- A study of the relationships of cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea) and its most closely related wild species using intron sequences and microsatellite markers. It’s a wise peanut that knows its parents: A. duranensis and A. ipaënsis, apparently.
- Creative Commons licenses and the non-commercial condition: Implications for the re-use of biodiversity information. The devil is in the detail. But basically, the Non-Commercial CC license is not what it sounds like.
- Projecting annual air temperature changes to 2025 and beyond: implications for vegetable production worldwide. The devil is in the detail.
- Essential Biodiversity Variables. There are even some on genetic diversity, and domesticated species get a mention. And no, not this sort of thing, do be serious.
- Genetic composition of contemporary proprietary U.S. lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) cultivars. Romaine and crisphead much less diverse than leaf types. About 10 cultivars main ancestors. Couple wild species used. Lots of other cool stuff in this issue of GRACE. Maybe one day we’ll do a Brainfood on a single issue of a journal? Would people like that? Is anyone listening?
- Insights into Brazilian agricultural structure and sustainable intensification of food production. That insight is spelled GMO. Ah, but with added agroecological and educational goodness.
- Development of a Natural Products Database from the Biodiversity of Brazil. No doubt soon to be patented. See above.
- Food production vs. biodiversity: comparing organic and conventional agriculture. There’s a tradeoff between biodiversity (off-farm) and yield (on farm), at least in lowland England.
- Laggards or Leaders: Conservers of Traditional Agricultural Knowledge in Bolivia. Abandonment of traditional practices, including crop diversity, more to do with getting work off-farm than with age or education.
- Sea cucumbers in the Seychelles: effects of marine protected areas on high-value species. They are positive.
- Creating novel urban grasslands by reintroducing native species in wasteland vegetation. Seeding can create diverse native meadows in urban settings, even if people use them. I don’t know why this should make me feel so happy.
- Crop Expansion and Conservation Priorities in Tropical Countries. So much for peak farmland.
- Role of culturally protected forests in biodiversity conservation in Southeast China. They’re important, especially for tree diversity.
- Peach palm (Bactris gasipaes) in tropical Latin America: implications for biodiversity conservation, natural resource management and human nutrition. They’re good for nutrition and income, but could be even better.
- Deep Sequencing of RNA from Ancient Maize Kernels. That’s right — RNA! It confirms previous ideas, and offers a new tool to look at domestication.
- Historical collections reveal patterns of diffusion of sweet potato in Oceania obscured by modern plant movements and recombination. Speaking of which, the old tools are not that bad. Yes, the sweet potato did come to Polynesia in prehistoric times from South America. But not only.
- On-Farm Diversity of Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera L) in Sudan: A Potential Genetic Resources Conservation Strategy. Yup, there’s potential alright. Now can we see made real?
Nibbles: Scorzonera, Pests and diseases, Deforestation, Yaks, Journal
- Patrick reckons black salsify (aka Scorzonera hispanica, or just plain scorzonera) will be “the next ‘powerfood’ in the US”. It certainly is delicious, but I reckon it needs some serious breeding to make it worthwhile.
- CABI news on pests and diseases; there’s a new banana wilt in town that would worry me.
- Oh no! Ammunition for the deforestation deniers. “[R]research flaw that has likely exaggerated the impact of logging in tropical forests“.
- Oh yes! The yak is back.
- Oh no! Elsevier launches new journal: Global Food Security. Freely available (for now).
Nibbles: Large pumpkin, Wheat genome, Timorese nutrition, Seeds for Needs, PPB, Fruit trees, Nutrition ROI, Ecosystem services, Coffee costs, Cacao flavour, Pig slaughtering, Goats threats, Dog diet, Australian migrations
- Wow, that’s one huge pumpkin!
- Genomic whiz-bangery, which was apparently not involved in producing the above pumpkin, continues to hold much promise for wheat yields. And your jetpack is in the mail. I would ban the use of the word promise in this type of article. But since I can’t do that, I promise not to link to them ever again.
- Jess gets to grips with Timorese nutrition. Get those local landraces back from any genebank that has them, Jess. And don’t forget to collect any remaining ones.
- Then you could do some cool Seeds-for-Needs-type stuff.
- And maybe some local breeding too?
- And don’t forget local fruit trees!
- Because you know investing in nutrition is really cost-effective.
- Though of course it’s not just about the money.
- Especially when it comes to coffee.
- Or cacao for that matter.
- They shoot hogs, don’t they? Maybe even in East Timor. Goats, alas, have problems of their own.
- And as for dogs, we forced them to digest starch. What even the dingo? I bet there are dingo-like dogs in East Timor.
Brainfood: Introductions, Diversified farming systems, Breadfruit, Rice, Aquaculture threats, Arthropods in rice, Diverse landscapes, Diverse pollinators, Species re-introduction, Ecosystem function, Grapes, Prunus africana
- Increases in crop pests caused by Wasmannia auropunctata in Solomon Islands subsistence gardens. Law of Unintended Consequences takes its toll. Or does it? Discussion at Pestnet suggests the Little Fire Ant may not have been introduced as a biological control agent as suggested by the paper.
- A Social-Ecological Analysis of Diversified Farming Systems: Benefits, Costs, Obstacles, and Enabling Policy Frameworks. Special issue of Ecology and Society on DFS. That would be Diversified Farming Systems. Bottom line is that you need to understand both their ecology and their politics to make sense of them, and make them work for you.
- Morphological diversity in breadfruit (Artocarpus, Moraceae): insights into domestication, conservation, and cultivar identification. 221 accessions provide exactly those insights.
- The original features of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genetic diversity and the importance of within-variety diversity in the highlands of Madagascar build a strong case for in situ conservation. Farms are more diverse than villages, which are more diverse than regions, so it may not take that much to conserve a lot of diversity in situ.
- More rapid and severe disease outbreaks for aquaculture at the tropics: implications for food security. Driven by environmental factors, and will get worse with climate change. Strangely, breeding for resistance, and genetic diversity in general, not mentioned.
- Cultivation of Domesticated Rice Alters Arthropod Biodiversity and Community Composition. Wild rice fields have different, less diverse arthropod communities.
- Quantifying habitat-specific contributions to insect diversity in agricultural mosaic landscapes. Some of the different bits of diverse landscapes in Switzerland have unique insects, which is apparently not the case in other places.
- Synergistic effects of non-Apis bees and honey bees for pollination services. And you do need lots of different insects, at least for pollination.
- Earth observation: overlooked potential to support species reintroduction programmes. Translocation and introductions are fraught, but if you still want to do them…
- An improved model to predict the effects of changing biodiversity levels on ecosystem function. Basically, the contribution of species 1 with relative abundance A and species 2 with relative abundance B to ecosystem function is AxB to the power of θ. Can it be extended to ecosystem services, I wonder?
- Pinot blanc and Pinot gris arose as independent somatic mutations of Pinot noir. So that’s where they came from. Insights into “[o]enological aptitude”.
- Divergent pattern of nuclear genetic diversity across the range of the Afromontane Prunus africana mirrors variable climate of African highlands. Sheds light on the history of Afromontane regions.
EarthStat has crop stats
Those of you last summer who followed a link in a post of ours on crop distribution mapping to
…the dataset of Monfreda et al. (2008), “Farming the planet: 2. Geographic distribution of crop areas, yields, physiological types, and net primary production in the year 2000″…
will have ended up on a file directory containing a whole bunch of crop-specific zip files, from which you could have eventually extracted the modeled distribution of, say, coffee:
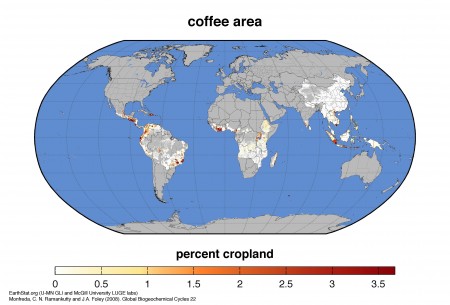
Or whatever. Nice, but all a bit fiddly. Well, now there’s a much nicer way of downloading the data in all kinds of useful forms, including Google Earth files. Though you do have to register.
I wonder if ICARDA used these data, or some others, to do their recent work on the impact of climate change on wheat in Central Asia. Difficult to tell from the blurb.