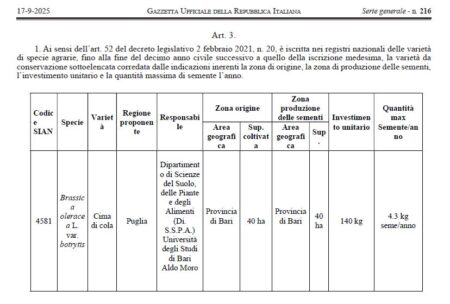
So it seems the first vegetable variety from Puglia has been added to Italy’s Registro nazionale delle varietà da conservazione, or National Register of Conservation Varieties.
The ‘Cima di cola’, a cauliflower variety historically linked to the agricultural tradition of Bari, received official recognition by Ministerial Decree of 9 September 2025, published in the Official Gazette No. 216 of 17 September 2025, which will allow its conservation and promotion also at the commercial level.
I know this because of a post on Facebook from an outfit called Biodiversità delle specie orticole della Puglia (BiodiverSO), translated above. Which unfortunately doesn’t include a link, but does provide this screenshot of Italy’s Official Gazette to prove its point.
Here’s more from the BiodiverSO post.
The inclusion of the ‘Cima di cola’ among conservation varieties is not only an institutional achievement, but also an act of recognition toward those who have preserved its seeds and traditions over the years; a milestone that opens new opportunities for scientific, educational, and gastronomic promotion, which we look forward to sharing with you.
Doubtless.
Which is why I was pretty disappointed to find that the Registro nazionale delle varietà di specie agrarie ed ortive is not actually up to date, so doesn’t yet include ‘Cima di cola’.
Quite apart from not being exactly easy to find. And there was also nothing in the relevant news section, which is actually on a different website, but nevermind.
Anyway, there are 135 “Varietà da Conservazione” registered therein. It’s unclear how to obtain seeds.
LATER: Thanks to Filippo Guzzon for advising me that ‘Cima di cola’ is indeed on the list. I was looking for it under the wrong crop name :(