecosystem services: a second-order meta-analysis. Diversity on farms is not just good for (ok, maybe) diets.
- Global evidence that plant diversity suppresses pests and promotes plant performance and crop production. Another way farm diversity is useful is via pest control. Well, actually, this could count as an ecosystem service, and so an example of the above.
- Ecological drivers of intercropping performance for enhanced global crop production. Ah, that explains how those farm ecosystem services actually works.
- Crop rotations synergize yield, nutrition, and revenue: a meta-analysis. Rotations are diversification too, and good for you too.
- Revitalizing orphan crops to combat food insecurity. But of course the diversification strategy de jour is opportunity crops.
- Value chain research and development: The quest for impact. And for that revolution to happen, we’ll need a better grip on value chains.
- Cultural innovation can increase and maintain biodiversity: A case study from medieval Europe. Yes, agricultural revolution can lead to increased biodiversity.
- Household vegetable agro-biodiversity in northern Vietnam requires diversity in seed sources. Any revolution is going to need good sources of good seeds though.