The Biodiversity Information System for Europe is a partnership between the European Commission and the European Environment Agency. It seems to have recently updated its website. Or at least that’s the impression I got from a recent tweet, so I checked it out. There’s no search function on the site, but some rapid browsing could not turn up any references to genebanks or agricultural biodiversity. So I googled “genebanks in:biodiversity.europa.eu” and I got a hit on a page that is no longer on the site. WayBackMachine turns up a 2016 version with some basic information on genetic resources for food and agriculture, including genebanks, that seems to have disappeared in the interim. Maybe the Biodiversity Information System for Europe has decided to focus on in situ conservation only? It seems a pity, if true.
A way forward on DSI?
You may remember an old blog post of mine over on the work website describing how an impasse over access and benefit sharing arrangements relating to “digital sequence information” (DSI) on plant genetic resources scuppered the most recent round of Plant Treaty negotiations. 1 No? Well, this is how I put it at the time:
Some countries, and many civil society organizations, contended … that seed companies would soon be able to produce and market new varieties simply by manipulating genomic data in open-access repositories. That is, without needing to access actual seeds, and thus triggering the ABS provisions of the Treaty. In their view, this is a loophole that should be closed.
Others said that this is far-fetched, and that DNA sequence data needs to be freely available for researchers and breeders to do their work properly, and deliver new, better varieties, faster. Charging scientists for using genomic data, even if a way could be found of doing it, would impede vital research.
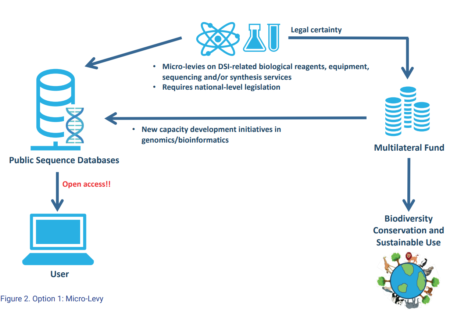
I was a bit worried about the binary at the time. It was an easy — though maybe a bit lazy — way to summarize the situation, but surely there was room for nuance? That was brought home to me by a recent paper from the project Wissenschaftliche Lösungsansätze für Digitale Sequenzinformation (Scientific approaches for digital sequence information) from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research.
In past DSI discussions, a stark contrast has often been presented: either the status quo with an open-access model and extensive non-monetary benefit-sharing but zero monetary benefit-sharing OR a closed-access system with monetary benefit-sharing but dramatically reduced or zero non-monetary benefit-sharing and a loss of open-access. We are convinced that the debate between open access and monetary benefit-sharing is a false choice and that both principles can thrive if innovative ideas and open-mindedness are brought to the table.
And the paper is actually a great contribution to the cause of finding a workable middle way. It’s worth reading the whole thing, or at least the executive summary, but basically, it suggests 5 options:
- micro-levy
- membership fees
- cloud-based fees
- commons licences
- metadata & blockchain
I particularly like the micro-levy idea.
Do any data jockeys on here care to share their thoughts?
Ceres2030 megareview spots problem with research on hunger
Shared with no comment…
The researchers found many studies that conclude that smallholders are more likely to adopt new approaches — specifically, planting climate-resilient crops — when they are supported by technical advice, input and ideas, collectively known as extension services.
…as I cry quietly…
Ceres2030 researchers found that the overwhelming majority of studies they assessed — more than 95% — were not relevant to the needs of smallholders and their families. Moreover, few studies included original data.
…in a corner.
Many researchers — most notably those attached to the CGIAR network of agricultural research centres around the world — do work with smallholder farmers. But in larger, research-intensive universities, small is becoming less desirable. Increasingly, university research-strategy teams want their academics to bid for larger grants — especially if a national research-evaluation system gives more credit to research income.
Full list of recommendations:
- Enable participation in farmers’ organizations.
- Invest in vocational programs for rural youth that offer integrated training in multiple skills.
- Scale up social protection programs.
- Investment in extension services, particularly for women, must accompany research and development (R&D) programs.
- Agricultural interventions to support sustainable practices must be economically viable for farmers.
- Support adoption of climate-resilient crops.
- Increase research on water-scarce regions to scale up effective farm-level interventions to assist small scale producers.
- Improve the quantity and quality of livestock feed, especially for small and medium-scale commercial farms.
- Reduce post-harvest losses by expanding the focus of interventions beyond the storage of cereals, to include more links in the value chain, and more food crops.
- Invest in the infrastructure, regulations, services and technical assistance needed to support SMEs in the value chain.
Crop diversity training resources
USDA and Colorado State University have a couple of neat new infographics on genebanks out. Here’s one.
They’re part of a project to develop training resources. Check them all out.
Brainfood: Amazon Neolithic double, Bean fixation, Maize stress, Collecting wild Musa, Bananas from space, Eleusine, Dioscorea, Genomics tool, Clover breeding, Red Data plus, Seed viability, Sustainable coffee, Camel conservation, Ryegrass diversity
- Archaeological expansions in tropical South America during the late Holocene: Assessing the role of demic diffusion. Some agricultural diffusion in lowland South America was the movement of ideas rather than people.
- The origins of Amazonian landscapes: Plant cultivation, domestication and the spread of food production in tropical South America. Where did the farming people and/or ideas move from? The sub-Andean montane forest of NW South America and the shrub savannahs and seasonal forests of SW Amazonia.
- Genetic Diversity, Nitrogen Fixation, and Water Use Efficiency in a Panel of Honduran Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) Landraces and Modern Genotypes. Landraces showed better N fixation, but lower yields, than modern varieties.
- Maize genotypes with deep root systems tolerate salt stress better than those with shallow root systems during early growth. Ok, but? There’s always a but.
- Challenges for Ex Situ Conservation of Wild Bananas: Seeds Collected in Papua New Guinea Have Variable Levels of Desiccation Tolerance. Avoid the basal end of the infructescence. Among other things.
- Detection of banana plants and their major diseases through aerial images and machine learning methods: A case study in DR Congo and Republic of Benin. Yeah but can you apply it to collecting the wild relatives?
- Genetic and genomic resources for finger millet improvement: opportunities for advancing climate-smart agriculture. No way this can be called neglected any longer. But is it still under-utilized?
- Genotyping-by-Sequencing to Unlock Genetic Diversity and Population Structure in White Yam (Dioscorea rotundata Poir.). More landrace variation within countries than among.
- BRIDGE – A Visual Analytics Web Tool for Barley Genebank Genomics. Do white yam next?
- Pedigree analysis of pre-breeding efforts in Trifolium spp. germplasm in New Zealand. Not a huge number of parents have been used, but reasonable diversity in most species.
- Pleistocene climate changes, and not agricultural spread, accounts for range expansion and admixture in the dominant grassland species Lolium perenne L. Lots more unused diversity out there. For now.
- IUCN Red List and the value of integrating genetics. Applying some genetic rules of thumb make some endangered species even more so.
- Variation in Seed Metabolites between Two Indica Rice Accessions Differing in Seed Longevity. Candidate biochemical indicators of impending seed death detected.
- Sustainability strategies by companies in the global coffee sector. They are close to non-existent.
- Camel Genetic Resources Conservation through Tourism: A Key Sociocultural Approach of Camelback Leisure Riding. Camel rides could be used for conservation, but they’ll have to deliver more than just conservation.