- Future flooding tolerant rice germplasm: Resilience afforded beyond Sub1A gene. You want to make rapid breeding progress? You need the “Transition from Trait to Environment” approach. As far as I can tell, this means that you fix your trait of interest in a pool of elite parents before using it in proper yield breeding.
- Prioritizing parents from global genebanks to breed climate-resilient crops. Yeah but how do you find your trait of interest in the first place. You start with passport and genotyping data from genebank collections of course.
- Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) landraces in Mozambique and neighbouring Southern African countries harbour genetic loci with potential for climate adaptation. You see what I mean?
- Genetic diversity and population structure of Colombian sweet potato genotypes reveal possible adaptations to specific environmental conditions. Ok, now do you see what I mean?
- Genetic diversity analysis and duplicates identification of new sweetpotato accessions collected in China. Manage your duplicates though, right?
- The lesser yam Dioscorea esculenta (Lour.) Burkill: a neglected crop with high functional food potential. This doesn’t have decent collections, let alone duplicates.
- Molecular screening of wild and cultivated tomato germplasm reveals potential materials for multi-locus disease resistance breeding. Again, thank goodness for genebanks — plural.
- First report on trait segregation in F1 hybrids between the cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) and the wild incompatible species A. glabrata Benth. I wonder if this could be used in tomato.
- A blueprint for tapping the wild relatives for crop improvement: A success story of CWR-derived rice varieties, Nông Dân 1 and Nông Dân 2. No need for embryo rescue here. No word on the need for submergence tolerance.
- Genetic diversity in in situ and ex situ collections of sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] landraces. Diversity is still out there, at least in India. Which is great. But how would you know without genebanks? And you need genebanks for breeders to use it.
- And to cap things off, a new occasional feature: A ChatGPT-generated one-sentence summary of the week’s Brainfood. “To breed crops for climate resilience and future food security, you need to systematically mine, manage, and mobilize the diversity stored in genebanks—especially landraces and wild relatives—and integrate it into elite breeding pipelines using smart, trait-targeted strategies.”
Modified ecosystems and the conservation of crop diversity
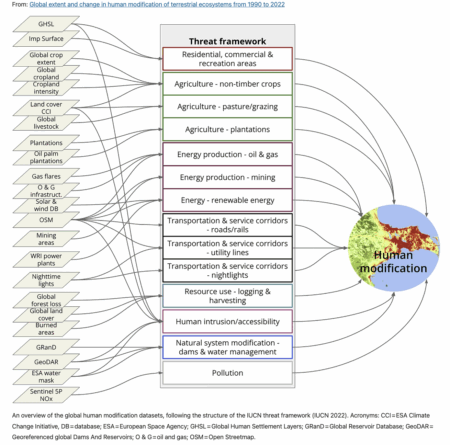
A new global assessment of the state of terrestrial ecosystems has just been published, focusing on the extent of human modification due to “industrial pressures based on agriculture, forestry, transportation, mining, energy production, electrical infrastructure, dams, pollution and human accessibility.” 1
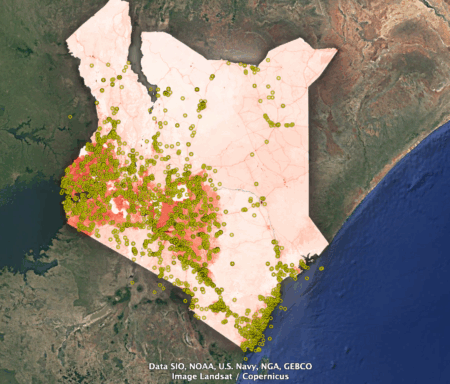
As is my wont, I tried to find a form of the data that I could shoehorn into Google Earth, but I failed. Fortunately GIS guru Kai Sonder of CIMMYT was able to snip out a kml file of overall human transformation as of 2020 covering Kenya — don’t ask me how. But thanks, Kai. I put on top of it genebank accessions from Kenya classified as wild or weedy in Genesys.
I don’t know quite what to make of this. The wild populations seem to have been mainly collected in areas that in 2020 were very highly affected by human activity. But is that good or bad?
It could be good — in a sense — if the high degree of human transformation means that the original populations are not there any more. 2 Phew, good thing they were collected! On the other hand, it could be bad if the concentration on easily accessible and modified areas means that the genetic diversity currently being conserved is not representative of what’s out there.
What do you think?
But of course what I really want is a version of this which focuses on agricultural areas and is updated in real time. Yes, a perennial favourite here: a real early warning system for erosion of crop diversity.
Brainfood: Complementarity, Temporality, Communality, Fonio trifecta, Atriplex domestication, Egyptian clover in India, Genebank information systems
- A significantly enhanced role for plant genetic resource centres in linking in situ and ex situ conservation to aid user germplasm access. On-farm conservation must result in use of the conserved diversity, and genebanks can help with that. Just another way of saying the two approaches are complementary?
- Looking back to look ahead: the temporal dimension of conservation seed bank collections. Those genebanks may need to do repeated sampling of the same population though.
- Landrace diversity and heritage of the indigenous millet crop fonio (Digitaria exilis): Socio-cultural and climatic drivers of change in the Fouta Djallon region of Guinea. Repeated sampling would defintely have helped.
- Community seedbanks in Europe: their role between ex situ and on-farm conservation. Repeated sampling is kind of what community seedbanks do, no?
- Impacts of climate change on fonio millet: seed germination and suitability modelling of an important indigenous West African crop. Community seedbanks may not be enough though.
- Phylogenetics, evolution and biogeography of four Digitaria food crop lineages across West Africa, India, and Europe. Maybe the wild relatives will help.
- Black Ash – a Forgotten Domestication Trait in Garden Orach (Atriplex hortensis L.). It’s amazing what people domesticated plants for in the past. And might in the future.
- Quality seed production scenario of Egyptian clover (Trifolium alexandrinum) in India: A 24-year retrospective analysis. But in the end, you have to get high quality certified seeds out, and that’s not always easy.
- The potential of seedbank digital information in plant conservation. Will definitely need a pretty good documentation system to keep all the above straight.
Nibbles: Nourishing investments, Genebank RoI, Seed science double, Ecuador genebank, Ethiopian genebank, MSSRF genebank, CG genebanks, Botanic gardens, SwissAid saves seeds, Brazil conservation, Indian diner, Kenyan food, Saladino on citrus, Lost apple, Seed Savers, Hybrids, Germplasm crime
- All of IFAD’s 5 investments that will help nourish the world need crop diversity. Prove me wrong.
- And yet we still have to have articles on communicating the importance of genebanks.
- Cosmos tries to do it by pointing to the science.
- Smithsonian Magazine tries to do it by saying it’s tricky.
- Genebanks try to do it by having nice new websites and talking to the media. Some of the biggest media.
- CGIAR tries to do it by calling them an Accelerator.
- IIED tries to do it by saying even botanic gardens can help farmers.
- SwissAid thinks “[n]ational and international gene banks should give farmers’ organizations low-threshold access to their collections.” No argument there.
- Maybe we should have songs about genebanks, like the Maxakali have about the Atlantic Forest.
- Or we could just talk about food, food, glorious food.
- Could also just fall back on the good old canonical lost-heirloom-apple-found story.
- Or the canonical medical case for “ancient grains” story.
- Though even there the heirlooms vs hybrids debate will rage I suppose…
- But, whatever we do, let’s not take it to extremes, shall we?
Coffee with everything
It might be because we happen to be doing something on the coffee diversity conservation strategy at work, but I have been noticing a lot of joe-related material online lately. There’s the bit on Sprudge (apparently, “the world’s most popular coffee publication”) about how coffee diversity needs a Svalbard. Seconded. And, from the same source, also comes a spotlight on Madagascar’s amazing coffee diversity.
Moving to West Africa’s diversity, there’s a Financial Times piece on Coffea stenophylla. And something that seems to be only on LinkedIn (for now) from Dr Steffen Schwarz of Coffee Consulate about how microbe diversity can do wonders with the flavour profile and caffeine content of C. liberica.
Finally, an official submission has gone in for Yemeni coffee to be included in UNESCO’s Intangible Cultural Heritage List. I wonder if all this bodes well for our thing.