- Real farmers …
- AGRA et al. seeks ways to make more affordable fertilizer available to Africa.
- Strengthening Community Gardening in Bangladesh, with lots of added ITPGRFA goodness.
Distributed herbarium documentation
Distributed computer projects are taking off in a big way. “Many are run on a volunteer basis, and involve users donating their unused computational power to work on interesting computational problems.” That usually means looking for extraterrestrial life or working out the structure of black holes or proteins while your computer idles away. Herbaria@home is a bit different. When you sign up as a volunteer, you receive scans of herbarium sheets, you digitize the label information, and these data are then added to the herbarium’s information system. Actually, there are other examples of such projects, which use the public’s spare brain-power, as well as their spare computer-power. I wonder if this approach could be used to improve genebank documentation. Perhaps to geo-reference tricky accessions? Or how about to characterize the morphology of different varieties from photos?
Submergence resistant rice on the airwaves
“It was not in use,” said Pamela Ronald. “Very, very low yield and very poor flavor, so no one was eating it. It’s really more like a grassy weed, but it had these properties.”
“It” is a rice from eastern India which was known 1 to survive under water. Listen on VOA to how Pamela Roland identified the sub gene in this variety and then introduced it into the popular Swarna.
“We wanted to hear what kind of difference it made to their families, and a couple of the women told me that they were able to feed their families and they had extra rice to sell, which is really important in those areas to bring in a little cash,” said Pamela Ronald.
Rice vs millet
We’ve mentioned before the efforts to support millet cultivation among the Hill Tribes of India. There’s even a BBC documentary about the work. The above video is not from the Kolli Hills, but the problem it illustrates is the same. Rice subsidies and mining are threatening the way of life of the Dongria Kondh.
Living Farms works with them to ensure availability of food for the entire year. This is being done by re-establishing their traditional farming system, by conserving the biodiversity of millet and uncultivated food.
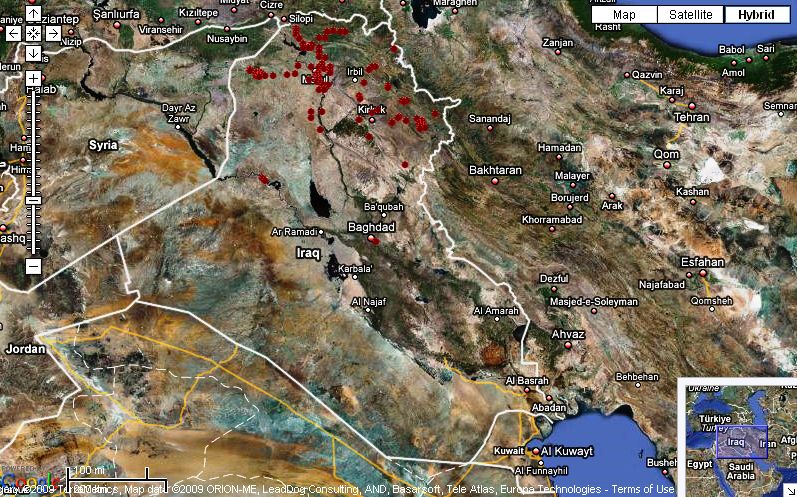
Iraqis let down again
Talking of disasters… Drought, salinity, violence, higher paying jobs in construction, the Coalition Provisional Authority and its Order 81, a corrupt Australian; and before that Saddam Hussein and the embargo: Iraqi agriculture has had a lot to deal with over the years. 2 The genetic erosion must have been phenomenal. But there’s always ex situ, right? Well:
ICARDA scientists are uncertain … about the fate of Iraq’s research facilities, especially its genebank. Prior to the war, the Abu Ghraib national genebank contained some 1,400 accessions of different crops. According to Shideed, virtually all of the country’s agricultural research centers have been destroyed or severely damaged. Large quantities of genetic materials for crops and livestock animals are feared lost, he said.
We now know that the Iraqi genebank was in fact destroyed, but that copies of the material had previously been sent to ICARDA. I wish I could say that such ex situ collections of Iraqi material maintained around the world are adequate in the face of what’s been happening there. But SINGER gives 1147 accessions, 402 of which geo-referenced, and these are all from the north of the country.
And GRIN returns 1150 hits. I just don’t think that can possibly fully represent the diversity that was present in even the main staples 20-30 years ago, let along the vegetables and fruits.
Ok, it’s probably not all gone on farm. But who’s going to go out and collect it?