- “…eleven models of regional food aggregation and distribution that are successful in linking local farmers with regional food chains.” Via.
- Hell hath no fury like a fig tree scorned.
- Tracking monkfish, saving monkfish.
- The history of the wild relative of the pea.
- Can coffee help rebuild Haiti?
- “Integrating bioclimate with population models to improve forecasts of species extinctions under climate change.”
- “The commoditization of products and taste: Slow Food and the conservation of agrobiodiversity.”
- CIAT promotes chayote in Vietnam. Why? Well, it’s not about the crop or the country. I suppose it’s about farmers and markets. But is there a diversity angle?
- How old is feeding corn (maize) to cows? Older than some people think, apparently.
- Shade-grown cacao sows seeds of its own demise.
- Waiting for the results of the USDA organic survey…
Nibbles: GIPB, NPGS, Dogs for conservation, Harare gardens, Goat milk value added, Equator Prize, Humanitarian relief, Peruvian maize, Pseudo-cereals, Katine, Vavilov goes web 2.0, Travel, Haggis ban, African road datasets, Dyes, Adaptation pix, Baltic, AnGR, Jatropha
- GIPB revamps its website. Knowledge Resource Centre is ver. 4.0, no less.
- US National Plant Germplasm System explained to Canadians. Why? They have their own!
- Armadillo sniffing dogs.
- More urban farming in Zimbabwe.
- Interesting stuff you can make with goat milk.
- Who do you like for Equator Prize 2010? Avatar? No, wait, that’s something else. Well, actually…
- Nutrition for humanitarian workers.
- Large-eared white maize is ‘cultural heritage’ of Peru. So that’s all good then.
- Minor cereals and a gluten-free diet.
- Wanna talk to Katine? Ask about what the project is doing with/about agrobiodiversity, of course!
- Nikolay tweets!
- Agricultural and other assorted musings along the Mekong. Can’t help thinking that if you somehow aggregated all similar observations and geo-referenced them you’d come up with a pretty interesting picture of agriculture worldwide.
- A blow for Scottish agrobiodiversity and cuisine.
- Digitizing Africa’s roads.
- Natural dyes 101.
- IUCN photos of climate change adaptation. Includes agriculture! Well, sort of.
- Nordic agricultural scientists to discuss climate change adaptation. Grow bananas?
- Breeding Strategies for Sustainable Management of Animal Genetic Resources from FAO. Via.
- ATREE questions Jatropha.
Yasuní National Park disappoints lovers of crop wild relatives
The Yasuní National Park in Ecuador is apparently the mother of all biodiversity hotspots, “home to the most diverse array of plants and animals in South America and possibly the planet.” And not only that, it may actually continue to be so, unlike many other protected areas.
There are hints that the park could have extra conservation value in a warming world. Yadvinder Malhi, an ecologist at Oxford specializing in the Amazon, said that nearly all climate models simulating the impacts of global warming show the area staying wet even as other parts of the vast basin get drier.
Yeah, but has it got any crop wild relatives, I hear you ask. Well, I asked our friend Julian Ramirez at CIAT, who works with Andy Jarvis. Alas, only one species turns up in Yasuní from the genera of the main South America crops for which he has a decent number of geo-referenced observations (Arachis, Solanum, Phaseolus and Manihot): Manihot brachyloba. Andy, who did his PhD in Yasuní, says he also saw wild cacao and pineapples there. No doubt Julian is putting together the data for those genera as we speak.
Yasuní is of course in the Amazonian lowlands. Wild relatives of Phaseolus and Solanum are in other, nearby protected areas in the Ecuadorian Andes. But that’s another story. For this one: thanks, Julian.
How fast will this climate change be anyway?
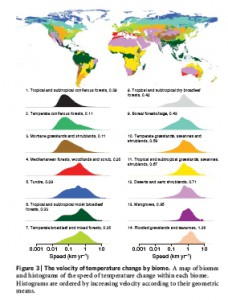
![]() Well, in terms of distance along the Earth’s surface, about 400 m per year on average, ranging from 80 m per year in mountainous regions to 1.26 km per year in deserts. That’s according to a new paper in Nature by Loarie et al. ((Loarie, S., Duffy, P., Hamilton, H., Asner, G., Field, C., & Ackerly, D. (2009). The velocity of climate change Nature, 462 (7276), 1052-1055 DOI: 10.1038/nature08649)) Compare that with figures of postglacial migration rates of <100 m per year for some trees. Here’s a map of the speed of temperature change by biome from the Nature paper (click to enlarge).
Well, in terms of distance along the Earth’s surface, about 400 m per year on average, ranging from 80 m per year in mountainous regions to 1.26 km per year in deserts. That’s according to a new paper in Nature by Loarie et al. ((Loarie, S., Duffy, P., Hamilton, H., Asner, G., Field, C., & Ackerly, D. (2009). The velocity of climate change Nature, 462 (7276), 1052-1055 DOI: 10.1038/nature08649)) Compare that with figures of postglacial migration rates of <100 m per year for some trees. Here’s a map of the speed of temperature change by biome from the Nature paper (click to enlarge).
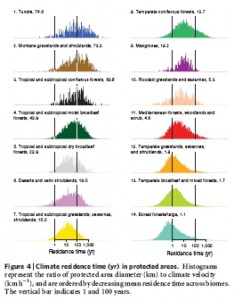
And here’s the “persistence time” for protected areas in different biomes, i.e. the diameter of protected areas divided by the climate velocity.
The persistence time — which is how long it takes for the current climate to cross a protected area — exceeds 100 years for only about 8% of protected areas. And that, dear reader, is why we need protected areas that are larger and more connected. Oh, and genebanks.
Nibbles: Goldman Environmental Prize, UK networking, European landraces publication, Seed Warriors, India agrobiodiversity sites, Beer books, Teosinte, Drought foods, Sugarcane genebank, Regional genebank in South Asia, Rhubarb, Annals, Food articles, Cryo
- Goldman Prizewinner Jesús León Santos: “It is time we recognize that traditional agricultural methods can make strong contributions to biodiversity conservation. We should encourage it and value it as a way to produce healthy foods that conserve and care for the environment.” Time indeed.
- British twofer: The Food Climate Research Network aims “to better understand how the food system contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, and to research and promote ways of reducing them.” Then there’s the Foresight Project on Global Food and Farming Futures. Will they talk to each other, I wonder.
- From Bioversity, “European landraces: on-farm conservation, management and use.” I wonder if the Foresight Project will download a copy.
- The “Seed Warriors” trailer. Oscar buzz, I hear.
- Agricultural biodiversity heritage sites in India. Ethnobotanist brings together information on food plants used during drought. Mashup, anyone?
- A book about beer. My two favourite things. Oooh, here’s another couple! And it’s not over: Spiegel weighs in on the old chestnut about beer being the reason for agriculture. My tankard runneth over.
- CIMMYT team monitors teosinte. Teosinte planning to fight back.
- Regional sugarcane genebank is actually being used! Heartwarming. Oh, and, coincidentally, here’s a history of Indian sugarcane breeding.
- “A SAARC Plant Genetic Resource Bank for rice, wheat and maize may be created to facilitate free exchange of germplasm between the member countries. To begin with, the Indian Gene Bank facilities may be utilized, with suitable modalities.” Not so heartwarming.
- The Russian roots of Alaskan rhubarb. Take that, Palin! Note the bit about St Isaac’s Cathedral, which of course sits opposite VIR. How apposite is that?
- Nigel Chaffey rounds up the usual suspects in presenting a potpourri of “plant-based items from the world’s media” for Annals of Botany. May well be one to watch. And not just because genebanks make an appearance.
- Amazing food roundup.
- Cryopreserving Chip, the Tennessee fainting goat.