For your information, we have been beavering away since then, collecting more recent and detailed sub-national livestock statistics and disaggregating these using a slightly modified modelling approach, and 1 km multi-temporal, Fourier-processed MODIS imagery from the University of Oxford. We hope in time to produce global coverage for the most important livestock species, and make these publically available, but we have focussed our initial efforts on poultry and pigs in Asia.
![]() That was Timothy Robinson in a comment on a post of ours back in 2012, and he’s been true to his word. There was a paper last year 1, and there’s a wiki for the data.
That was Timothy Robinson in a comment on a post of ours back in 2012, and he’s been true to his word. There was a paper last year 1, and there’s a wiki for the data.
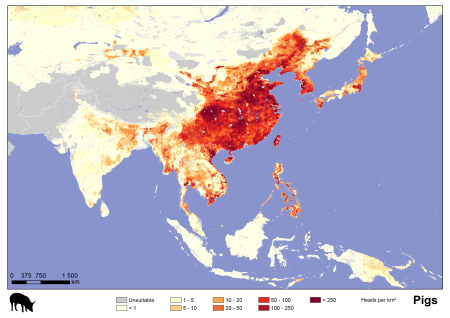
I suggested in my earlier post that it was possible to get the impression that a lot of different players were working in parallel, if not in actual competition, on livestock distribution mapping. If that was indeed the case, and perhaps it was just an impression, it all seems to have been resolved in the intervening couple of years, thank goodness. According to the wiki:
In a multi-partner collaboration centered on the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI), the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the Université Libre de Bruxelles (ULB-LUBIES), global maps of livestock distributions and production systems are being revised and updated.
Only fair to add that I landed on this via a blogpost on Vox, of all places, which has been getting quite a lot of attention on Twitter, for some reason. It seems to have escaped my early warning system last year.