- Hunting wild sheep relatives in Armenia.
- Counting earthworms in Scotland.
- Making charcoal in Africa. Money stat: Rural electrification rate in sub-Saharan Africa is 8%.
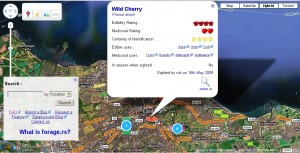
Mapping free fruit
Free-fruit enthusiasts have put together a Google Maps application to help them forage. Only has a few sites around Britain and Germany at the moment, but I bet it will grow.
Would it be so difficult to have something similar to report threats of genetic erosion, for example? I know Jacob thinks that would be useless, as a threat is only really a threat if it is likely to have an effect on overall genetic diversity, not just on what is available locally. But I’m not so sure. And it would be fun to do.
Agrobiodiversity in Eden
I’ve mentioned before that — contrary to my original expectation — the Eden Project does try to get to grips with the domesticated side of plant biodiversity. The latest celebration of agricultural biodiversity down in Cornwall is cider-pressing. But you can also see bananas in the Crops That Feed the World exhibit, and sweet potatoes in the Global Garden, an allotment inspired by cultures around the world.
A story of agrobiodiversity and agglomeration from Scotland
Dundee was Juteopolis? Who knew.
Nibbles: Légumes oubliés, Mazes, Poultry, Business, Roquefort, Herb, Evolution, Benin, Egyptian pigs, New York food, Cabbage pest control, Cider making
- Francophones! Watch this. Report back.
- Geographers! Play with this. Global collection of crop mazes.
- Chicken fanciers and development officers! Read this (pdf). Increase assets, income and nutrition.
- Agro-business! Respond to this. Please.
- Cheese lovers! Watch this. Salivate.
- Chemists! Find out why Teucrium tastes like apple. Or is it that apple tastes like Teucrium?
- Females! Why are you horny?
- Farmers! Get information to adapt to climate change.
- Egyptian pig cull! Bad. No, good. No, bad…
- Brooklynites! Wallow in ethnic cuisine.
- Africans! Why bother with cabbage when you have so many much more interesting leafy greens?
- Scrumpers! Get thee to Eden!