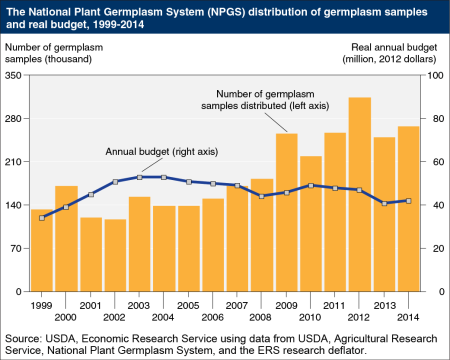
As agriculture adapts to climate change, crop genetic resources can be used to develop new plant varieties that are more tolerant of changing environmental conditions. Crop genetic resources (or germplasm) consist of seeds, plants, or plant parts that can be used in crop breeding, research, or conservation. The public sector plays an important role in collecting, conserving, and distributing crop genetic resources because private-sector incentives for crucial parts of these activities are limited. The U.S. National Plant Germplasm System (NPGS) is the primary network that manages publicly held crop germplasm in the United States. Since 2003, demand for crop genetic resources from the NPGS has increased rapidly even as the NPGS budget has declined in real dollars. By way of comparison, the NPGS budget of approximately $47 million in 2012 was well under one-half of 1 percent of the U.S. seed market (measured as the value of farmers’ purchased seed) which exceeded $20 billion for the same year.
Couldn’t have put it better myself, though admittedly I’m more likely to have done it for the CGIAR genebanks than for the NPGS. The diagram, and the sentiment, derive from a USDA publication that came out back in April: Using Crop Genetic Resources to Help Agriculture Adapt to Climate Change: Economics and Policy. We did blog about it at the time, but USDA seem to be plugging it again, and I see no reason why we shouldn’t too.