The third edition of “Strategies and guidelines for developing, managing and utilising ex situ collections” from the Australian Network for Plant Conservation is out and it’s nothing short of monumental. Here’s the contents.
Chapter 1: Introduction.
Chapter 2: Options, major considerations and preparation for plant germplasm conservation.
Chapter 3: Genetic guidelines for acquiring and maintaining collections for ex situ conservation.
Chapter 4: Seed and vegetative material collection.
Chapter 5: Seed banking: orthodox seeds.
Chapter 6: Identifying and conserving non-orthodox seeds.
Chapter 7: Seed germination and dormancy.
Chapter 8: The role of the plant nursery in ex situ conservation.
Chapter 9: Tissue culture.
Chapter 10: Cryopreservation.
Chapter 11: Living plant collections.
Chapter 12: Isolation, propagation and storage of orchid mycorrhiza and legume rhizobia.
Chapter 13: Special collections and under-represented taxa in Australasian ex situ conservation programs.
Chapter 14: Risk management and preparing for crises.
Chapter 15: Maintenance, utilisation and information storage.
There are also 50 case studies, focusing on Australian examples, including this on sorghum wild relatives.
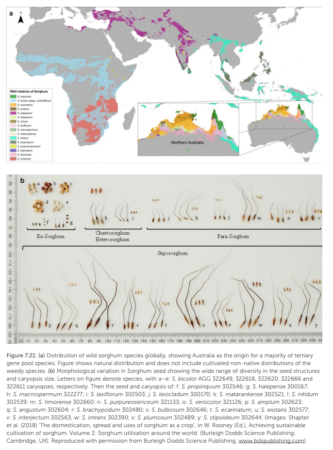
And, given the news about the threats to crop wild relatives and trees, it’s all just as well.