- ICRISAT: “The impact of climate change on the yields under low input agriculture is likely to be minimal as other factors will continue to provide the overriding constraints to crop growth and yield.” So that’s all right then.
- Book and CD-ROM on African indigenous veggies.
- CD-ROM of wood characteristics.
- The agrobiodiversity of “…the oldest and largest area of detached town gardens in Britain” being surveyed. Cultivated since 1605. Wow.
- Earthworm Week! Yay!
- “This is an exciting time for salmon conservation in the Pahsimeroi.”
- Hawaiian native bees in trouble. Get in line.
- The world has a malaria map. Very cool.
- The Canary Islands tries to save its potatoes, sweet and otherwise.
- The Forgotten Fruits Summit. You heard me.
Department of Silver Linings, part 387
Yes, sure, climate change will cause sea level rise, which is going to be bad for places like Bangladesh and its rice and shrimp farmers, who will all end up in Dhaka. But. Yep, there might actually be a but. The same climate change is also causing increased flows of water — and, crucially, suspended sediment — from Himalayan glaciers. All you have to do is damn up the water and the silt will build up the land, counteracting the rise in sea level. With any luck, the net result will be stasis. And farmers can keep farming. Until the glaciers run out, that is.
Rust never sleeps
Wanna do a study of the state of knowledge on breeding for durable resistance to rust in wheat or soybean? Then GIPB would like to hear from you….
Nibbles: Community forestry, Fresh water, Salinity, Seed systems, Acacia, Iron, Cambodia
- Community forestry not making enough money in Namibia. Yeah, but who is?
- Southern African freshwater bodies in trouble. Gotta be some worried rice wild relatives out there.
- Salinity increasing in Bangladesh. That can’t be good.
- Let the people have seeds of local varieties!
- Australian takes acacias to Niger, coals to Newcastle.
- Breeding rice for tolerance to high Fe in West Africa.
- “One of the most abundant sources of fish in Asia, the lake feeds a hungry nation.”
Bhutan agricultural statistics go online
Yes, that’s what the news item said, and it got me all excited. So I rushed off to SINGER first to see if there’s any germplasm from that country in the international collections, and if any of that was geo-referenced. And I was happy to find some 30 barleys at ICARDA, strung all along the main road, from east to west.
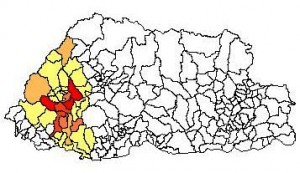
And so then I went off to CountrySTAT-Bhutan to see how well this material covered the distribution of the crop. The results were a little weird. This is the distribution of barley cultivation in Bhutan in 2005.
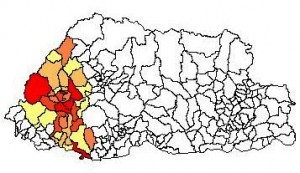
As you can see, the crop is concentrated in the west of the country, whereas in 1981, when the ICARDA collection was made, that seemed not to be the case. Ok, things change. The oldest data in CountrySTAT-Bhutan is 1999, but the pattern is the same.
Has the distribution of barley in Bhutan really changed so drastically in the past 30 years or so? And if so, what has that done to genetic diversity? Have the landraces formerly found in the east migrated, or are they only to be found in genebanks now?