You may remember a little Brainfood item about the Brazilian collection of ornamental bananas. Ok, now thanks to ProMusa you can see some of these cool plants.
Getting to grips with hairy vetch
A post over at Biofortified entitled “Will cover crops feed the world?” asked an intriguing question:
Why not take a survey of red clover and hairy vetch germplasm, looking for those that fix nitrogen at high rates, have good winter survival, and decay at a reasonable rate to provide fertilizer for crops the following year, and then combine those traits? (And while you’re at it, you could try to do something about hairy vetch’s horrendous seed yield. Non-shattering trait, anyone?)
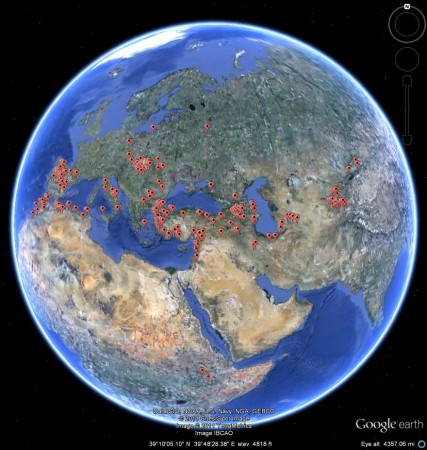
Well, I thought to myself, maybe you can find those traits already combined. So I looked on Genesys to see what germplasm of Vicia villosa, or hairy vetch, we have to play with. Quite a bit as it turns out: 1374 accessions from 60-odd countries, conserved in 30-odd genebanks. These are the accessions which have georeferences:
I looked in a little more detail at the USDA collection over at GRIN. As luck would have it, there are data on 40-odd accessions from a 2001 evaluation trial. Among the descriptors recorded are N content and winter survival. I downloaded the Excel spreadsheet, and some quick sorting revealed a couple of accessions which are both high in N and have decent winter survival, eg PI 232958 from Hungary and PI 220880 from Belgium. Another dataset shows that some accessions in the collection are non-shattering. Alas, neither of the previous two accessions were characterized for that trait, or at least I couldn’t find the data online, but I was intrigued to see that PI 220879, also from Belgium, is non-shattering.
I posted Biofortified’s question on Facebook too and Dirk Enneking came back almost immediately with more advice:
Provorov and Tikhonovich suggest that the recently domesticated species such as Vicia villosa are better at N-fix. For non-shattering, try the named cultivars such as Ostsaat etc. and grow them where there is sufficient humidity at harvest time to reduce shattering.
Now, where’s my finder’s fee?
Nibbles: Pre-Columbian ecology, Huitlacoche, Nutrition, COP17, Walnuts, Custodians, Price Volatility, Kenyan farmers, Education, Peach pests, Unhappy Talk
- Special Journal issue on Environmental changes and pre-Columbian human influence in the Amazon region.
- Porn on the cob. A smut story with a headline so good, I’m sure to steal it.
- A practical field manual cum guide to Improving nutrition with agricultural biodiversity.
- Ag researchers “speak with a single voice” to “call on climate negotiators to endorse a work programme for agriculture”. We shall see.
- And will it come in time to Save the Walnut?
- New book on “Custodians of Biodiversity“.
- Brussels Briefing on Food Price Volatility. Today! Soon!
- China hears how Kenyan farmers can benefit from traditional vegetables.
- “Are plants like us?” It depends …
- A minor increase in biodiversity protects peaches from nematode pests.
- Climate change in the Pacific: The problem, according to the Aussies. The solution, according to the ADB.
Frank Bisby

I was very sorry to hear of the death of Frank Bisby of the University of Reading on 25 October. Prof. Bisby was a renowned plant systematist who very early on saw the potential of databases in advancing the taxonomic project, and devoted his career to see that promise fulfilled. He was an ardent conservationist, for example participating in numerous legume genetic resources collecting expeditions. 1 He will be much missed.
Searching British newspapers for agrobiodiversity now virtually possible
The British Newspaper Archive is potentially a great resource for research into agricultural biodiversity in the past.
We have scanned millions of pages of historical newspapers and made them available online for the first time ever.
Search millions of articles by keyword, name, location, date or title and watch your results appear in an instant.
I did a search on the apple variety Pearmain and got 44 hits from 1753 to 1944.
So, for example, the Caledonian Mercury has a classified on Monday 1 January 1753 which says:
…glifh Apples, fuch as Nonpareis, Holland Pippens, Royal Rennets, Kentilh Pippens, Pearmains, and Rulfets, inno IcfsQuantity than a Box containing two bufhels; alfo very Hne and large Chcfhire Cheefe, from a 200 Pound-weight and do^tovard, the beft Gl…
Alas, if you want any more than that, you have to pay, and rather steeply too. Pity.
LATER: All the more so as Google seems to have discontinued its Timeline feature in News Archive search. Which I hadn’t noticed and I’m quite sad about now.