CTA’s seminar to identify ways of improving access to climate change information for agriculture and rural development in ACP countries is off and running in Ouagadougou. There’s a blog to help you follow the proceedings. Agrobiodiversity is not explicitly listed as a theme, but I suspect it will come up.
What is a landrace anyway?
When plant genetic resources people are tired and emotional, and sometimes when they’re not, talk can turn to landraces. What are they? Can they be identified unequivocally? Can they be associated with a geographical location? Are names anything other than a convenient fiction? Whole chapters, if not entire books, have been written on the subject. ((I should know; I wrote one, five years ago, which I’d link to if it had been published.)) There are definitions aplenty, of course, but that’s not the same as an answer.
Wrapped up in the definitions, and the answers, are notions of genetic variability within the landrace population and an element of selection being needed to maintain the landrace’s properties and maybe guide it in new directions. But that, of course, is crucially affected by the breeding biology of the species concerned. Bluntly, species that are reproduced clonally, like figs, say, or potatoes, are unlikely to have any variability within the landrace while those that are obligate outbreeders, such as maize, are going to be much more variable within the population and likely to change over time too. And then there are inbreeders — beans like Phaseolus vulgaris — in which the landrace is probably a mixture of different genetically pretty uniform types, each of which may well breed true, although the proportions of each may vary from season to season and from place to place.
All of which is a long and roundabout introduction to three recent papers in Theoretical and Applied Genetics that tackle the problem of landrace identity, all of them using molecular markers.
Oat (Avena sativa) is normally self-pollinating, but occasional crossing does occur. So we would not expect much variation within a population. Good thing that, because Hermann Buerstmayr and his colleagues sampled DNA from only three individuals in each of 114 oat varieties gathered from around the world. ((Ref to come DOI 10.1007/s00122-008-0843-y))
Six million and counting
So the Missouri Botanical Garden herbarium reached its 6 millionth specimen. ((Incidentally, that’s about the number of germplasm accessions in all the world’s genebanks, give or take half a million.)) ((And another thing: if you’ve got nice photos of botanic gardens, you can enter them into a competition.)) Pretty impressive, as these things go, and as good an opportunity as any to sing the praises of natural history collections. The specimen in question is Anthurium centimillesimum, a new aroid species from Ecuador. I wonder if it will ever join the ranks of the world’s 35,000 cultivated plants.
Are species like cans of soup?
A longish article in the latest Wired does what seems to this untutored eye a good job of describing the controversy about barcoding. Here’s the case against in a nutshell:
“We’re not accusing Hebert of being a creationist, just of acting like one,” says Brent Mishler.
and the case for:
The space ship lands. He steps out. He points it around. It says “friendly – unfriendly – edible – poisonous – dangerous – living – inanimate.”
There are a lot of pithy quotes like those and astute observations, such as the one that Charles Darwin was a parataxonomist. Well worth reading. We have, of course, blogged about barcoding before.
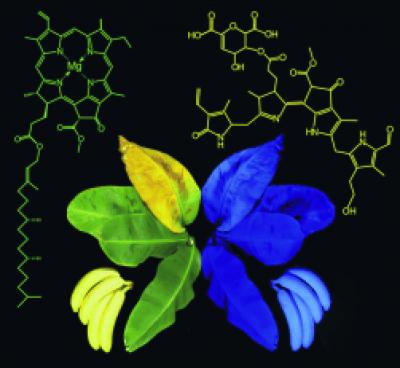
Blue bananas
Ripe bananas are of course yellow. However, under black light, the yellow bananas are bright blue, as discovered by scientists at the University of Innsbruck (Austria) and Columbia University (New York, USA). The team, headed by Bernhard Kräutler, reports in the journal Angewandte Chemie that the blue glow is connected to the degradation of chlorophyll that occurs during ripening. In this process, colorless but fluorescing breakdown products of chlorophyll are concentrated in the banana peel.
I kid you not.